3D Object PropertiesJavaFX allows us to set the various properties of 3D objects. There are the special classes defined for each property in JavaFX. In this part of the tutorial, we will discuss the types of the properties which can be applied to the 3D objects for the better appearance. Cull FaceCulling can be simply defined as the process of removing the part of the 3D objects which are not visible in the view area. In JavaFX, 3D shapes contain the property of the type CullFace. This property can be set to an appropriate value by using the following instance method which is to be called on the 3D shape class object. .
setCullFace(CullFace value) there are three type of strokes defined in the CullFace class that are:
ExampleIn the following example, we have created three spheres and set three of the cull faces for each one of them. 
3D Object MaterialJavaFX provides different kinds of material which can be applied to the surface of a 3D shape. The class Material of the package javafx.scene.paint provides all the classes to deal with the material of a 3D shape. The class PhongMaterial is the subclass of the class Material. We just need to instantiate this class to create the desired material. This class provides various types of materials as the properties of this class which can be set to a certain value by using the setter methods. However, the material can be applied to a shape by using the following method. PropertiesThe properties of the class javafx.scene.paint.PhongMaterial along with their setter methods are described in the following table.
Example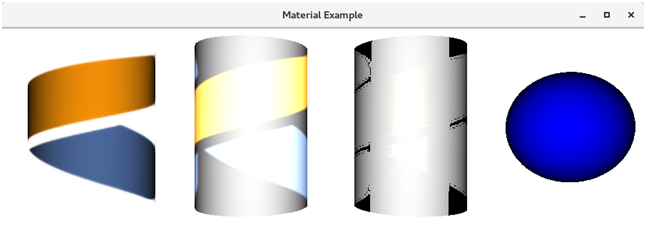
Drawing ModesJavaFX provides various Drawing modes to draw the 3D shapes. This property is of the type DrawMode. The following types of DrawMode are defined in the class.
Use the following setter method to set a drawmode for the 3D shape. ExampleIn the following example, we have created two boxes, one is by using DrawMode Fill while the other is by using DrawMode Line. 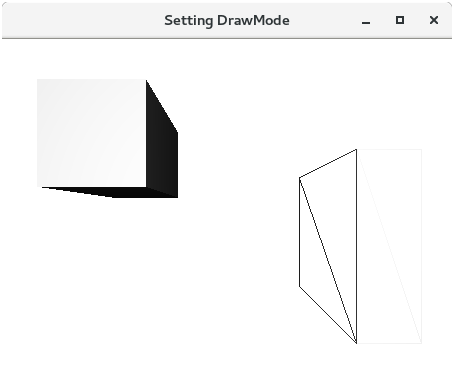
JavaFX CameraIn JavaFX, the camera is treated as an object which can be moved around a 3D layout and change the view of the Scene accordingly. The class javafx.scene.Camera represents camera. However, it is different from a 2D space where we don't need to move camera around the screen. In JavaFX, camera coordinate system, the X-coordinate points to the right, the Y-coordinate points to the down, and the Z-coordinate points away from the viewer or into the screen. For creating camera and adding it to the scene, we must use the following lines of code. // creating the instance of javafx.scene.Camera //setting the camera to 50 in the right X direction camera.setTranslateX(50); //setting the camera to 20 into the screen //Adding the camera to the scene JavaFX SubsceneA subscene node can be defined as a container which can hold the some node of the scene for which the camera angle needs to be specified. It is used for scene separation. We can use the subscene node if we need to set the different camera for a part of the scene. Subscene can be used in one of the following cases.
Use the following syntax to instantiate a subscene.
Next TopicJavaFX Box
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










