Difference between Primary Key and Foreign KeyKey in MySQL are the fundamental elements for constructing a relationship between two tables. They are very useful in the maintenance of a relational database structure. The main difference between them is that the primary key identifies each record in the table, whereas the foreign key is used to link two tables together. In this article, we are going to cover the essential differences between Primary and Foreign Keys based on various parameters. Before making a comparison, we will discuss in brief these keys. 
What is Primary Key?The primary key is a unique or non-null key that uniquely identifies every record in a table or relation. Each database needs a unique identifier for every row of a table, and the primary key plays a vital role in identifying rows in the table uniquely. The primary key column can't store duplicate values. It is also called a minimal super key; therefore, we cannot specify more than one primary key in any relationship. For example, we have a table named customer with attributes such as ID, Name, and City. Only the ID column can never contain duplicate and NULL values because each customer has a unique identification number. This feature helps to identify each record in the database uniquely. Hence, we can make the ID attribute a primary key. 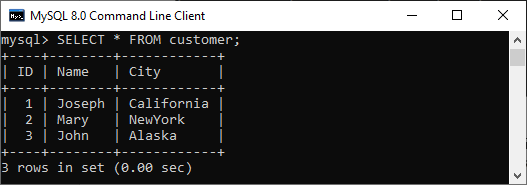
What is Foreign Key?The foreign key is a group of one or more columns in a database to uniquely identify another database record in some other table to maintain the referential integrity. It is also known as the referencing key that establishes a relationship between two different tables in a database. A foreign key always matches the primary key column in another table. It means a foreign key column in one table refers to the primary key column of another table. A foreign key is beneficial in relational database normalization, especially when we need to access records from other tables. A foreign key creates a parent-child relationship with the tables where the parent table holds the initial column values, and the child table references the parent column values. We can achieve this relationship only when the foreign key constraint is found on the child table. For example, we have a table named contact with attributes such as ID, Customer_Id, Customer_Info, and Type. Here we can make the Customer_Id column a foreign key. 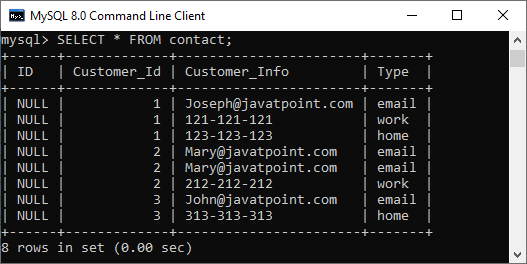
If we want to delete the referential data that removes records from both tables, we can define the foreign key in the contact table as below: When we delete any record from the customer table, the related rows will also delete in the contact table, and both tables update automatically. Key differences between Primary Key and Foreign KeyThe following points explain the differences between primary and foreign keys:
Primary Key vs. Foreign Key Comparison ChartThe following comparison chart explains their main differences in a quick manner:
ConclusionIn this article, we have made a comparison between primary key and foreign key constraints. Here we have concluded that both keys play an essential role in the relational database schema as they establish relations between multiple tables. The primary key column always stores the unique value for each record in the table, whereas foreign key value can be duplicated. Both constraint structure is the same, but their function differs as the primary key identifies a record in a table or relation uniquely. And the foreign key link two tables together.
Next TopicPrimary Key vs Unique key
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









