Private CloudDefinition and Characteristics:A private cloud computing environment is one that is only used by one organization or firm, as opposed to being shared by several organizations, as is the case with public clouds. The private cloud infrastructure may be set up on-site or hosted by a different company.
The following are the main traits of private cloud computing:
Private cloud computing environments are solely used by one organization, which implies that all of the hardware, storage, and networking are devoted to that organization.
Due to the high degree of customization private clouds provide, businesses can adapt the infrastructure to suit their requirements. In addition to the flexibility to configure the infrastructure to suit particular security and compliance standards, this customization may encompass the option of hardware, operating systems, and application selection.
Private cloud environments give businesses a lot of power over the infrastructure, enabling them to manage and tailor the environment to their own needs. The capacity to alter security rules, regulate user access and permissions, and govern the distribution of computing resources are all examples of control.
Because the infrastructure is devoted to a single organization, private clouds provide high security and data privacy. This enables organizations to put their own security policies and processes into place and guarantee that their data is always safeguarded.
Since private cloud environments need specialized infrastructure and qualified IT people to operate and maintain the environment, they can be expensive to set up and maintain. However, because they provide more control and flexibility over the infrastructure and can be customized to match the organization's unique demands, private clouds may become more affordable than public clouds in the long term. Private Cloud Deployment Examples:Various private cloud computing deployment strategies can be used, depending on the requirements of the organization. 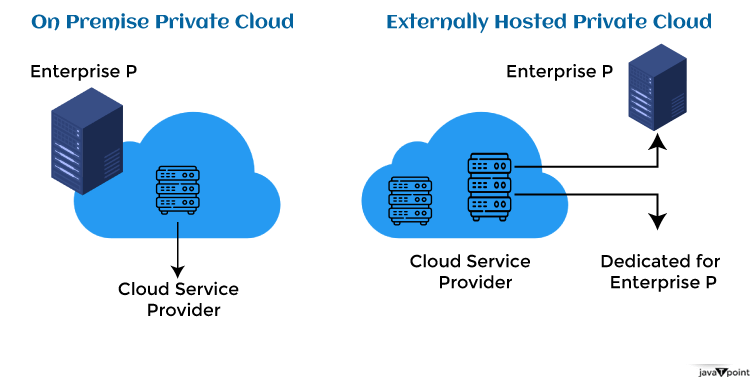
The following are some instances of private cloud deployment:
Advantages of Private Cloud
There are the following advantages of Private Cloud - More Control Private clouds have more control over their resources and hardware than public clouds because it is only accessed by selected users. Security & privacy Security & privacy are one of the big advantages of cloud computing. The private cloud improved the security level as compared to the public cloud. Improved performance The private cloud offers better performance with improved speed and space capacity. Customization Private clouds enable organizations to better customize infrastructure, security procedures, and applications to match unique business requirements. Enhanced Data Protection Since the infrastructure is devoted to a single organization, private clouds offer a better level of data protection and privacy, lowering the danger of unauthorized access or data breaches. Regulatory Compliance Private clouds are advantageous for sectors with stringent rules since they make it easier to comply with general standards and data protection legislation. Scalability and Resource Optimisation: Private clouds provide these features, enabling businesses to flexibly deploy computer resources according to demand for the best performance and financial effectiveness. Reliability and Availability: Private clouds frequently provide high levels of availability and dependability, with backup systems, failover mechanisms, and disaster recovery plans in place to reduce downtime and guarantee business continuity. Greater Network Performance: By removing any bottlenecks brought on by shared resources in public clouds, private clouds improve network performance. This leads to quicker data transfer rates and lower latency. Cost Management: Private clouds can reduce costs in the long run by maximizing IT spending and resource usage, even though they may require an upfront investment. Together, these advantages show how private cloud computing can be advantageous in terms of control, security, customization, data protection, compliance, scalability, dependability, network performance, and cost management. Considerations When Using Private Cloud:
Next TopicHybrid Cloud
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










