What is the full form of SRMSRM: Supplier Relationship ManagementSRM stands for supplier relationship management. Manufacturing professionals must understand supplier relationship management (SRM). Reaching a target market is essential to your business. That can happen with a consistent supply of raw materials and other vital supplies. Therefore, maintaining positive connections with suppliers and vendors is essential for the survival of a manufacturing business. 
What is Supplier Relationship ManagementManaging relationships with vendors who provide a manufacturer with goods, materials, and services are known as supplier relationship management (SRM). It entails assessing each of those connections and devising a plan of action to boost their efficiency in light of a manufacturing company. This is accomplished by evaluating each vendor that provides goods or services to a manufacturer and deciding which is most crucial to the company in terms of continuity and performance. Managers can build stronger working relationships with the suppliers they work with thanks to these evaluations. SRM is a tool used by experts in supply chain management. Due to their management of operations, project management, and procurement, they are the ones who communicate with vendors most frequently. SRM is frequently referred to as supply chain management because of this. Additionally, it resembles procurement and vendor management processes, as they are known. However, supply relationship management and various other related fields differ from one another. Vendor management is to manage costs and service agreements between businesses and providers. Since procurement deals with the ordering, contracting, invoicing, and repayment of those purchases, the purchases themselves are the aim of procurement. Online software called Project Manager provides real-time connectivity, making collaborating with suppliers and inventory easier. Kanban boards assist managers in maintaining inventory balance with their team's capability and visualize the workflow. This game requires a lot of quick footwork to win. Each participant must cooperate across supplier networks, particularly when handling the unexpected. Strategy is important. The most recent equipment and technology might also give you a competitive advantage. 
Today's greatest supply chain management strategies focus on creating a large-picture vision and the supporting activities required to make it a reality. We can only attain successful omnichannel strategies, supply chain visibility, and sustainability objectives with intensive orchestration and cooperation. The connectedness of digital manufacturing and a digital supply chain, as well as analytics, IoT, and blockchain, are all examples of sophisticated technology that a well-oiled supply chain is increasingly incorporating. This guide on supply chain management best practices provides a greater understanding of each of these topics. It provides you with the necessary tools, counsel, and other necessities to accomplish your business goals and score significant victories. Background of SRMPeter Kraljic, a director at the consulting company McKinsey & Company, is credited with helping supplier relationship management get off the ground. He talked about segmenting the supplier base and mapping it against two crucial dimensions: risk and profitability, in an article titled "Purchasing Must Become Supply Management," published in the September 1983 issue of the Harvard Business Review. According to Kraljic, firms must handle the dangers, complexities, and potential supply and price disruptions. "Management needs to develop the ability to influence events for its benefit. This necessitates nothing less than a complete paradigm shift: from supply management, a strategic role, to purchasing, an operating function." Others expanded upon Kraljic's fundamental concept, and SRM has continued to improve as technologies and procedures advance. 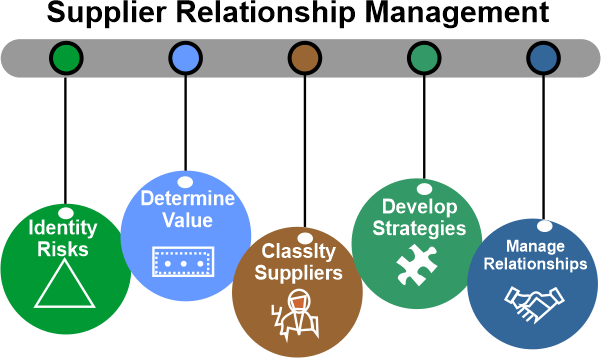
How to Handle the Issues of Omnichannel, Supply and Demand?The necessity to develop a successful omnichannel strategy is one of the main factors influencing supply chain management today. Every step of the supply chain, from product sourcing to delivery, is impacted by providing customers with a seamless in-store and online shopping experience. Still, procedures like inventory and demand management are particularly impacted by the external functionality of the supply chain. Competition between businesses is a supply chain competition. Effective coordination of complex interdependencies is necessary for the efficient movement of materials and goods, which demands knowledge. Information is surfaced and used to get insight using various technologies, including AI, blockchain, IoT, and even more conventional ones like ERP. Risk, Cooperation, and SuppliersThe supply chain is a complex web of interdependencies, and supply chain management best practices acknowledge the possibility of a disruption, which businesses must prepare for with a solid plan. A cooperative relationship with suppliers and other partners is at the core of the situation. Supplier relationship management (SRM) is a systematic process for assessing a company's suppliers of goods, materials, and services, determining how each supplier contributes to the success, and creating plans to raise performance levels. The SRM discipline assists in identifying the value each supplier offers and which are most important for business success and continuity. Additionally, it enables managers to develop stronger relationships with suppliers based on the significance of each provider. Supply chain professionals frequently work with suppliers in procurement, project management, and operations using supplier relationship management. One of the numerous subfields of supply chain management is SRM, sometimes known as supply chain relationship management. Despite some notable differences, it is comparable to vendor management and procurement processes. What Supplier Relationship Management is Meant to AccomplishEven though different industries have distinct types of important suppliers, the overall goal of SRM stays the same. To improve and streamline the procedures between the organization acting as a buyer of products and services and the companies that supply them, each organization has its unique mix. 
