Flutter Navigation and RoutingNavigation and routing are some of the core concepts of all mobile application, which allows the user to move between different pages. We know that every mobile application contains several screens for displaying different types of information. For example, an app can have a screen that contains various products. When the user taps on that product, immediately it will display detailed information about that product. In Flutter, the screens and pages are known as routes, and these routes are just a widget. In Android, a route is similar to an Activity, whereas, in iOS, it is equivalent to a ViewController. In any mobile app, navigating to different pages defines the workflow of the application, and the way to handle the navigation is known as routing. Flutter provides a basic routing class MaterialPageRoute and two methods Navigator.push() and Navigator.pop() that shows how to navigate between two routes. The following steps are required to start navigation in your application. Step 1: First, you need to create two routes. Step 2: Then, navigate to one route from another route by using the Navigator.push() method. Step 3: Finally, navigate to the first route by using the Navigator.pop() method. Let us take a simple example to understand the navigation between two routes: Create two routesHere, we are going to create two routes for navigation. In both routes, we have created only a single button. When we tap the button on the first page, it will navigate to the second page. Again, when we tap the button on the second page, it will return to the first page. The below code snippet creates two routes in the Flutter application. Navigate to the second route using Navigator.push() methodThe Navigator.push() method is used to navigate/switch to a new route/page/screen. Here, the push() method adds a page/route on the stack and then manage it by using the Navigator. Again we use MaterialPageRoute class that allows transition between the routes using a platform-specific animation. The below code explain the use of the Navigator.push() method. Return to the first route using Navigator.pop() methodNow, we need to use Navigator.pop() method to close the second route and return to the first route. The pop() method allows us to remove the current route from the stack, which is managed by the Navigator. To implement a return to the original route, we need to update the onPressed() callback method in the SecondRoute widget as below code snippet:
Now, let us see the full code to implement the navigation between two routes. First, create a Flutter project and insert the following code in the main.dart file. Output When you run the project in the Android Studio, you will get the following screen in your emulator. It is the first screen that contains only a single button. 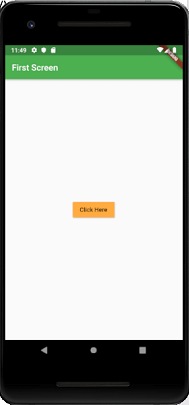
Click the button Click Here, and you will navigate to a second screen as below image. Next, when you click on the button Go Back, you will return to the first page. 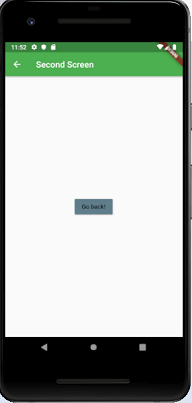
Navigation with Named RoutesWe have learned how to navigate to a new screen by creating a new route and manage it by using the Navigator. The Navigator maintains the stack-based history of routes. If there is a need to navigate to the same screen in many parts of the app, this approach is not beneficial because it results in code duplication. The solution to this problem can be removed by defining the named routes and can use the named routes for navigation. We can work with named routes by using the Navigator.pushNamed() function. This function takes two required arguments (build context and string) and one optional argument. Also, we know about the MaterialPageRoute, which is responsible for page transition. If we do not use this, then it is difficult to change the page. The following steps are necessary, which demonstrate how to use named routes. Step 1: First, we need to create two screens. The following code creates the two screens in our app. Step 2: Define the routes. In this step, we have to define the routes. The MaterialApp constructor is responsible for defining the initial route and other routes themselves. Here the initial route tells the start of the page and routes property defines the available named routes and widgets. The following code explains it more clearly. Step 3: Navigate to the second screen using the Navigator.pushNamed() function. In this step, we need to call Navigator.pushNamed() method for navigation. For this, we need to update an onPressed() callback in the build method of HomeScreen like below code snippets. Step 4: Use a Navigator.pop() function to return to the first screen. It is the final step, where we will use Navigator.pop() method to return on the first screen. Let us see the full code of the above explanation in the Flutter project and run it in the emulator to get the output. Output 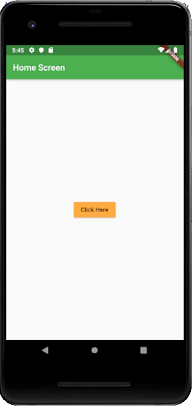
Click the button Click Here, and you will navigate to a second screen as below image. Next, when you click on the button Go Back, it will return to the Home Page. 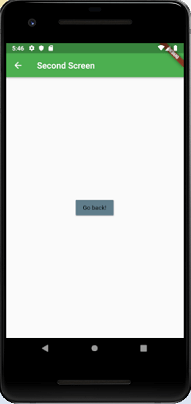
Next TopicAndroid Platform-Specific Code
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









