Dementia DefinitionLike heart disease, dementia is a general word for various medical diseases, including Alzheimer's. Abnormal brain alterations are the main reason for the disorders called "dementia" in general. 
Due to these modifications, cognitive abilities, also known as thinking skills, start to decline, and the impairment may be so severe as to disrupt daily lives and independence. Moreover, they affect emotions, conduct, and relationships. Alzheimer's disease causes 60 to 80 percent of cases. The second most prevalent type of dementia is vascular dementia, brought on by little bleeding and blockages in the blood arteries supplying the brain. The simultaneous presence of different forms of dementia brain abnormalities characterizes mixed dementia. Several other medical diseases, some treatable, such as thyroid issues and vitamin shortages, can also produce dementia-like symptoms. The inaccurate perception that substantial mental deterioration is a natural aspect of aging is reflected in the frequent use of "senility" or "senile dementia" to describe dementia. Definition of Dementia
A loss of thinking capacity, memories, concentration, logical reasoning, and other mental capacity is referred to as dementia. These alterations are significant enough to disturb social or professional functioning. The causes of dementia are numerous. It occurs when the brain areas linked to decision-making, language, and learning become damaged or ill. It may also be referred to as a significant neurocognitive disorder. Dementia is not a disease. Instead, it's a collection of symptoms brought on by various illnesses. In persons over 65, dementia affects 5% to 8% of them. Until you reach 65, this proportion doubles every five years. Up to fifty percent of adults in their eighties have dementia. Dementia Symptoms and Indicators
Dementia indicators may differ significantly. Many difficulties include
The symptoms of dementia develop slowly at first and then progressively worsen since many diseases are progressive. If you or someone you know is suffering from memory issues or other changes in cognitive abilities, do not ignore them. The quickest way to determine the cause is to see a doctor. A treatable problem may be discovered through professional assessment. Even if signs point to dementia, early diagnosis enables patients to get the most from existing therapies and allows them to enroll in clinical trials or research. Also, it gives you time to make plans. Types of Dementia
Depending on which brain region is damaged, there are two types of dementia. 1. Cortical Dementia
Problems with the cerebral cortex, the brain's outer layer, create cortical dementias. They serve a significant role in language and memory. Severe memory loss, verbal comprehension problems, and word forgetfulness mark certain forms of dementia. Alzheimer's disease and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease are two instances of cortical dementia. 2. Subcortical Dementia
Problems in the areas of the brain below the cortex create subcortical dementias. Subcortical dementia patients frequently experience variations in their capacity to begin tasks and their quickness of thinking. Those with subcortical dementia typically do not have forgetfulness or linguistic difficulties. Huntington's, Parkinson's, HIV, and three conditions can result in these types of dementia. Certain dementias have an impact on both hemispheres of the brain. Lewy Body dementia is one such instance of a cortical and subcortical disorder. Causes of DementiaDementia is caused by damage to brain cells. Damage that affects brain cells from forming connections. Thinking, behavior, and feelings may be affected when brain cells cannot communicate effectively. The brain is organized into several distinct regions, each carrying out a specific task (judgment, memory, and movement). Damaged cells in one place inhibit that area from performing normal functions. Certain forms of brain cell damage are linked to specific brain areas and various types of dementia. For instance, large quantities of certain proteins within and outside of brain cells contribute to Alzheimer's disease by making it difficult for brain cells to maintain their health and interact with one another. The brain's hub for memory and learning is the hippocampus, and it is this area of the brain where damage to brain cells frequently occurs first. As a result, memory loss is typically one of the initial symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Although many of the brain alterations that cause dementia are permanent and worsen with time, the following illnesses' effects on thinking and memory may be helped by medical treatment or attention.
The following are dementia's most typical causes Degenerative Neurological DiseasesThey consist of all followings condition
Vascular DisorderThese diseases impact the circulation of blood to your brain. Traumatic brain injuries brought on by vehicle accidents falls and slips, concussions, etc. Central nervous system infections. Meningitis, HIV, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease are some of them. Long-term usage of drugs or alcohol Many forms of hydrocephalus, a fluid collection in the brain Dementia can have reversible causes, such as
Factors at Risk for DementiaSome physical and nutritional factors, such as
Dementia's Different Stages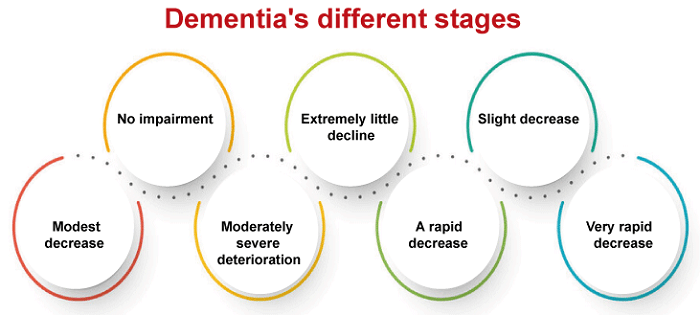
Dementia often progresses via these stages. Yet, it could differ according to the part of the afflicted brain. 1. No impairment A person at this stage won't show any symptoms, although testing can find a problem. 2. Extremely Little Decline Your loved one may experience modest behavioral changes, but they will remain independent. 3. Slight Decrease Their reasoning and way of thinking will keep shifting. They could find it difficult to make plans and frequently speak similarly. They could also struggle to recollect recent events. 4. Modest Decrease They'll need help remembering recent events and making plans. They could need help with handling money and travel. 5. Moderately Severe Deterioration They could be unable to recollect their contact number or grandkids' names. They might need to find out the time or day of the week. At this time, kids will require assistance with fundamental daily duties, such as choosing to clothe. 6. A Rapid Decrease They will begin to forget the name of their spouse. Kids will require assistance eating and going to the bathroom. Furthermore, they could have developed emotions and personalities. 7. Very Rapid Decrease They are unable to express their ideas properly. They cannot move and will spend almost all their time in bed. Identify of Dementia
The doctor will evaluate the patient's medical history using a physical examination and cognitive tests. According to the history and physical, more tests could be conducted. These tests might consist of the following
They utilize certain standards to identify dementia. They consist of the following
Next TopicCommunicable Disease Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









