Infrastructure as a Service | IaaSIaas is also known as Hardware as a Service (HaaS). It is one of the layers of the cloud computing platform. It allows customers to outsource their IT infrastructures, such as servers, networking, processing, storage, virtual machines, and other resources. Customers access these resources on the Internet using a pay-as-per-use model. In traditional hosting services, IT infrastructure was rented out for a specific period of time, with pre-determined hardware configuration. The client paid for the configuration and time, regardless of the actual use. With the help of the IaaS cloud computing platform layer, clients can dynamically scale the configuration to meet changing requirements and are billed only for the services actually used. The IaaS cloud computing platform layer eliminates the need for every organization to maintain its IT infrastructure. 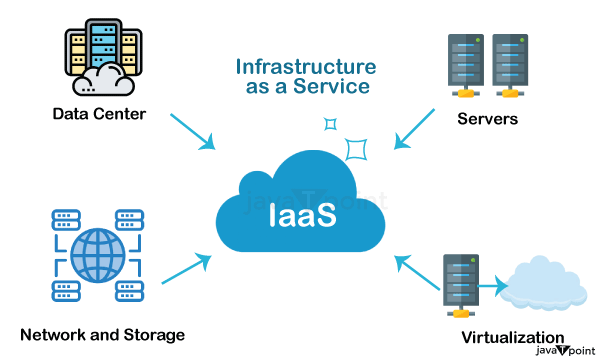
IaaS is offered in three models: public, private, and hybrid cloud. The private cloud implies that the infrastructure resides at the customer's premise. In the case of the public cloud, it is located at the cloud computing platform vendor's data center, and the hybrid cloud is a combination of the two in which the customer selects the best of both public cloud and private cloud. Some of the Primary Characteristics of IaaS are:
IaaS, or infrastructure as a service, is a cloud computing model that offers users virtualized computer resources on a pay-per-use basis. Users can scale their resources up or down in accordance with their demands while taking advantage of high availability, security, and customization possibilities. IaaS provider provides the following services - 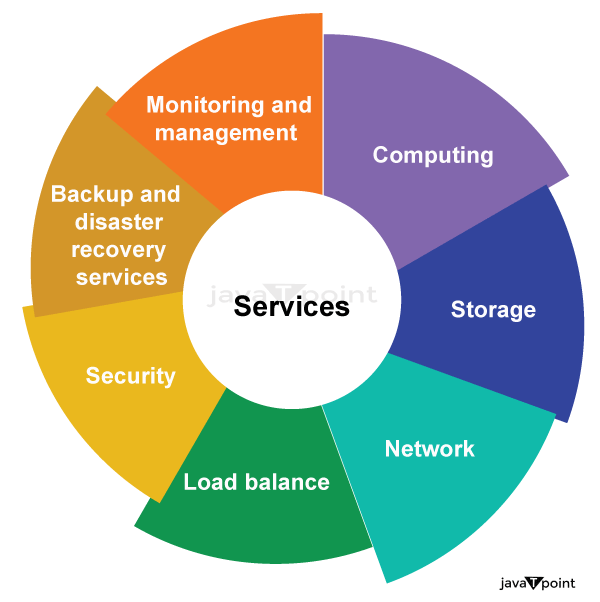
Computing: To provision virtual machines (VMs) for end users, IaaS providers offer virtual central processing units (CPUs) and virtual main memory. As a result, users may run their workloads and apps on the provider's infrastructure without having to worry about managing the underlying hardware. Storage: Back-end storage services are provided by IaaS providers, enabling users to store and access their files and data. This offers scalable and trustworthy storage solutions for a variety of use cases and can include block storage, object storage, or file storage alternatives. Network: IaaS providers provide networking tools, including routers, switches, and bridges for the VMs through Network as a Service (NaaS). This enables connectivity and communication between VMs and other resources while also allowing customers to create and maintain their network architecture within the IaaS environment. Load balancers: Infrastructure-layer load balancing services are provided by IaaS providers. Incoming network traffic is split up among many virtual machines (VMs) or resources by load balancers, resulting in effective resource management and excellent application and service availability. Security: Security features and services are frequently offered by IaaS providers as part of their offering. To safeguard data and resources housed on the IaaS platform, this can include network security, firewall configurations, access controls, encryption, and other security measures. Backup and disaster recovery services are provided by some IaaS providers, enabling customers to create backup copies of their data and software and put recovery plans in place in the event of data loss or system problems. This promotes business continuity and data security. Monitoring and Management: IaaS suppliers provide tools and services for monitoring and controlling the resources and infrastructure. This can involve managing VMs, storage, and network configurations using management panels or APIs, as well as measuring resource utilization, automating scaling, and monitoring performance. It's vital to remember that depending on the provider and their offerings, the precise services offered by IaaS providers may change. The list above illustrates some typical IaaS providers' common services. Virtualized Computing Resources:
