History of Cloud ComputingSince the beginning days of computing, when mainframe computers were accessible remotely through terminals, "cloud computing" has evolved. However, with the development of internet technologies and the demand for more effective and scalable computing solutions in the 1990s and early 2000s, the contemporary idea of cloud computing as we know it today first emerged. 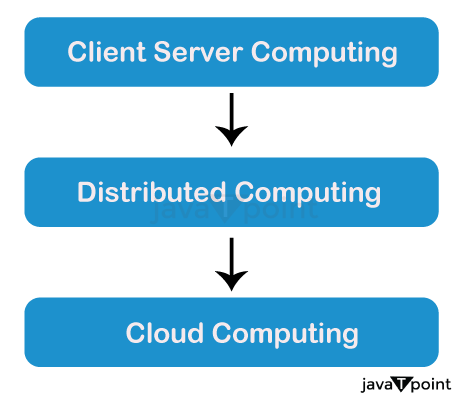
Before the advent of cloud computing, Client/Server computing was the dominant approach. The server side of this architecture served as the central location for all software programs, data, and controls. Users connected to the server and obtained the necessary access permissions to access specific data or run programs. Networked computing was built on top of client/server computing, but it had drawbacks in terms of resource efficiency and scalability.
The idea of distributed computing evolved as computers grew increasingly networked. Multiple computers could cooperate and share resources and processing power thanks to distributed computing. This model allowed for parallel processing and increased efficiency by dividing tasks across various processors. The centralized approach underwent a dramatic change with the advent of distributed computing, opening the door for more scalable and adaptable computer structures.
Client/server and distributed computing paradigms served as the cornerstones for the paradigm that eventually developed as cloud computing. The objective was to offer network-based, primarily the Internet, on-demand access to shared computer resources and services. The goal of cloud computing was to offer consumers flexible, scalable, and economical access to computing resources, storage, and applications. It shifted the emphasis to distant services and pay-as-you-go business models from local infrastructure and ownership.
As early as 1961, the idea of computers as a utility, comparable to water or electricity, was put out. Computer scientist John McCarthy proposed that computing resources may be bought and sold on demand while delivering a speech at MIT. But at that time, technology was not developed enough to support this goal. It was a brilliant idea, but like all brilliant ideas, it was ahead of its time; as for the next few decades, despite interest in the model, the technology simply was not ready for it. But of course, time has passed, and technology caught that idea.
Delivering applications over the internet in 1999, Salesforce.com transformed the software sector. Their creative strategy enables businesses to obtain software via a straightforward website, doing away with the requirement for difficult on-premises installs. This was an important step towards making the idea of computing as a utility a reality since it allowed companies to use cloud-based apps without having to worry about managing infrastructure.
Launched in 2002, Amazon Web Services (AWS) first provided computing and storage services. However, Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)'s launch in 2006 was what truly revolutionized cloud computing. With the help of EC2, users were able to hire virtual servers as needed, which was a scalable and economical solution. The success of AWS illustrated cloud computing's promise and inspired the quick growth of cloud services.
Other significant firms entered the cloud computing business after Amazon. Businesses can now take advantage of productivity tools and collaboration platforms on the cloud thanks to Google Apps, which started offering cloud-based enterprise apps in 2009. Microsoft introduced Windows Azure, a feature-rich cloud computing platform, in the same year. Businesses like Oracle and HP adopted cloud computing as well, providing a variety of services to meet various corporate demands. The presence of these major players in the industry as a whole has sped up the adoption of cloud computing in numerous industries.
Cloud computing's mainstream adoption is shown by the fact that businesses of all sizes are now reaping their advantages. Scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and improved collaboration are all benefits of the cloud. Businesses may easily link services, store and analyze enormous amounts of data, scale resources up or down as necessary, and launch applications quickly. Organizational operations have been altered by cloud computing, which has made it possible to innovate, be more agile, and cut costs.
Emerging technologies and shifting business requirements are driving the continued evolution of cloud computing. Edge computing is becoming more popular because it enables real-time data analysis and lower latency by processing data closer to the source. Serverless computing, which focuses on writing code rather than managing infrastructure, is also gaining popularity because it offers improved scalability and financial efficiency. The portability and simplicity of deployment across various cloud environments are provided by containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes. The future of cloud computing is also being shaped by developments in machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI). Organizations can use complex algorithms and models for data analysis, automation, and prediction using cloud-based AI and ML services. By enabling firms to gain useful insights, enhance decision-making, and automate procedures, these technologies foster creativity and productivity. Security, data privacy, and regulatory compliance issues are becoming more prominent as the cloud computing environment develops. To overcome these obstacles and offer a secure and reliable cloud environment, service providers are making significant investments in strong security measures, encryption methods, and compliance frameworks. 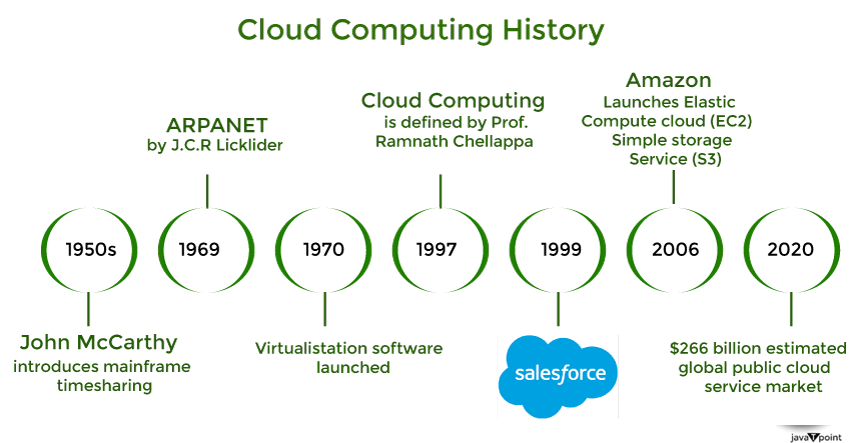
ConclusionIn conclusion, the development of cloud computing as a paradigm-shifting idea can be traced back to a remarkable excursion from the client/server model to distributed computing. The development of pioneers like Salesforce.com and Amazon Web Services has given cloud computing momentum and enabled it to become a crucial component of contemporary IT infrastructure. The widespread use of cloud computing has completely changed how companies run since it provides previously unheard-of levels of scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Future trends, including edge computing, serverless computing, and AI/ML integration, are anticipated to influence the cloud environment as technology develops, fostering innovation and upending several sectors throughout the world. Next TopicCloud Computing Architecture
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










