What is a Linear Bus Topology?
Topology means the arrangement of nodes in a network where a node may be referred to as a computer, server, printer, etc. It deals with how nodes are interconnected. It also describes how data is transmitted between nodes. The physical topology of a network explains the physical layout of devices or cables. The logical topology of a network describes how data can be transferred between different devices in a network. Also, network topology describes the network performance. Linear Bus, Mesh, Star, Ring, and Hybrid are examples of physical Topology.
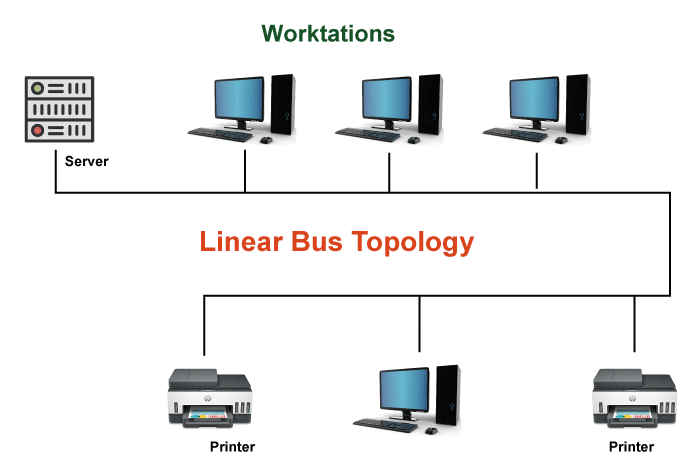
Linear Bus Topology is a network topology in which all devices are connected to a single communication line, called a bus. This Bus acts as a shared communication medium that connects all the devices in the network. In this Topology, each device is connected to the Bus using a T-connector or a tap.
When data is transmitted over the network, it travels in a single direction along the Bus from one end to the other. Each device on the network receives all the data transmitted on the bus, but only the device intended to receive the data processes it.
One of the main advantages of Linear Bus Topology is its simplicity and low cost, making it a popular choice for small networks. However, it has some limitations, such as a limited number of devices connected to the Bus, a potential for network congestion, and a single point of failure in the Bus.
Linear Bus Topology is a basic network topology suitable for small networks with few devices and relatively low traffic.
Advantages of Linear Bus Topology
- This Topology is simple and easy to set up, making it a cost-effective solution for small networks.
- Linear Bus Topology requires fewer wires and hardware. Thus, it saves a lot of costs. It is a low-cost solution for small networks.
- Adding a new device to the linear bus network is very easy. It can be done by adding a new tap or T-connector to the existing Bus.
- All the devices are connected to a single bus, so it is very easy to identify any issues.
- In a Linear Bus Topology, devices are connected to a single bus, so the amount of cabling required is minimized.
- Furthermore, Linear Bus Topology can handle a moderate amount of data traffic and does not experience network congestion due to excessive data transfer.
Disadvantages of Linear Bus Topology
Linear Bus Topology also has some disadvantages. Following are some of its disadvantages.
- In Linear Bus Topology, if the Bus fails, the entire network goes down because it is connected with a single cable.
- The number of devices that can be connected to the Bus is limited. Adding more devices can slow down the network performance.
- In this network, multiple devices try to transmit data simultaneously. This can cause network congestion.
- In Linear Bus Topology, all devices on the Bus can receive all data transmitted over the network. This can make it less secure than other topologies.
Physical Layout of Linear Bus Topology
The physical layout of Linear Bus Topology is relatively simple. All devices in the network are connected to a single communication line, called a bus. The Bus typically consists of a coaxial, twisted pair, or fiber optic cable.
Each device in the network is connected to the Bus using a T-connector or a tap, which allows data to be transmitted to and from each device on the network. The T-connector or tap connects to the main bus cable and branches off to each device on the network.
The network devices are typically arranged linearly, with the bus cable running from one end of the network to the other. The cable can be run above or below the floor, in a conduit, or along the ceiling.
In some cases, repeaters may be used to extend the length of the bus cable, as the length of the cable is limited, and signal degradation and attenuation can occur beyond a certain point.
The physical layout of Linear Bus Topology is relatively straightforward, and the simplicity of the network makes it easy to set up and maintain. However, it is essential to ensure that the cable length and the number of devices in the network are within the limits of the Topology to maintain reliable network performance.
How Does Data Transmission Take Place?
The logical layout of Linear Bus Topology is also relatively simple. In this Topology, all devices are connected to the same communication line or Bus, a shared medium for transmitting data.
