Linux MeaningWhat is Linux?An operating system can be described as an interface among the computer hardware and the user of any computer. It is a group of software that handles the resources of the computer hardware and facilitates basic services for computer programs. An operating system is a necessary component of system software within a computer system. The primary aim of an operating system is to provide a platform where a user can run any program conveniently or efficiently. On the other hand, Linux OS is one of the famous versions of the UNIX OS. It is developed to provide a low-cost or free OS for several personal computer system users. Remarkably, it is a complete OS including an X Window System, Emacs editor, IP/TCP, GUI (graphical user interface), etc. It obtained the reputation as a very efficient and fast performing system. Linux is an operating system similar just like Mac OS, iOS, and Windows. Android is powered by Linux OS which is one of the most widely used platforms in the world. An operating system is software that handles each resource of hardware related to our laptop or desktop. The operating system handles the communication process between our hardware and our software to simply put it. But, when we have to select a platform to run embedded, servers, and desktop systems around the world, Linux is one of the most worry-free, secure, and reliable operating systems available. Pieces of LinuxThe Linux OS consists of various distinct pieces. Some of them are defined as follows: 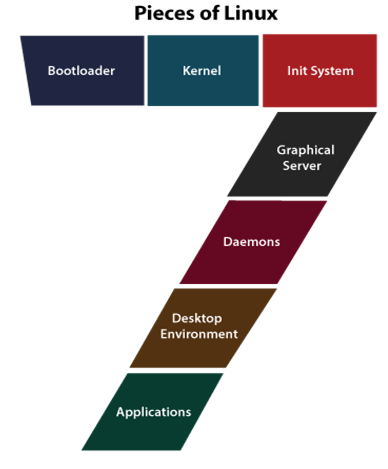
Most of the latest Linux distributions contain App Store-like resources that simplify and centralize the installation of the application. For example, Ubuntu Linux includes the Ubuntu Software Center which permits us to search quickly between the several applications and install them through a single centralized location. Why we should use Linux?Linux has derived into the safest ecosystem of the computer in the world. It includes the reliability with zero entry cost and we have the best solution for the desktop platform. We can install Linux over several computers without having to pay money for server or software licensing. Generally, Linux is less susceptible to various types of attacks such as viruses, malware, or ransomware. Open-sourceAlso, Linux is distributed upon the open-source license. There are a few key tenants that are followed by open-source:
These key points are necessary to understand the community that implements together for creating the Linux environment. Linux is the operating system i.e., for the people and by the people without any doubt. Also, these tenants are the main aspect in why several people select Linux. It is all about freedom, freedom of selection, and freedom of use. What is "distribution?"Linux includes several variations to suit their users. We will find several types of Linux flavors to match our requirements from novice users to hard-core users. These types of versions are known as distributions (or "distros"). All Linux distributions can nearly be free downloaded, installed (on as many machines as we like), and burned over the disk (or USB thumb drive). All of the distributions have a distinct take over the desktop. A few opt for various user interfaces like Elementry and GNOME OS's Pantheon. Besides, others interact with a traditional environment (KDE used by openSUSE). It is an OS that is composed of a software-based collection on Linux kernel or we can say the distribution includes the Linux Kernel. It is supporting software and libraries. We can obtain Linux-based OS by downloading any Linux distribution. These types of distributions exist for distinct types of devices such as personal computers, embedded devices, etc. Around more than 600 Linux distributions are existed and a few of the famous Linux distributions are listed as follows:
There are also some server distributions available:
A few of these above distributions of the servers are free (like CentOS and Ubuntu Server) and a few include an associated price (like SUSE Enterprise Linux and Red Hat Enterprise Linux). But, those servers with the associated price include support as well. Distribution SelectionWhich distribution we use will rely on the fact to three general questions:
If our computer proficiency is basic, we can use the distributions like Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Deepin, or Elementry OS. If our skillset increases into the above range, we can use the distributions like Fedora or Debian. However, if we are master of system or computer administration, we can use the distributions such as Gentoo. If we wish for any challenge, we can create our Linux distribution using Linux through Scratch. If we are searching for a server-only interface, we will wish to determine if we wish to do it by command-line only, or if we need any desktop interface. The Ubuntu Server doesn't install a Graphical User Interface. It means two things our server would not be annihilated downloading graphics and we will need to have a good knowledge of the Linux command line. We can however install the GUI package over the top of the Ubuntu Server along with an individual command such as Sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop. Also, system administrators will want to see a distribution with various features. Linux Operating System ApplicationsLinux is a billion-dollar corporation nowadays. Thousands of governments and companies are using Linux operating systems across the world because of lower money, time, licensing fees, and affordability. Linux can be used within several types of electronic devices. These electronic devices are easily available for users worldwide. A few of the famous Linux-based electronic devices are listed below:
Drawbacks of Linux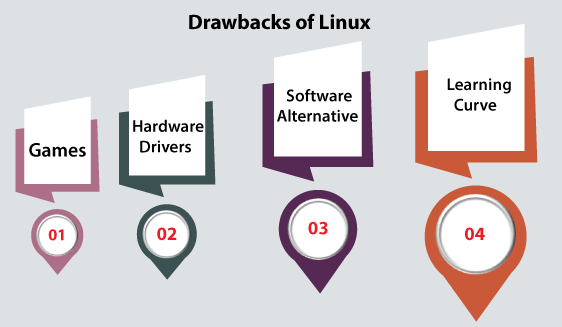
Installing LinuxThe idea to install an operating system may seem like a complex task for several people. Linux facilitates the easiest installations of each operating system. Most of the Linux versions facilitate live distribution. It means we execute the OS from either a USB or DVD/CD flash drive without creating any modifications to our hard drive. We can get the complete functionality without committing to the installation. Simply, we double-click on the install icon and proceed with the general installation wizard once we have tried it out and determined we wanted to use it. The installation wizards typically walk us through the procedure with the below steps: 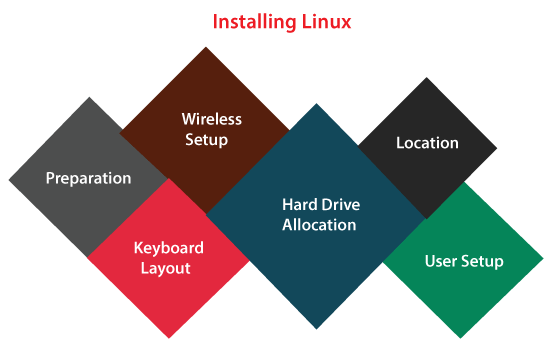
When the system installation is complete, restart, and we are ready to proceed.
Next TopicLinux Foundation
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










