What is the Full Form of FNACFNAC: Fine Needle Aspiration CytologyThe abbreviation FNAC stands for Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a rapid, easy, and affordable technique that is typically employed in outpatient clinics to sample superficial masses like those found in the neck. It practically poses no risk of problems and causes extraordinarily slight damage to the patient. Using this method, it is simple to diagnose head and neck masses, such as lesions of the thyroid gland and salivary gland. The method is a low-cost, straightforward, and quick means to sample extraneous lumps and masses that may be seen in the breasts, neck, etc. A small gauge needle is used to take a sample, which is then examined under a microscope after being inserted into the suspicious mass. As was already explained, it includes a straightforward surgical operation. 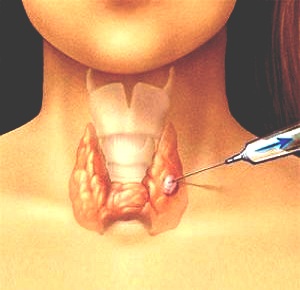
The test also aids in the diagnosis of cancer and inflammatory diseases. Contrary to open surgery, biopsy is significantly easier, faster, and safer. The likelihood of any difficulties following the test is extremely low. Is the FNAC test done on an empty stomach?An FNAC examination is a straightforward exam for which little preparation is necessary. Before the test, there is no need to fast. It is always advisable to speak with your doctor about any special safety measures to take before the test. Tell your doctor about any medications you are taking right now. Test preparation
Uses of FNAC testThe technique is employed for several testing types. The use of ultrasound-guided aspiration is used for chorionic villus sample, body fluid sampling, breast abscess, breast cysts, and for seromas. The Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology aids in the early detection of breast cancer and tests swellings for TB, Toxoplasmosis, Granulomatous Lymphadenitis, Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma, and other diseases. It also aids in understanding the cytological alterations a patient is experiencing. Material needed
FNAC Procedure
Complications in FNAC procedureAlthough complications are extremely uncommon in FNAC, they are possible, including hematoma and bacterial infection. The puncture location is experiencing haemorrhagic haemorrhage. Pressure is applied to the puncture site to prevent complications after specimen collection. Even though it is extremely rare, collecting liquid samples from deeply seated organs can result in bacterial infection. Precaution
Advantages of FNAC
Disadvantages of FNAC
Post-operative care and complicationsComplications from thin-needle aspiration biopsies are possible, just like with any surgical procedure, but they are mild and less common than major ones. The organs used for a biopsy or the organs through which cells were obtained determine the type and severity of complications. Mild analgesics are used to manage post-operative pain after the surgery. After the surgery, you should not consume aspirin or aspirin alternatives for 48 hours (unless aspirin is prescribed for a cardiac or neurological condition). Infection is uncommon because sterility is maintained throughout the operation. However, if an infection does develop, it will be managed with medications. The most frequent side effect of this surgery is bleeding. There can also be a tiny bruise. It is extremely typical to find a small amount of blood in sputum or urine following a lung or kidney biopsy. Only a little bleeding ought to happen. Bleeding should gradually lessen over the course of the observation period following the procedure. If there is additional bleeding, it will be watched until it stops. Rarely will significant surgery be required to stop the bleeding. Depending on the body part being biopsied, there could be other issues.
Price for FNAC testThe test costs on average between Rs. 450 and Rs. 2200, depending on the city, quality, and availability. ConclusionMost patients are referred to the pathologist who performs this test in a laboratory setting by their primary care physician. In addition to examining lumps and bumps, FNAC biopsy is helpful in the detection of other illnesses such lymph node TB, which is widespread in the nation. This examination can also be used to detect issues with deeper-seated organs such as lung, liver, and kidney." "Although additional testing, typically involving a surgical biopsy, may be necessary in some circumstances to make an accurate diagnosis, a FNAC biopsy can still provide significant insight into the illness. It can exclude the possibility of cancer, which is frequently the main fear, reducing patient anxiety and indicating prompt action, such as the removal of the tumour, if necessary." "In addition to being quick and precise, the FNAC biopsy is safe and has many other advantages. It is an outpatient diagnosis that is given to the primary doctor within 48 hours to allow for the start of treatment. The technique does not need extensive preparation, hospitalisation, or scarring. "Many patients worry about the discomfort from a needle stick. Although there is some discomfort during the biopsy, it is manageable and minimal. Additional relief from the soreness comes with a local anaesthetic spray. Another prevalent concern among patients who have a malignant tumour is if getting a FNAC exam may lead to the cancer spreading. This is quite uncommon and is not a reason to avoid performing the operation.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