When data is transmitted over the network, it travels in a single direction along the Bus from one end to the other. Each device on the network receives all the data transmitted on the Bus, but only the device intended to receive the data processes it.
In terms of addressing, each device on the network has a unique address or identifier, which is used to direct data to the intended recipient. However, there is no centralized control or hierarchy in Linear Bus Topology, so devices communicate with each other in a peer-to-peer fashion.
All devices on the network share the same communication line, so there is no need for switches or routers in Linear Bus Topology. This simplicity and lack of hierarchy make it popular for small networks with low to moderate traffic.
Common Protocols Used in Linear Bus Topology
In Linear Bus Topology, several protocols can facilitate communication between devices. Some of the most common protocols used in this Topology include:
- Ethernet: It defines how data is transmitted over the network, including the format of data packets and the addressing scheme used to direct data to the intended recipient.
- Token Ring: A token-passing protocol allows devices to take turns transmitting data over the network. In Token Ring, a special data packet called a token is passed between devices, and only the device holding the token can transmit data.
- LocalTalk: LocalTalk is a protocol developed by Apple for use in Macintosh computers. It is designed for small networks and uses a modified CSMA/CD protocol version to avoid collisions and ensure reliable data transfer.
- ARCNET: ARCNET is a protocol used in industrial control systems and other specialized applications. It uses a token-passing protocol designed for high-speed networks with multiple bus segments.
- FDDI: Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) is a high-speed protocol that uses token-passing to transmit data over fiber optic cables. It is designed for use in large networks with high bandwidth requirements.
Network Performance in Linear Bus Topology
The performance of a network in Linear Bus Topology depends on several factors, including the number of devices on the network, the type of data being transmitted, and the speed of the communication line or Bus.
- One of the advantages of Linear Bus Topology is that it is relatively simple and easy to set up, which makes it a cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized networks. However, as more devices are added to the network, the performance can degrade due to increased collisions and slower data transmission speeds.
- Another factor affecting network performance in Linear Bus Topology is the distance between devices on the network. As devices are located farther from each other, the signal strength can weaken, leading to slower data transmission speeds and potentially more errors in data transfer.
- To maintain optimal network performance in Linear Bus Topology, it is important to ensure that the number of devices on the network is kept within reasonable limits and that the communication line or Bus is of sufficient quality to support the required data transfer speeds.
- Linear Bus Topology can be a cost-effective and reliable solution for small to medium-sized networks. Still, larger networks or those with high bandwidth requirements may require a more complex topology or a different type of network architecture to achieve optimal performance.
How to Troubleshoot Linear Bus Topology
There are several steps to identify and resolve the issue with the network. Following are some troubleshooting steps that can be used for Linear Bus Topology.
- Checking the physical connections: First, it is very important in Troubleshooting to ensure that all the physical connections between the devices and the communication line or Bus have been properly established. You will make sure that all the cables are properly connected or not. If there is any sign of damage, we can remove that cable or that part.
- Check for signal interference: Next Issue that is very common is the lack of Signal in Linear Bus Technology. If there are many devices on the network, communication line, or Bus, signal interference is quite likely. In that case, you must detect the sources of interference. The source of interference can be electrical devices or radio signals. You must try to reduce or remove them.
- Check for data transmission errors: In a Linear Bus Topology, errors occur. You can use a network monitoring tool to detect such errors and also for the source of the error.
- Check for network congestion: Network congestion can occur when too many devices are on the network or your bandwidth is low. When there are too many devices on the network, or the bandwidth is limited, try to reduce the number of devices or increase the bandwidth if possible.
- Reset or restart devices: If all these fails. You can try resetting or restarting devices on the network to see if this resolves the issue. This can help clear any temporary device issues or network configuration issues.
Implementation of Linear Bus Topology in Real World
Linear Bus Topology is a relatively simple and cost-effective network topology that can be used in different sectors of today's real-world life. It has a very large impact on our daily life. Following are some conditions that depict how useful Linear Bus Technology is in today's real world:
- This Topology is a popular choice for small businesses with a big need to connect to a small number of devices for their daily need, such as computers, Printers, and servers. This Topology is very easy to set up and is cost-effective. It can be a good option for the small business network.
- Linear Bus Topology is also used in industrial automation applications, such as factory automation or process control systems. This Topology can connect sensors, actuators, and other devices reliably.
- Linear Bus Topology is used in building automation systems. This Topology can connect sensors and control devices in a building, making it easy to manage and control different systems.
- Linear Bus Topology is also used in transportation systems, such as trains, buses, and airplanes. This Topology can connect sensors and control devices in a vehicle, making monitoring and controlling different systems easy.
