RANK Function in SQL ServerThe RANK Function in SQL Server is a kind of Ranking Function. This function will assign the number to each row within the partition of an output. It assigns the rank to each row as one plus the previous row rank. When the RANK function finds two values that are identical within the same partition, it assigns them with the same rank number. In addition, the next number in the ranking will be the previous rank plus duplicate numbers. Therefore, this function does not always assign the ranking of rows in consecutive order. The RANK function is also a sub-part of window functions. The following points should be remembered while using this function:
NOTE: Rank assigns temporary values for rows within the partition when the query is executed.SQL Server provides the following rank functions:
Let us learn each rank function in detail. First, we will create a table for demonstration of all these functions. The following statements create a table named rank_demo with three columns: Next, we will insert some rows into this table as below: We can verify the table using the SELECT statement. It displays the below output: 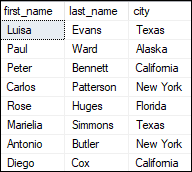
RANK() FunctionThis function is used to determine the rank for each row in the result set. The following syntax illustrates the use of a RANK function in SQL Server: In this syntax,
ExampleLet us see how the RANK() function works in SQL Server. The below statement will use the rank function to assign numbering for each row: Since we have not used the PARTITION BY clause, the function treated the whole result as a single partition. Executing the statement will display the below output: 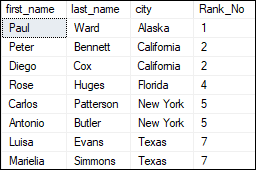
In this output, we can see that some of the rows get the same rank because they have the same value in the city column. And the next number in the ranking will be its previous rank plus a number of duplicate numbers. The following statement is another example where we are going to use a partition by clause that will divide the rows based on the city column and assign a ranking to each row within a partition. The order of the output is based on the first_name: It will display the below output: 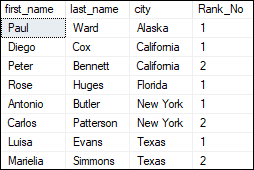
ROW_NUMBER() FunctionThis function is used to return the unique sequential number for each row within its partition. The row numbering begins at one and increases by one until the partition's total number of rows is reached. It will return the different ranks for the row having similar values that make it different from the RANK() function. The below syntax illustrates the use of a ROW_NUMBER() function in SQL Server: ExampleExecute the following query to assign a sequence number for each row: It will assign the ranking for the table as per their city. Here we can see that it assigns different ranks for the row which has the same city values. 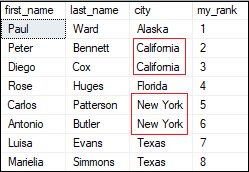
If we change the sorting order from ascending to descending with the ORDER BY clause, this function will also change the RANK accordingly. See the below statement: Here is the result: 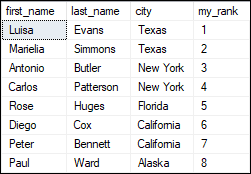
DENSE_RANK() FunctionThis function assigns a unique rank for each row within a partition as per the specified column value without any gaps. It always specifies ranking in consecutive order. If we get a duplicate value, this function will assign it with the same rank, and the next rank being the next sequential number. This characteristic differs DENSE_RANK() function from the RANK() function. The below syntax illustrates the use of a DENSE_RANK() function in SQL Server: ExampleThe following query uses the DENSE_RANK() function to assign a rank number for each row: It will return the below output where we can see that the duplicate values have the same rank, and the following rank will be the next sequential number. 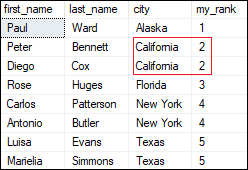
It is another example of the DENSE_RANK() function by using the PARTITION BY clause. This clause will divide the rows based on the city column, and the order of a result set is based on the first_name: We will get the below output because no two names are the same. In this case, the output is similar to the RANK() function. 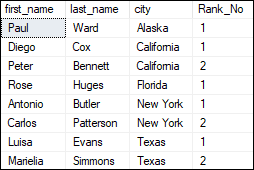
Let's update the name with the following query: Now, execute the same query again. We will see that this table got the same name in California City. Therefore, rank is also the same for both names. 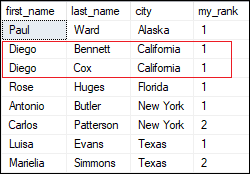
NTILE(N) FunctionThis function is used to distribute rows of an ordered partition into a pre-defined number (N) of approximately equal groups. Each row group gets its rank based on the defined condition and starts numbering from one group. It assigns a bucket number for every row in a group representing the group to which it belongs. The following syntax illustrates the use of a NTILE() function in SQL Server: Example The following query uses the NTILE() function to assign a rank number for each row: The specified table has eight records. Therefore, the NTILE(3) tells that the result set must have a group of three records. Executing the statement will display the below output: 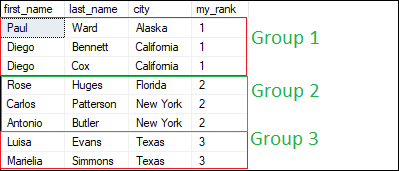
This article will explain all the RANK functions used in the SQL Server with various examples. It also shows the main differences between these functions. These functions are very useful for developers for exploring and managing their data well.
Next TopicSQL Server PIVOT
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