Advantages of IaaS Cloud Computing LayerThere are the following advantages of the IaaS computing layer - 1. Shared infrastructure IaaS allows multiple users to share the same physical infrastructure. 2. Web access to the resources Iaas allows IT users to access resources over the internet. 3. Pay-as-per-use model IaaS providers provide services based on a pay-as-per-use basis. The users are required to pay for what they have used. 4. Focus on the core business IaaS providers focus on the organization's core business rather than on IT infrastructure. 5. On-demand scalability On-demand scalability is one of the biggest advantages of IaaS. Using IaaS, users do not worry about upgrading software and troubleshooting issues related to hardware components. Disadvantages of IaaS Cloud Computing LayerSecurity: In the IaaS context, security is still a major problem. Although IaaS companies have security safeguards in place, it is difficult to achieve 100% protection. To safeguard their data and applications, customers must verify that the necessary security configurations and controls are in place. Maintenance and Upgrade: The underlying infrastructure is maintained by IaaS service providers, but they are not required to automatically upgrade the operating systems or software used by client applications. Compatibility problems could come from this, making it harder for customers to maintain their current software. Interoperability Issues: Interoperability Problems: Because of interoperability problems, moving virtual machines (VMs) from one IaaS provider to another can be difficult. As a result, consumers may find it challenging to transfer providers or integrate their IaaS resources with other platforms or services. This may result in vendor lock-in. Performance Variability: Due to shared resources and multi-tenancy, the performance of VMs in the IaaS system can change. During times of high demand or while sharing resources with other users on the same infrastructure, customers' performance may fluctuate. Dependency on Internet Connectivity: Internet access is crucial to IaaS, which is largely dependent on it. Any interruptions or connectivity problems could hinder access to cloud infrastructure and services, which would have an impact on productivity and business operations. Learning Curve and Complexity: Learning Curve and Complexity: Using and administering IaaS calls for a certain amount of technical know-how and comprehension of cloud computing principles. To efficiently use and manage the IaaS resources, organizations may need to spend money on IT employee training or turn to outside experts. Cost Management: Cost Control: IaaS provides scalability and flexibility, but it can also result in difficult cost control. In order to prevent unforeseen charges, customers must keep an eye on and manage their resource utilization. Higher costs may be the result of inefficient use of resources or improper resource allocation. Some Important Points About IaaS Cloud Computing LayerIaaS cloud computing platform cannot replace the traditional hosting method, but it provides more than that, and each resource that is used are predictable as per the usage. IaaS cloud computing platform may not eliminate the need for an in-house IT department. It will be needed to monitor or control the IaaS setup. IT salary expenditure might not reduce significantly, but other IT expenses can be reduced. Breakdowns at the IaaS cloud computing platform vendors can bring your business to a halt stage. Assess the IaaS cloud computing platform vendor's stability and finances. Make sure that SLAs (i.e., Service Level Agreement) provide backups for data, hardware, network, and application failures. Image portability and third-party support are a plus point. The IaaS cloud computing platform vendor can get access to your sensitive data. So, engage with credible companies or organizations. Study their security policies and precautions. Top Iaas Providers who are providing IaaS cloud computing platform
Next TopicPlatform as a Service
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










