What is the Full Form of ICSIICSI: Intracytoplasmic Sperm InjectionICSI is an abbreviation for Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection. The cytoplasm is a phenomenon that says that before a man's sperm can fertilize a woman's egg, the head of the sperm must attach to the outside of the egg. Once attached, the sperm pushes through the outer layer to the inside of the egg (cytoplasm), where fertilization takes place. 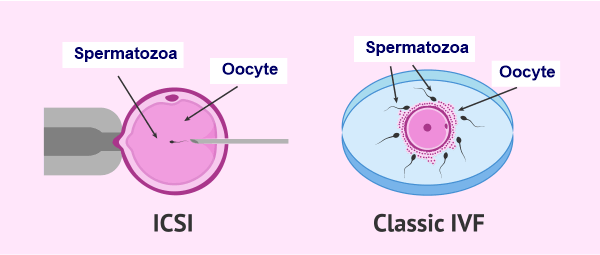
There exists a variety of reasons why sperm cannot penetrate the outer layer:
In cases like these, a procedure called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can be done along with the In Vitro fertilization (IVF) to help fertilize the egg. During ICSI, a single sperm is injected directly into the cytoplasm of the egg. How does Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection work?Generally, there are two ways that an egg may be fertilized by IVF: the traditional method and ICSI. Fifty Thousand or more swimming sperm are placed next to the egg in a laboratory dish in traditional IVF. Fertilization takes place when one of the sperm enters the cytoplasm of the egg. Whereas in the ICSI process, a tiny needle called a micropipette, is used to inject a single sperm into the center of the egg. With either traditional IVF or ICSI, once fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg (now called an embryo) grows in a laboratory for 1 to 5 days before it is transferred to the woman's uterus (womb). When does a person need ICSI?The fertility problems could be overcome with the help of ICSI, such as:
Will Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection work?ICSI fertilizes 50 % to 80 % of the eggs. But the following problems may occur during or after the ICSI process:
After fertilization has taken place, a couple's chance of giving birth to a single baby, twins, or triplets is the same if they have IVF with or without ICSI. Is baby's development affected by ICSI?There is only a 1.5 percent to 3 percent chance that the baby will have a major birth defect if a woman gets pregnant naturally. ICSI and IVF both have a similar chance of having birth defects, but slightly higher than in natural conception. The slightly higher risk of birth defects may actually be due to infertility and not the treatments used to overcome infertility. Certain conditions have been associated with the use of ICS, such as Beckwith- Wiedemann syndrome, Angelman Syndrome, hypospadias, or sex chromosome abnormalities. They are thought to occur in far less than 1 percent of children conceived using this technique. Some of the problems that cause infertility may be genetic. For example, male children conceived with the use of ICSI may have the same infertility issues as their fathers. Differences between IVF and ICSIThe key difference between IVF and ICSI is how the sperm fertilizes the egg. In IVF, the egg and sperm (of which there are many) are left in a laboratory dish to fertilize on their own. In ICSI, the selected sperm is directly injected into the egg. Satisfactory results are yielded from ICSI. ICSI helps in reducing problems with abnormal fertilization caused by eggs and sperm- such as fertilization by multiple sperm and the inability of the sperm to penetrate the eggs (Zona Pellucida) and fertilize, etc.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









