What is the full form of DNADNA: Deoxyribonucleic AcidDNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It is the hereditary material found in all living organisms. It contains the genetic instructions for the development and functioning of an organism. These instructions are passed from one generation to the next generation. DNA is present in the nucleus of each cell of the body and the genetic instructions are stored in the form of codes made of 4 nitrogen bases; Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T). 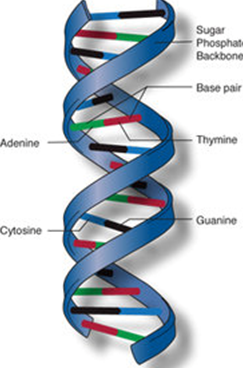
The nitrogen bases pair with each other (A pairs with T, C pairs with G) to form base pairs. The bases are attached to a sugar molecule and phosphate molecule to form nucleotides. The nucleotides lie adjacent to each other to form two long strands which entwine like vines to form a shape called double helix. DNA is known for its ability to replicate. It can make copies of itself. Each strand of DNA serves as a template to form a new strand so that each new cell can have an exact copy of the DNA present in the old cell. Functions of DNAGenetic Information: It carries genetic information from one generation to the next generation. Replication: DNA produces carbon copies through replication. It allows DNA transfer genetic information from old cells to new cells (from one generation to the next generation). Transcription: DNA produces RNAs (Ribonucleic Acid) through the process of transcription. Cellular Metabolism: It regulates the metabolic reactions of the cells with the help of enzymes, hormones and specific RNAs. Development: It controls the development of organisms through internal genetic clock. DNA Finger Printing: Each individual has its own DNA sequence that does not match with others. This property of DNA is used in DNA finger printing, a technique used to identity an individual from his or her DNA.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










