MySQL GROUP BY ClauseThe MYSQL GROUP BY Clause is used to collect data from multiple records and group the result by one or more column. It is generally used in a SELECT statement. You can also use some aggregate functions like COUNT, SUM, MIN, MAX, AVG etc. on the grouped column. Syntax: Parametersexpression1, expression2, ... expression_n: It specifies the expressions that are not encapsulated within an aggregate function and must be included in the GROUP BY clause. aggregate_function: It specifies a function such as SUM, COUNT, MIN, MAX, or AVG etc. tables: It specifies the tables, from where you want to retrieve the records. There must be at least one table listed in the FROM clause. WHERE conditions: It is optional. It specifies the conditions that must be fulfilled for the records to be selected. (i) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with COUNT functionConsider a table named "officers" table, having the following records. 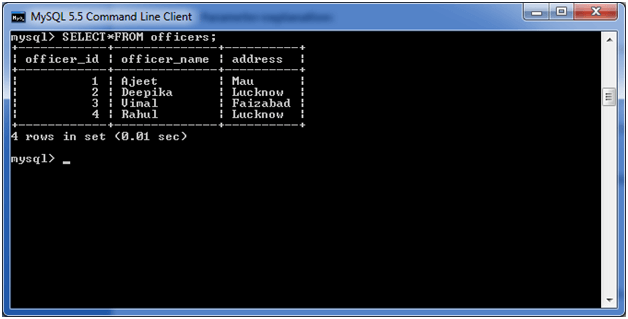
Now, let's count repetitive number of cities in the column address. Execute the following query: Output: 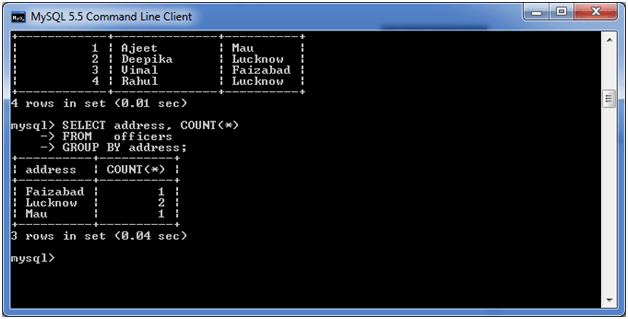
(ii) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with SUM functionLet's take a table "employees" table, having the following data. 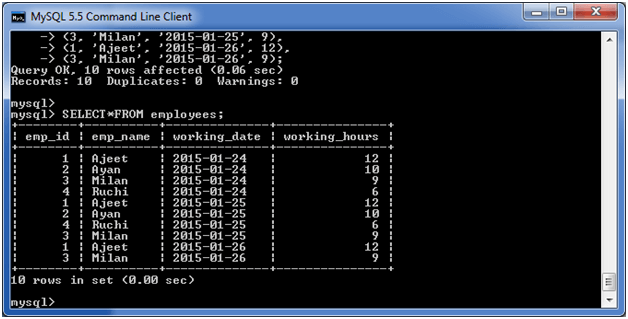
Now, the following query will GROUP BY the example using the SUM function and return the emp_name and total working hours of each employee. Execute the following query: Output: 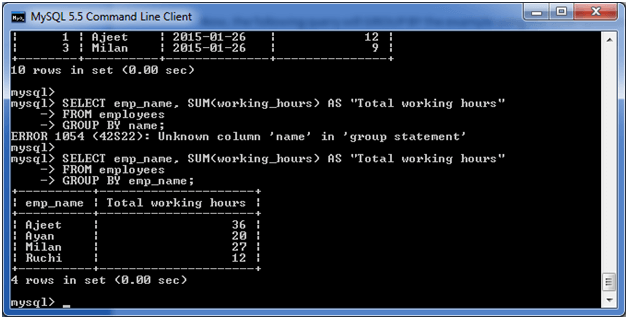
(iii) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with MIN functionThe following example specifies the minimum working hours of the employees form the table "employees". Execute the following query: Output: 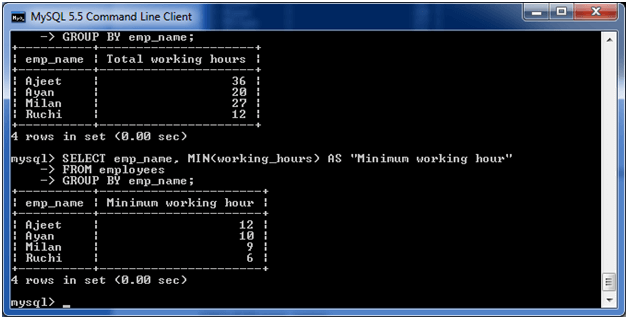
(iv) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with MAX functionThe following example specifies the maximum working hours of the employees form the table "employees". Execute the following query: Output: 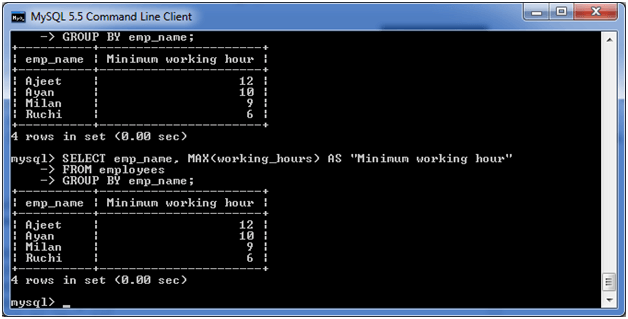
(v) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with AVG functionExecute the following query: Output: 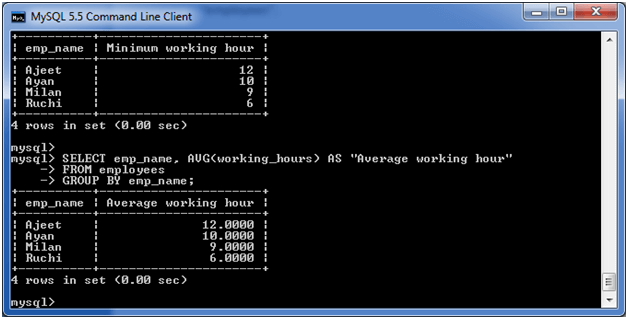
Next TopicMySQL Having
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









