Contraception Definition
Contraception refers to the use of a variety of procedures or approaches to delay the fertilization or implantation of a fertilized egg to avoid becoming pregnant. Contraception's main objective is to give people and couples more control over their reproductive life and stop unplanned pregnancies.
Types of Contraception Method:
Contraception refers to the intentional use of various ways to avoid pregnancy. Today's contraceptive methods can be divided into two categories: hormonal methods and non-hormonal methods.
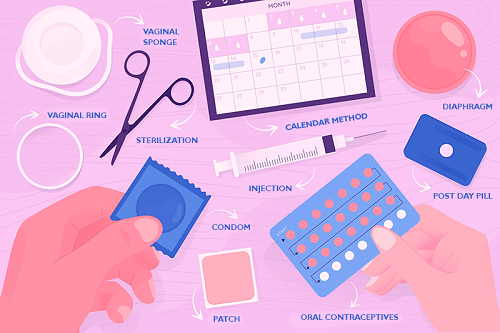
Hormonal Methods
Hormonal methods of contraception operate by modifying hormone levels in the body, blocking ovulation, or thickening cervical mucus to stop sperm from reach to the egg. Common hormonal contraceptive methods include the following:
- Birth control pills- It is the most widely used hormonal method of birth control. These pills come in two different forms: combination pills and mini pills. The mini-pill only includes progestin, whereas the combo pill contains both estrogen and progestin.
- Injection- The body is given an injection containing hormones every few months. No particular medication is required because this stops pregnancy for 8 to 13 weeks.
- Implant- The implant, which is a tiny rod implanted under the skin, distributes hormones over time. But it must be taken away or changed when the time limit expires.
- Vaginal ring- The vaginal ring is implanted once a month and progressively releases hormones over time. The ring is worn for three weeks, removed the week before your period, and replaced with a new ring.
- Patch- The patch is a little square that is put to the skin and delivers hormones into the bloodstream. After three weeks, you get a week without a patch. Each patch lasts for a week.
- Intrauterine devices are tiny, T-shaped objects placed into the uterus. Over time, they gradually produce a small quantity of progestin, suppressing ovulation and thickening cervical mucus. Depending on the kind, hormonal IUDs can be left in place for several years and are quite successful.
Non-Hormonal Methods
Non-hormonal contraceptives function by physically obstructing the path of sperm to the egg. Common non-hormonal contraceptive methods include:
- Condom- A common type of non-hormonal contraception is the condom. During sexual activity, they are worn on top of the penis and are constructed of latex or polyurethane. In addition to preventing pregnancy, condoms also offer protection from STDs.
- Copper IUDs- The way copper IUDs function is by making the environment unfavorable to sperm. The IUD's copper releases toxic ions that prevent sperm from fertilizing.
- Vasectomy- This surgical procedure prevents sperm from traveling from the testicles to the penis. These methods are considered permanent and are not easily reversible. However, they provide a high level of protection against pregnancy.
- Diaphragms and Cervical caps- Before sexual activity, barrier devices like cervical caps and diaphragms are put into the vagina. They function by covering the cervix and obstructing sperm entry to the uterus.
- Emergency contraception- A method of contraception that may be taken after unprotected intercourse to prevent pregnancy is emergency contraception, sometimes referred to as the morning-after pill. It comes in tablet form and inhibits or delays ovulation to work.
Advantages of Contraception:
- Prevents unintended pregnancies- Preventing unintended pregnancies is one of the main benefits of contraception, giving individuals and couples more control over their reproductive life.
- Enhances women's health- By lowering the risk of pregnancy-related disorders such as maternal mortality, pre-eclampsia, & ectopic pregnancy, contraception can also improve women's health.
- Reduces abortion rates- It has been demonstrated that access to contraception lowers the rates of unwanted pregnancies, which lowers the abortion rate.
- Improves economic and educational opportunities- By allowing women to put off having children and concentrate on their professions and education, contraception can also boost economic and educational prospects for women.
- Reduces the risk of pregnancy-related difficulties- Contraception can lower the risk of pregnancy-related complications such as pre-eclampsia, ectopic pregnancy, & maternal mortality. Reduces the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases (STIs): Condoms are one kind of contraception that can aid in STI prevention.
- Promotes Gender Equality- Access to contraception helps women have more control over their reproductive lives as well as decisions about their bodies, which advances gender equality.
- Reduces the need for abortion- Having access to contraception can help minimize the number of unwanted pregnancies and, as a result, lessen the necessity for abortion.
- Supports sustainable growth- By reducing population growth, assisting in the reduction of poverty, and enhancing health outcomes, contraception can promote sustainable development.
- Offers a variety of choices- Contraception comes in a wide variety, permitting people to select a suitable, safe, and effective technique.
Disadvantages of Contraception:
- Side effects- Various contraceptive techniques may result in undesirable and disruptive side effects, including nausea, headaches, body weight, and mood swings.
- Health risks- Some forms of contraception, like hormonal contraceptives, can raise your chance of developing breast cancer, blood clots, and stroke.
- Cost- For some people and families, particularly those without insurance or with low financial means, the price of contraception might be a barrier.
- Religious and cultural objection- Contraception usage may be prohibited by some religious and cultural views, which might restrict access to and use of the method on a social and cultural level.
- Inconsistent use- Using contraception inconsistently can make it less effective, resulting in unintended pregnancies.
- Limited protection from STIs- Hormonal contraceptives, for example, do not offer protection from sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Decreased spontaneity- Certain methods of contraception, especially barrier methods like condoms, need planning and may reduce the spontaneity of sex.
- Environmental impact- The disposal of medicine and packaging for some kinds of contraception, like hormonal contraceptives, may affect the environment.
- Ethics- The use of some methods of contraception, like emergency contraception, which some people could consider to be similar to abortion, could raise ethical issues.
The Conclusion
In conclusion, contraception is crucial for people and couples to manage their reproductive life better and avoid unexpected pregnancies. While choosing a contraceptive technique, it is essential to balance each strategy's possible advantages and disadvantages and consider personal preferences and health issues, including cultural and religious views. Individuals must have access to complete reproductive health treatments, such as contraception, to make educated decisions about their bodies & reproductive health.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