Similar to how customer relationship management (CRM) is intended to speed up and enhance the processes between an organization and its customers, SRM aims to create a beneficial relationship between the firm and its suppliers, particularly those considered to be the most strategic. The Objectives of Supplier Relationship ManagementThe overarching objective of SRM remains the same even though different industries have different categories of critical suppliers. SRM aims to establish a beneficial relationship between the organization, and its suppliers, particularly those deemed to be most strategic to the organization's brand, much like customer relationship management (CRM) is intended to streamline and improve processes between an enterprise and its customers. Additionally, it aims to advance innovation, efficiency, and quality. Successful SRM disciplines aim to optimize suppliers' value to achieve a competitive edge in the market and cost savings. To organize the relationship lifetime and identify the strategic supply partners, SRM develops a framework. With the help of its procedures, an organization can effectively communicate with its suppliers and gauge their performance. 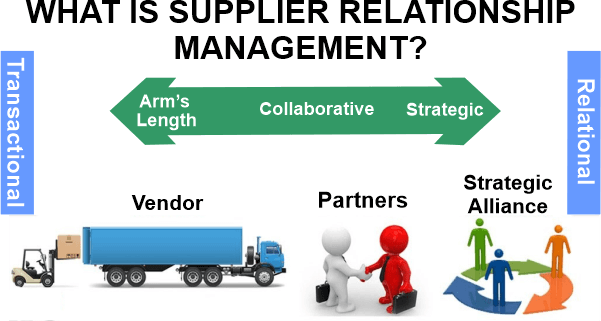
Some suppliers are more important for maintaining business operations, scalability, and profitability. For instance, a smartphone manufacturer's main electronics supplier significantly impacts profitability, whereas its stationery supplier has little to no impact, making it a crucial strategic partner. Any threat to the business of the electronics manufacturer poses a significant risk to the smartphone maker. Tasks Involved in Managing SuppliersInstead of being reactive and engaging suppliers on an as-needed basis or in response to specific challenges, an organization's SRM program must be strategic, outlining objectives and developing a plan before meeting suppliers. To assure supply continuity, enterprise leaders with a strategic mindset may decide that long-term agreements with particular suppliers are desirable. In contrast, short-term agreements with other suppliers can better provide business agility and flexible pricing. To implement an effective SRM strategy, we must personally cultivate suppliers. Partnerships must also be established based on trust and mutual benefit when suitable. This can entail including them in developing important initiatives or cooperative innovation projects. Leaders working in SRM must also ensure that everyone shares the program's aims in their organization and its objectives are followed. Additionally, they ought to have a procedure for figuring out the benefits the SRM program brings to the company. Process for Managing Relationships with SuppliersThe strategic sourcing procedures connected to SRM can differ from one firm to the next. However, SRM typically consists of these three major steps:
SRM Usage ExamplesMany use cases for applying SRM have been noted by organizations, who note that the discipline aids them in the better utilization of the skills of suppliers, cut costs, guarantee supply chain continuity, decrease supply chain risks, boost supplier responsiveness, obtain visibility into future prices, and protect against price volatility. Take into account the conclusions of a case study written by the State of Flux, a management consulting firm focusing on global supply chains and procurement. Even though its SRM was already regarded as mature, the USPS chose to upgrade its SRM governance approach in 2018. The USPS uses four standard parameters for the timeliness, quality, cost, and innovation to rate suppliers instead of the previous nine. 
However, the relationship managers in charge of each supplier can provide optional measures like corporate social responsibility or the calibre of product categories like software. Suppliers can contribute to the SRM process in several ways, such as by joining a supplier council SRM SoftwareThe following crucial features and capabilities of SRM software are just a few of the many functions it provides to support effective supplier management operations:
SRM AdvantagesGaining efficiency is a necessary component of running a successful business. This is more difficult to state than done, especially in the manufacturing industry, where external vendors provide your company with the ingredients it needs to produce. Businesses use supplier relationship management, among other strategies, to operate their operations more efficiently and profitably. SRM has several advantages, but they all help to improve the bottom line. Cost Reduction Financial incentives serve as the foundation of vendor relationships. Setting up fees might be high when starting new vendor connections. SMR is a cost reduction method involving establishing a long-term, mutually beneficial relationship. Building these cooperative ties with vendors can also aid in lowering availability concerns, delays, and issues with material quality, all of which benefit customers in the long run. Enhanced Effectiveness Having ties with suppliers helps to prevent issues that would otherwise happen due to bad or inadequate communication. Building trust with a vendor implies developing a relationship, which makes for better working circumstances. This will facilitate a more fluid supply chain. This implies fewer disruptions, and when problems arise, a good relationship with suppliers will speed up their resolution. Fewer Price Changes Customers dislike seeing the price of their items rise, and commodity pricing can be erratic. When a manufacturer employs SRM, they may frequently set a price for the materials, ensuring that their costs remain the same regardless of market fluctuations. 
Continual Development Building a trusting relationship between manufacturers and their suppliers allows for the free exchange of ideas and feedback. This communication results from greater efficiency, more streamlined procedures, and improved customer service. We can improve these advantages by connecting orders, inventory control, and other processes with project management software. SRM DifficultiesThe COVID-19 pandemic caused disruptions for 70% of respondents, according to a 2020 survey of 715 supply chain decision-makers for the report "Supply chain resilience in a post-pandemic world" conducted by Jabil, a manufacturing services company and Dimensional Research. In addition, 44% of respondents reported supply constraints, and 35% reported dealing with global trade and tariff issues. Additionally, 95% of respondents claimed component shortages impacted their business. These results emphasize the value of establishing a strong SRM program, but other research also highlights the numerous obstacles we must overcome to accomplish that goal. The problems that can hinder supplier relationship management could be lack of knowledge about suppliers, their significance to the organization, and the value they can provide an overemphasis on using it to cut costs rather than develop value and strategic ties.
Next TopicFull Forms List
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










