MySQL UPDATE QueryMySQL UPDATE query is a DML statement used to modify the data of the MySQL table within the database. In a real-life scenario, records are changed over a period of time. So, we need to make changes in the values of the tables also. To do so, it is required to use the UPDATE query. The UPDATE statement is used with the SET and WHERE clauses. The SET clause is used to change the values of the specified column. We can update single or multiple columns at a time. SyntaxFollowing is a generic syntax of UPDATE command to modify data into the MySQL table: Parameter ExplanationThe description of parameters used in the syntax of the UPDATE statement is given below:
Note:
The UPDATE command supports these modifiers in MySQL: LOW_PRIORITY: This modifier instructs the statement to delay the UPDATE command's execution until no other clients reading from the table. It takes effects only for the storage engines that use only table-level locking. IGNORE: This modifier allows the statement to do not abort the execution even if errors occurred. If it finds duplicate-key conflicts, the rows are not updated. Therefore, the full syntax of UPDATE statement is given below: Example:Let us understand the UPDATE statement with the help of various examples. Suppose we have a table "trainer" within the "testdb" database. We are going to update the data within the "trainer" table. 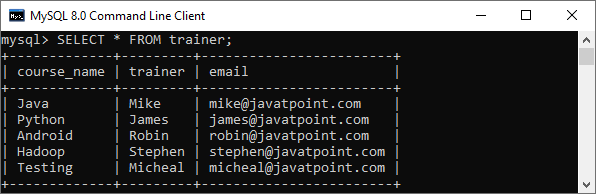
Update Single Column This query will update the email id of Java course with the new id as follows: After successful execution, we will verify the table using the below statement: In the output, we can see that our table is updated as per our conditions. 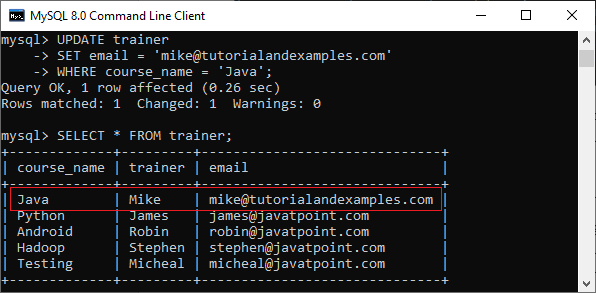
Update Multiple Columns The UPDATE statement can also be used to update multiple columns by specifying a comma-separated list of columns. Suppose we have a table as below: 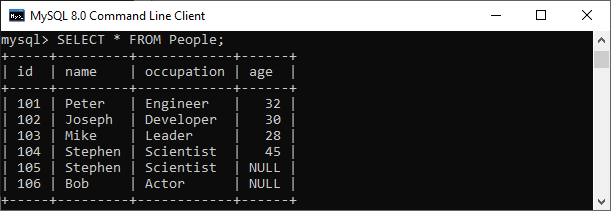
This statement explains will update the name and occupation whose id = 105 in the People table as follows: We can verify the output below: 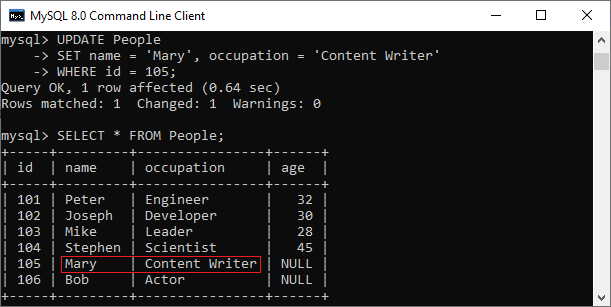
UPDATE Statement to Replace String We can also use the UPDATE statement in MySQL to change the string name in the particular column. The following example updates the domain parts of emails of Android course: It will give the following output: 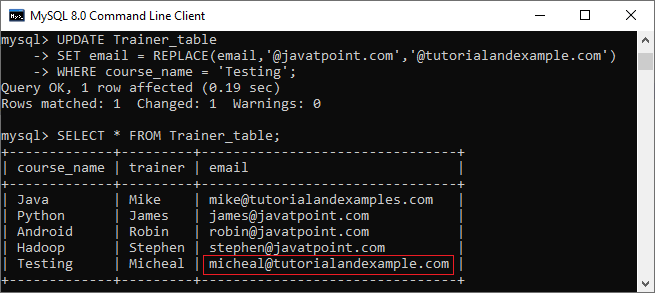
Next TopicMySQL Delete Query
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









