Radiation DefinitionRadiation is a phenomenon that has been studied for centuries, and it encompasses a vast range of phenomena, from the light that we see to the ionizing radiation that can cause cancer. In this essay, we will provide an overview of the different types of radiation, their properties, and their effects on living organisms. Radiation can be broadly classified into two categories: ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation. 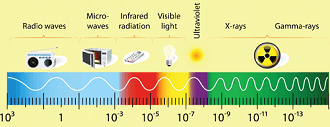
Ionizing RadiationIonizing radiation is radiation that has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms, creating ions. This type of radiation includes X-rays, gamma rays, and particles such as alpha and beta particles. 1. Electromagnetic radiation One of the most well-known types of radiation is electromagnetic radiation, which includes visible light, X-rays, and gamma rays. Electromagnetic radiation is characterized by its wavelength and frequency. Wavelength is the distance between the peaks of the electromagnetic wave, and frequency is the number of waves that pass a given point per second. The relationship between wavelength and frequency is inverse, meaning that shorter wavelengths have higher frequencies. Electromagnetic radiation can be further classified based on its wavelength, with radio waves having the longest wavelength and gamma rays having the shortest. Ionizing radiation is a particular concern because it can cause damage to living organisms at the cellular level. When ionizing radiation interacts with living tissue, it can create free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage DNA and other molecules. This damage can lead to mutations, which can in turn lead to cancer and other diseases. The severity of the damage depends on the type of ionizing radiation, the dose received, and the sensitivity of the tissue. 2. X-rays and gamma rays X-rays and gamma rays are two types of ionizing radiation that are commonly encountered in medical settings. X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength between 0.01 and 10 nanometers. They are commonly used for medical imaging because they can penetrate tissues and create images of bones and other dense structures. However, prolonged exposure to X-rays can increase the risk of cancer. Gamma rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than 0.01 nanometers. They are emitted by radioactive materials and can penetrate deep into tissues. Gamma rays are a particular concern in nuclear power plants and other settings where radioactive materials are present. 3. Alpha and beta particles Alpha particles and beta particles are two other types of ionizing radiation. Alpha particles are made up of two protons and two neutrons and have a positive charge. They have a short range and can be stopped by a sheet of paper or the outer layer of skin. However, if they are inhaled or ingested, they can cause significant damage to internal tissues. Beta particles are high-energy electrons that can penetrate deeper into tissues than alpha particles. They can be stopped by a layer of clothing or a few millimeters of plastic, but they can still cause damage if they are ingested or inhaled. Non-Ionizing RadiationNon-ionizing radiation is generally considered to be less harmful to living organisms than ionizing radiation. However, there are still concerns about the potential health effects of prolonged exposure to certain types of non-ionizing radiation. For example, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. In addition, exposure to high levels of radiofrequency (RF) radiation from cell phones and other electronic devices has been linked to an increased risk of brain cancer and other health problems. However, the scientific consensus is that the levels of non-ionizing radiation that most people are exposed to on a daily basis are not harmful. Other types of radiationsIn addition to the types of radiation described above, there are several other phenomena that are also referred to as radiation. For example, there is particle radiation, which includes subatomic particles such as protons, neutrons, and electrons that are emitted by radioactive materials. These particles can be ionizing or non-ionizing depending on their energy level. Neutron radiationNeutron radiation is another type of radiation that is commonly encountered in nuclear power plants and other settings where radioactive materials are present. Neutrons are subatomic particles that have no charge, and they can penetrate deep into tissues. Neutron radiation can cause damage to living tissue by interacting with the nuclei of atoms, creating free radicals and other reactive species. Health effects of radiationOne of the most important factors in assessing the potential health effects of radiation is the dose received. The dose of radiation is typically measured in units of gray (Gy) or sievert (Sv). Gray is a measure of the amount of energy deposited by radiation in a particular material, while sievert is a measure of the biological effects of that energy. Different types of radiation have different levels of ionizing power, meaning that they can cause different amounts of damage at the same dose level. For example, alpha particles have a high ionizing power and can cause significant damage to living tissue, even at low doses. There are several ways to protect against the harmful effects of radiation. In medical settings, shielding materials such as lead and concrete can be used to protect against X-rays and gamma rays. Personal protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and respirators, can also be used to protect against exposure to radioactive materials. In addition, radiation monitoring equipment can be used to measure radiation levels and alert workers to potential hazards. In the event of a nuclear accident or another radiation release, it is important to take steps to minimize exposure. This may include evacuating the area, staying indoors, and taking potassium iodide tablets to protect the thyroid gland from radioactive iodine. ConclusionIn conclusion, radiation is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that encompasses a wide range of phenomena, from non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation to highly ionizing alpha particles. While ionizing radiation can cause damage to living tissue and increase the risk of cancer and other diseases, non-ionizing radiation is generally considered to be less harmful. However, the potential health effects of radiation depend on many factors, including the type of radiation, the dose received, and the sensitivity of the tissue. By taking appropriate precautions and following recommended safety guidelines, it is possible to minimize the potential health risks associated with radiation exposure.
Next TopicRancid Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









