VSBSC (Vestigial Sideband Suppress Carrier)VSB is the modulation lying between SSB and DSBSC. SSB has a single spectrum, while DSB produces two sidebands on both sides of the carrier frequency. In VSB, a vestige is added to the SSB (Single Sideband) spectrum, as shown below: 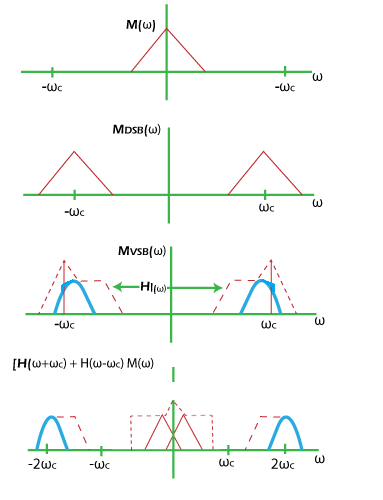
The vestige added to the spectrum is marked with the dotted lines. The additional spectrum added to the VSB is less than 1/4th of one sideband. Gradual tapering is irregularly added to the SSB spectrum. A small amount of lower sideband (<1/4th of one sideband) transmission is allowed with the upper sideband to make the transmission relaxed and efficient. Thus, both the SSB and VSB are highly efficient. VSB includes the advantages and covers the drawbacks of both the modulation. The advantage of SSB is the spectrum conservation, while that of DSB is demodulation simplicity. The drawback of SSB is the requirement of a sharp cut-off filter or a phase shift filter, and that of DSB is the high spectrum. Vestigial Sideband transmission avoids the phase shifter with a low bandwidth compared to DSBSC. In DSBSC, demodulation uses a coherent detection method. It multiplies the modulated signal with the coherent carrier signal for synchronization and uses LPF (Low Pass Filter) to recover the baseband signal. Similar modulation and demodulation are used in the VSB transmission. It multiplies the signal with the synchronous carrier and passes it to the low pass filter, which filters the original message signal. VSB transmission processAs discussed, the modulation process of VSB is similar to the other modulation processes. Let's discuss a short description about the VSB modulation and demodulation. The block diagram is shown below: 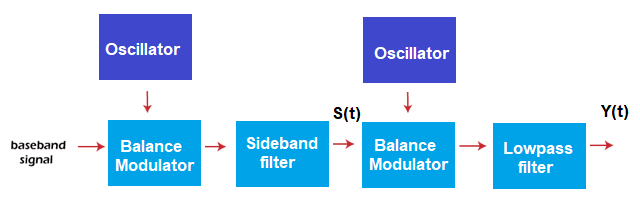
The message signal or the baseband signal is applied at the input of the balance modulator. The local oscillator provides the high carrier frequency. The modulator multiplies the message signal with the carrier signal. It helps in improving the frequency of the message signal. It is represented by: Let the message signal be m(t) and the carrier signal be AcosωCt. Where, A is the amplitude constant ωC is the carrier frequency The output of the modulator will be: S(t) = Am(t)cosωCt It will generate two sidebands like DSB (Double Sideband) transmission. The output of the modulator is applied to the sideband filter. The function of the filter is to select only one sideband based on the frequency of the first oscillator. The resulted sidebands will be the single sideband. The sideband filter adds vestige to the SSB spectrum. The output of the first filter will be the VSBSC. The above discussed process is the modulation process. The carrier, along with the signal, does not appear at the output of the first balance modulator. It is suppressed to improve its efficiency. The modulator cannot effectively balance both the message and carrier signal. The signal is further sent to the second balance modulator and filter, which is the demodulation process. The process of demodulation of VSBSC is defined as coherent detection. Here, a carrier signal is selected in coherence with the carrier during the first multiplication. It helps in recovering the message signal. It is also known as synchronous detection. At the input of the second modulator, the modulated signal is again multiplied with the coherent carrier signal. The equation can be represented as: Y(t) = [Am(t)cosωCt] cosωCt The resulting signal is passed to the low pass filter. It removes the carrier frequency component from the signal and recovers the original message signal. Mathematical representation of VSBSCLet the modulated signal and carrier signal be MVSB(t) and cosωct. The input of the VSB demodulator will be: Input of demodulator = Modulated signal x carrier signal Y(t) = MVSB(t)cosωct The Fourier transform of the above equation is given by: Y(ω) = 1/2 [M(ω + ωc) + M(ω - ωc)] Y(ω) = 1/4 [H(ω + ωc) M(ω + ωc + ωc) + H(ω + ωc) M(ω + ωc - ωc)] + 1/4 [[H(ω - ωc) M(ω + ωc - ωc) + H(ω - ωc) M(ω - ωc - ωc)] Y(ω) = 1/4 [H(ω + ωc) + H(ω - ωc)] M(ω) + 1/4 [H(ω + ωc) M(ω + 2ωc) + H(ω - ωc) M(ω - 2ωc)] The above component is passed to the filter, which removes the frequency component centered around 2ωc to recover the baseband signal. Applications of VSBThe main application of VSB is television broadcasting. Let's discuss it in detail. Television BroadcastingSSB is not preferred for video transmission because it can introduce complexity in various receivers. Thus, for efficient video transmission, VSBSC is used. The video signal occupies a bandwidth of 4.5M Hz. A carrier signal of a frequency higher than the message signal is selected, with a bandwidth of 9M Hz. It comprises two amplitude-modulated sidebands. The demodulation simplicity and reduced bandwidth in VSB make it suitable for video transmission. The modulated signal with the synchronous carrier is passed through the filter before transmitting to the receiver. The filter separates the two sidebands and adds a vestige to the SSB spectrum, forming the VSBSC wave. The upper sideband and lower sideband are transmitted so that they do not interfere. The upper sideband of the picture carrier is transmitted without attenuation at the frequency upto 4M Hz. Similarly, the lower sideband is transmitted without attenuation at 0.75M Hz. If the lower sideband signal is transmitted at 1.25M Hz, it will be fully attenuated. Thus, the transmission range of various sidebands can be represented as: Double Sideband: 0 to 0.75M Hz Single Sideband: > 1.25M Hz Intermediate range: 0.75M Hz to 1.25M Hz The maximum range for the transmission is upto 6M Hz. It saves two-thirds of the bandwidth. For the frequencies above 1.25M Hz, the sum of amplitudes of the two sidebands will be equal to the single sideband. The bandwidth of a single sideband is half compared to the double sideband. The filter used after the first balance modulator of the VSB process also helps to remove any uniformity in the signal. Advantages of VSBSCThe advantages of VSBSC are as follows:
Disadvantages of VSBSCThe disadvantages of VSBSC are as follows:
Next TopicQAM
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