- Linear Bus Topology is used in entertainment systems like home theatres or audio systems. This Topology can connect devices, such as speakers, amplifiers, and media players, simply and reliably.
Security Consideration in Linear Bus Topology
Like any other network topology, Linear Bus Topology has some security considerations that need to be considered. Here are some of the main security considerations for this Topology:
- Unauthorized access: In Linear Bus Topology, any device connected to the communication line can potentially access all the data transmitted over the network. This means unauthorized devices can easily intercept sensitive data and compromise network security. It is important to use strong authentication and access control measures, such as passwords, encryption, and firewalls, to reduce this risk.
- Data interception: Data transmitted over the communication line can be easily intercepted and read by any device connected to the network. To protect against data interception, it is important to use encryption technologies, such as SSL/TLS or VPNs.
- Data modification: Any device connected to the network can also easily modify data transmitted over the communication line. To protect against data modification, it is important to use integrity checks, such as digital signatures or message authentication codes (MACs).
Comparison of Linear Bus Topology with Other Topology
Linear Bus Topology is one of several network topologies that can connect devices. Here is a comparison of Linear Bus Topology with some other common topologies:
1) Linear Bus Topology Vs. Star Topology
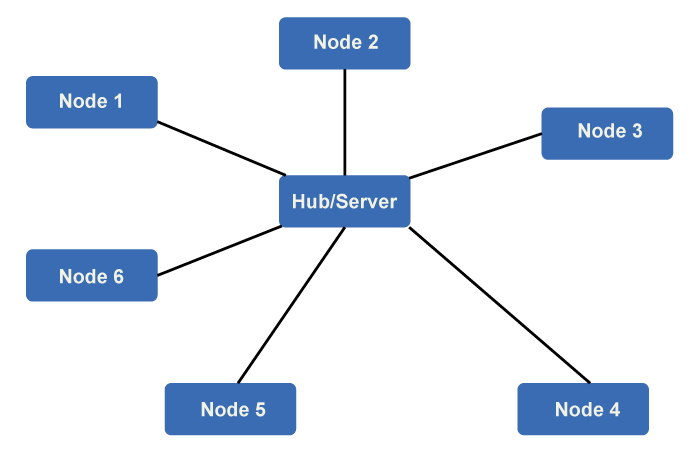
- In linear Bus Topology, you use a single cable, whereas star topology uses a central hub.
- It is difficult to diagnose the fault in linear Bus Topology, whereas it is very easy to diagnose the fault in star bus Topology.
- Adding a new node in a linear bus topology is difficult, whereas adding or removing a node in a Star bus topology is easy.
- The switch is used in linear bus Topology, whereas the switch is not in star bus topology.
- The speed of data and its transfer time is slow, whereas star topology has a faster transfer time.
- If a part of the linear Bus Fails, the whole network fails, whereas in a star topology, if one device fails, the entire network does not collapse.
- In Star Topology, each device is connected to a central hub or switch, which acts as a central point of communication.
- Star Topology can be more expensive and complex to set up compared to Linear Bus Topology.
2) Linear Bus Topology vs. Ring Topology
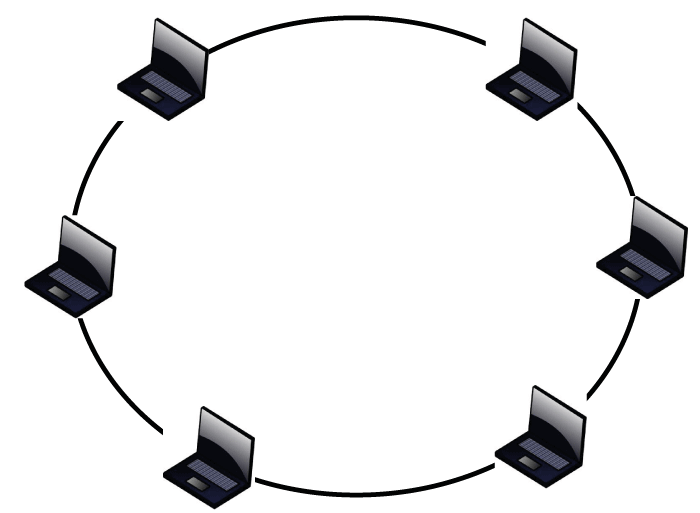
- In Linear bus topology, devices are connected to a common cable, and data is sent to all devices. While in a ring topology, devices are connected in a closed loop, and data flows in one direction around the ring.
- If the bus cable fails, the network goes down in the bus topology. In a ring topology, if a device or cable fails, the network can still function if the ring is not broken.
