What is the full form of PPLOPPLO: Pleuro Pneumonia Like OrganismsThe full name for PPLO in biology is Pleuro Pneumonia Like Organisms, also called Mycoplasma. The smallest cell or organism is PPLO, which has a diameter of about 0.1 to 0.3 mm. Mycoplasma species have been found in the pleural fluid of calf Pleuro Pneumonia patients. 
Mycoplasma is referred to as PPLO because it is found in the pleural fluid, which comprises the area between an animal's internal thoracic wall and the lungs. These animals(sheep and cow )suffered from Pleuro Pneumonia, sometimes known as lung illness. Pleuro PneumoniaPleuro Pneumonia is a lung condition that affects sheep and calves. It is brought on by the bacteria Mycoplasma mycoides and is characterized by lung inflammation. 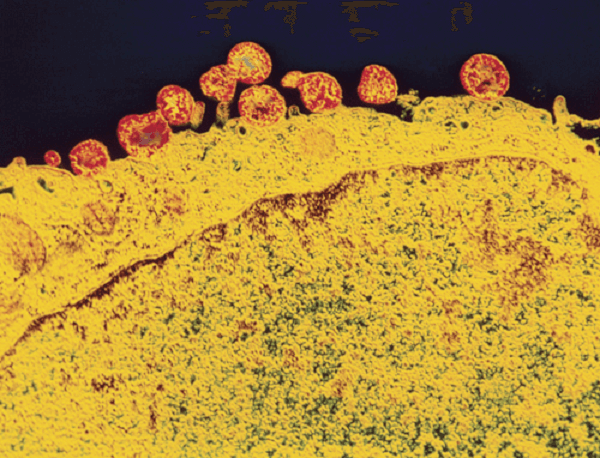
The disease's symptoms include fever, thirst, lack of appetite, and breathing difficulties. By the late 19th century, the illness was eliminated in Europe and the United States. Vaccines protect regions where the disease is still present, such as Asia, Australia, and Africa. Characteristics of MycoplasmaScientists have isolated Mycoplasma from the soil, water, and air samples. Mycoplasma organisms must be cultured in a culture medium in two steps. The cultural media must first be changed to one that permits mycoplasma growth. Neither glucose nor FOS is required to be used as the medium. Usually, a basic chlorine bleach solution will do. Approximately one teaspoon of salt should be added to the culture media if you use glucose. The culture dishes are then filled with Mycoplasma and stored in the dark. A thermometer ought to be used to monitor the development. A soft light can be used if there is little or no sunshine. On cloudy days, Mycoplasma will not grow well. As with other aerobic bacteria, Mycoplasma thrives at around 72 degrees Fahrenheit. The following stage in mycoplasma culture is to isolate and cultivate the organism. M. capriculans and M. chevalier are used during this stage. You can also use a culture medium that contains M. spirochetes. Purity should be assessed using a spectrophotometer once all the Mycoplasma have been cultivated. The Significance of MycoplasmaMycoplasma can effectively decrease the number of bacteria in our environment. A class of bacteria known as anaerobic bacteria can survive without oxygen. It's important to remember that these animals don't generate waste and may exist in very small numbers in the ecosystem. When anaerobic bacteria are within the environment, it is possible to restrict aerobic species' development rate and population. 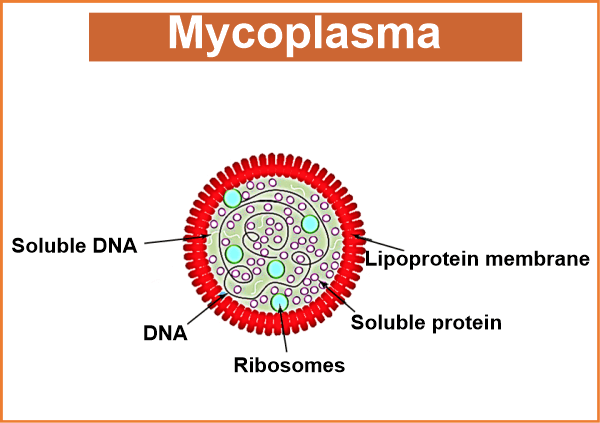
Pharmaceutical firms use Mycoplasma to create medicines, and drug trials are conducted to determine how many microorganisms must be eliminated to get results. Selecting the most efficient dose and method for removing problematic microorganisms lowers the cost of creating a new drug. PPLO DiscoveryMycoplasma has been discovered, which has led to several theories. One of the most common notions is that certain organisms were suspected of the fast spread of HIV. In the 1970s, these microorganisms were believed to be the root of the AIDS pandemic, and antibiotics later proved to be quite effective in treating the disease. Mycoplasma L. comprise is considered to be the main cause of AIDS, according to scientists. They arrived at this conclusion after doing culture and identification on ill animals. Additionally, they found molecular proof that Mycoplasma was the culprit. This revelation would influence future research on very potent antibiotics like amoxicillin. Although the cause of AIDS is uncertain, Mycoplasma has effectively treated the condition. Additionally, it is used to treat hepatitis and gonorrhoea. Facts about the PPLO
Similarities between PPLO and Mycoplasma
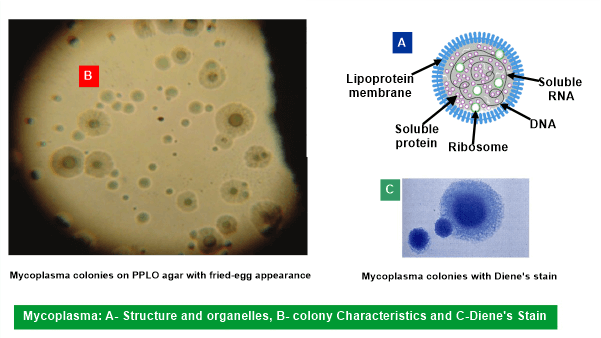
Differences between PPLO and Mycoplasma
They are not infectious. In contrast, PPLO is a pathogenic bacterium that resembles Pleuro Pneumonia and is found in the pleural fluid of animals. Mycoplasma and PPLO vary from one another primarily in terms of their pathogenicity.
Next TopicFull Forms List
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









