JavaFX ArchitectureThe following image shows the complete architecture of JavaFX platform. There are various built-in components which are interconnected with each other. However, JavaFX contains a rich set of APIs which are more than enough to develop rich internet applications which run consistently across many platforms. JavaFX public APIThe top layer of JavaFX architecture contains a JavaFX public API which provides all the necessary classes that are responsible for executing a full featured JavaFX application. The list of all the packages of this API are as follows.
Scene GraphIt is the starting point of constructing a JavaFX application. It is a hierarchical tree of nodes that represent all the visual elements of user interface. It also have the capability of handling event. In general, scene graph can be defined as a collection of nodes. Each node has its separate id, style and volume. Every node of a scene graph can only have single parent and zero or more children. All the implementation on a scene graph are actually applied to its node. Their are various classes present in javafx.scene package that are used for creating, modifying and applying some transformations on the node. We will discuss Scene graph later in detail. Graphics EngineThe JavaFX graphics engine provides the graphics support to the the scene graph. It basically supports 2D as well as 3D graphics both. It provides the software rendering when the graphics hardware present on the system is not able to support hardware accelerated rendering. The two graphics accelerated pipelines in the JavaFX are: Prismprism can be seen as High Performance hardware-accelerated graphics pipeline. It has the capability to render both 2D and 3D graphics. Prism implements different ways to render graphics on different platforms.
Quantum Tool kitQuantum Tool Kit is used to bind prism and glass windowing tool kit together and makes them available for the above layers in stack. Glass Windowing tool kitIt is present on the lowest level of JavaFX graphics stack. It basically can be seen as a platform dependent layer which works as an interface between JavaFX platform and native operating system. It is responsible for providing the operating system services such as managing the windows, timers, event queues and surfaces. Web ViewWe can also embed the HTML content to a JavaFX scene graph. For this purpose, JavaFX uses a component called web view. Web view uses web kit which is an internal open source browser and can render HTM5, DOM, CSS, SVG and JavaScript. Using web view, we can render the HTML content from JavaFX application , and also apply some CSS styles to the user interface. Media EngineBy using Media engine, the JavaFX application can support the playback of audio and video media files. JavaFX media engine depends upon an open source engine called as G Streamer. The package javafx.scene.media contains all the classes and interfaces that can provide media functionalities to JavaFX applications. 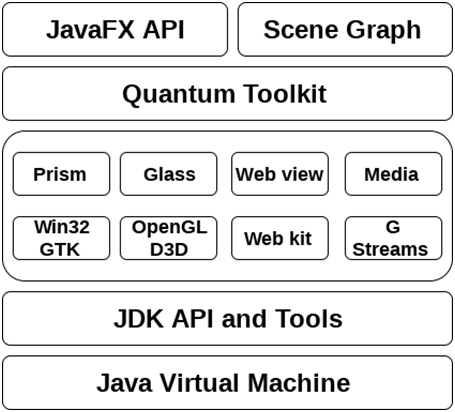
Next TopicJavaFX Application Structure
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