- Linear bus Topology has a lower level of security, while Ring topology offers higher levels of security as data can only flow in one direction.
- It's easy to add new devices to a Linear bus topology network while adding or removing devices in a ring topology network requires shutting down the entire network.
- Linear Bus topology's performance degrades as more devices are added, and many devices may lead to data collisions. In contrast, Ring topology is the deterministic delivery of frames, which is desirable in real-time applications.
- Bus topology has distance limitations for cable runs, which means the maximum length for a bus cable is limited. Ring topology is more expansive by distance, as the data is constantly flowing in a loop, which means it can connect devices over longer distances.
- Bus topology is easy to install and maintain and is simple to expand by adding new devices to the Bus. Ring topology is less flexible regarding topology changes, as adding or removing devices requires reconfiguring the entire network.
- Bus topology is cheaper, as only a cable is needed to connect all devices. Ring topology can be more expensive, requiring specialized equipment and complex cable runs.
- All devices must be physically close to the main cable in the Bus topology. In a ring topology, devices can be placed at any location since the data flows in a loop.
3) Linear Bus Topology Vs. Mesh Topology
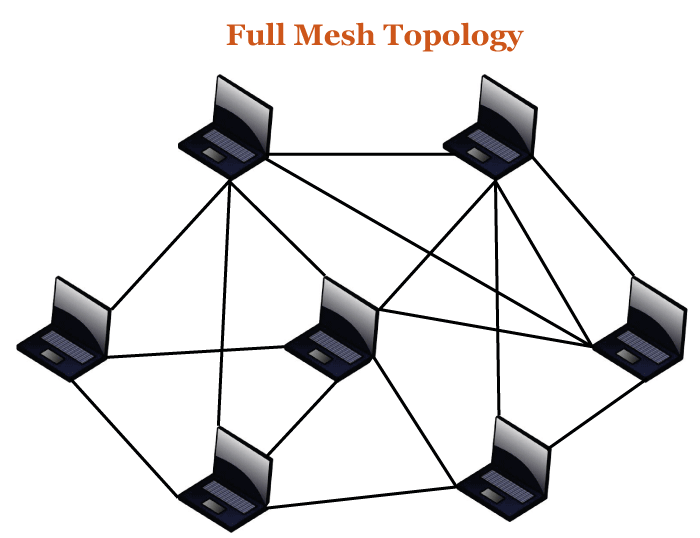
- In Mess Topology, each device is connected to another device in the network structure. In Bus Topology, each device is connected to other devices with a single string.
- In Mess Technology, if one device fails, data transfer will not be affected. In Linear Bus Topology, there will be no data transfer if one device fails.
- Mesh topology is stronger than Linear bus Topology. Linear bus topology is less strong than mess topology.
- Mesh Topology can manage large traffic, whereas Linear bus Topology cannot.
- There are many wires in Mesh Topology, whereas there is no such mesh of wires in linear bus topology as there is only a single wire.
- Mesh Topology is more complicated, whereas linear bus topology is simple in its structure.
4) Linear Bus Topology Vs. Tree Topology
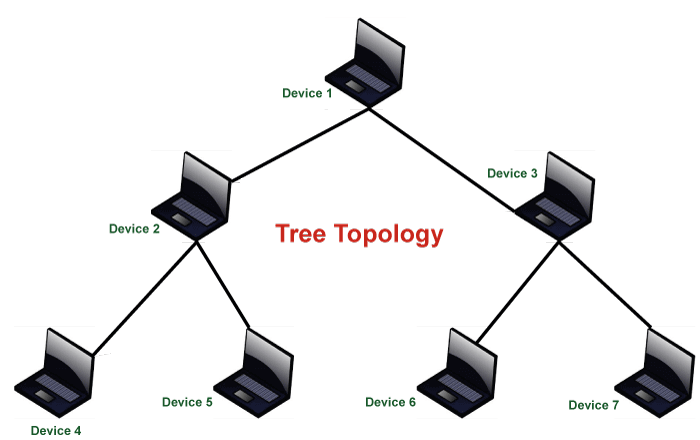
- Tree Topology is in the form of a hierarchy. There are many branches, and each can have a different type of Topology. In Linear bus Topology, there are no branches, and you will only see one type of Topology.
- Tree Topology is mainly used in Wide area Networks where many Local Area networks are connected.
- It is easy to detect any fault in the Tree Topology, whereas you need to check from the beginning to the end to check for any fault in linear bus topology.
- Tree Topology is expensive and complex, whereas Linear Topology is less expensive and simple.
|





 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










