What is the full form of NICUNICU: Neonatal Intensive Care UnitNICU Stands for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. NICU is a type of intensive care unit with a focus on the treatment of newborns who are preterm or unwell. Neonatal is a term that describes the first 28 days of life. Since the 1960s, there have been intensive care units (ICUs) and specialized nurseries for the treatment of newborns. In a hospital's pediatric department, there is a specific area called the neonatal intensive care unit, or NICU. Depending on the baby's level of prematurity, newborns are detained there for days or weeks at a time. Following their exit from the mother's womb, newborns undergo a number of bodily changes. They depend on the placenta's blood supply to survive when they are in the womb (a temporary organ that connects the developing fetus and provides oxygen & nutrients to the fetus). If they are delivered out, though, that is no longer the case. The neonatal ICU units are so designated for the treatment of newborns who require intensive medical attention. Each of these specialist NICU units is outfitted with cutting-edge equipment, as well as expert doctors who have undergone extensive training and experience to help and treat these infants with exceptional care. Even babies that need specialist nursing care can be cared for in NICUs, which are not just intended to care for sick infants. 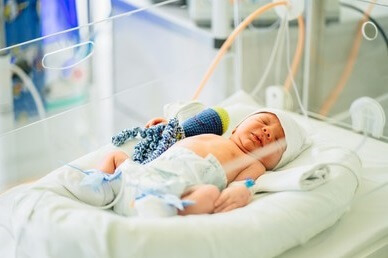
Risk FactorsYour infant may be at a higher risk and have a higher likelihood of being admitted to the NICU as a result of the variables listed below.
According to their serious condition, newborns typically leave the NICU within 48 to 72 hours. But if they exhibit symptoms of an infection, jaundice, inadequate weight gain, or any other illness, they are readmitted. Healthcare Providers In NICU1. Neonatologist The pediatrician in question has further education in the treatment of ill and preterm infants. The neonatologist, also known as the attending physician, is in charge of supervising the pediatric fellows, residents, nurse practitioners, and nurses who take care of the infants in the NICU. 2. Neonatal fellow In order to better care for sick and premature babies, this pediatrician is receiving additional training. They could oversee your child's care and perform operations. 3. Pediatric resident This doctor is undergoing additional training in pediatric medicine. They could carry out operations or help, and they could also help manage your child's care. 4. Neonatal nurse specialist This registered nurse has additional training in caring for newborn children. They can carry out operations and assist in overseeing your child's care. 5. Respiratory specialist A person with specialized expertise in providing breathing support is this individual. This includes controlling oxygen and breathing apparatus. 5. Occupational, physical, and speech therapists These therapists monitor a baby's growth and development. They also assist with care, including positioning and calming techniques. Speech therapists assist infants in mastering oral feeding. 7. Dietitians Dietitians monitor the diet and growth of the infants. They keep an eye on your baby's calorie, protein, vitamin, and mineral intake. 8. Lactation consultants These healthcare professionals have additional training and certification in supporting moms and infants who are breastfeeding. They can assist in starting and continuing breastfeeding, maintaining a milk supply, and pumping. 9. Pharmacists The optimum medications are selected with the aid of pharmacists by the NICU staff. They monitor medication levels and doses. They keep the team informed of potential adverse effects and any potential need for monitoring. 10. The social workers When a kid is ill, social workers assist families with a variety of issues. They offer emotional assistance. They aid families in obtaining information from medical professionals. They also assist the family with other, more fundamental care requirements. Money issues, transportation issues, or coordinating home healthcare are a few examples. 11. Medical chaplain The hospital chaplain could be a minister, priest, lay pastor, or another type of religious leader. To assist families in coping with the stress of the NICU, the chaplain can offer counseling and spiritual assistance.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










