Software as a Service | SaaSSaaS is also known as "On-Demand Software." It is a software distribution model in which services are hosted by a cloud service provider. These services are available to end-users over the internet, so the end-users do not need to install any software on their devices to access these services. 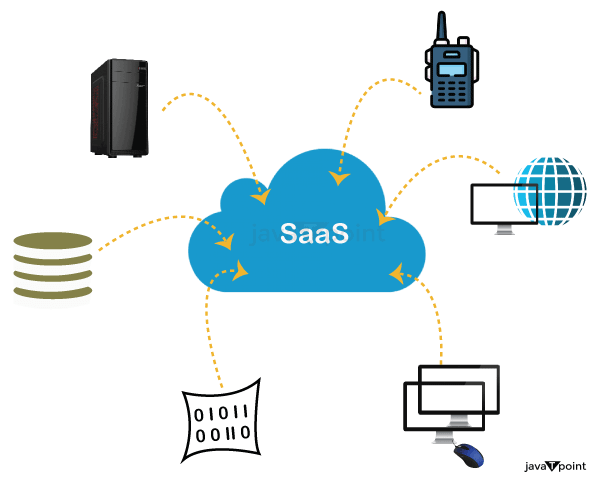
Characteristics of SaaS:
In conclusion, SaaS is a type of cloud computing where software applications are distributed online. Web-based SaaS solutions provide multi-tenancy, providing data protection, automatic updates, scalability, and subscription-based pricing. Businesses can access and use software applications cost-effectively with SaaS without having to worry about infrastructure or program upkeep. Access to Software Applications Over the Internet:
Pricing Models: Subscription or User-Based
Services Provided by SaaS:Business Services - SaaS Provider provides various business services to start up the business. The SaaS business services include ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), billing, and sales. Document Management - SaaS document management is a software application offered by a third party (SaaS provider) to create, manage, and track electronic documents. Examples: Slack, Samepage, Box, and Zoho Forms. Social Networks - As we all know, social networking sites are used by the general public, so social networking service providers use SaaS for their convenience and handle the general public's information. Mail Services - To handle the unpredictable number of users and load on e-mail services, many e-mail providers offer their services using SaaS. Collaboration Tools: SaaS companies provide collaboration solutions that let teams collaborate effectively no matter where they are physically located. Platforms for project management, apps for team communication, and file-sharing services are some of these resources. Examples include Slack, Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace (formerly G Suite). Human Resources Management: SaaS-based HR management systems give companies tools to simplify key HR procedures, such as employee onboarding, payroll administration, timekeeping, performance reviews, and employee self-service portals. Workday, BambooHR, and ADP Workforce Now, as examples. Customer Support and Help Desk: SaaS platforms provide customer support and help desk solutions that enable firms to manage customer inquiries, track support tickets, and promptly address customer issues. For instance, Salesforce Service Cloud, Freshdesk, and Zendesk. Marketing and Sales Automation: To increase productivity and boost income, firms can automate marketing campaigns, lead generation, customer relationship management, and sales activities using SaaS marketing and sales automation technologies. Examples include Marketo, Pardot, and HubSpot. E-commerce Platforms: SaaS-based e-commerce platforms make it simpler for businesses to launch and run online storefronts, maintain product catalogs, handle payments, and keep track of orders. Examples include WooCommerce (a WordPress plugin), BigCommerce, and Shopify. Advantages of SaaS Cloud Computing Layer1. SaaS is easy to buy SaaS pricing is based on a monthly fee or annual fee subscription, so it allows organizations to access business functionality at a low cost, which is less than licensed applications. Unlike traditional software, which is sold as a licensed base with an up-front cost (and often an optional ongoing support fee), SaaS providers are generally pricing the applications using a subscription fee, most commonly a monthly or annual fee. 2. One to Many SaaS services are offered as a one-to-many model means a single instance of the application is shared by multiple users. 3. Less hardware required for SaaS The software is hosted remotely, so organizations do not need to invest in additional hardware. 4. Low maintenance required for SaaS Software as a service removes the need for installation, set-up, and daily maintenance for organizations. The initial set-up cost for SaaS is typically less than the enterprise software. SaaS vendors are pricing their applications based on some usage parameters, such as the number of users using the application. So SaaS does easy to monitor and automatic updates. 5. No special software or hardware versions are required All users will have the same version of the software and typically access it through the web browser. SaaS reduces IT support costs by outsourcing hardware and software maintenance and support to the IaaS provider. 6. Multidevice support SaaS services can be accessed from any device, such as desktops, laptops, tablets, phones, and thin clients. 7. API Integration SaaS services easily integrate with other software or services through standard APIs. 8. No client-side installation SaaS services are accessed directly from the service provider using an internet connection, so they do not need to require any software installation. Disadvantages of SaaS Cloud Computing Layer:1) Security Actually, data is stored in the cloud, so security may be an issue for some users. However, cloud computing is not more secure than in-house deployment. 2) Latency issue Since data and applications are stored in the cloud at a variable distance from the end-user, there is a possibility that there may be greater latency when interacting with the application compared to local deployment. Therefore, the SaaS model is not suitable for applications whose demand response time is in milliseconds. 3) Total Dependency on the Internet Without an internet connection, most SaaS applications are not usable. 4) Switching between SaaS vendors is difficult Switching SaaS vendors involves the difficult and slow task of transferring very large data files over the internet and then converting and importing them into another SaaS also. Popular SaaS Providers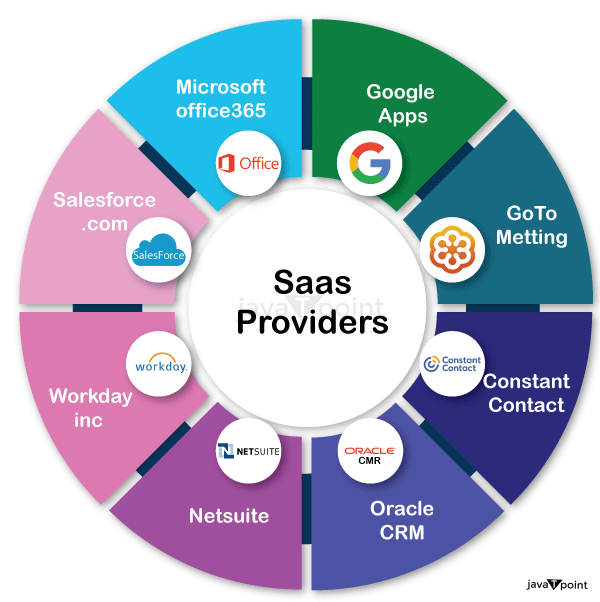
The below table shows some popular SaaS providers and services that are provided by them -
Next TopicVirtualization in Cloud Computing
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









