Spring Boot JDBCSpring Boot JDBC provides starter and libraries for connecting an application with JDBC. In Spring Boot JDBC, the database related beans such as DataSource, JdbcTemplate, and NamedParameterJdbcTemplate auto-configures and created during the startup. We can autowire these classes if we want to use it. For example: In application.properties file, we configure DataSource and connection pooling. Spring Boot chooses tomcat pooling by default. JDBC Connection PoolingJDBC connection pooling is a mechanism that manages multiple database connection requests. In other words, it facilitates connection reuse, a memory cache of database connections, called a connection pool. A connection pooling module maintains it as a layer on top of any standard JDBC driver product. 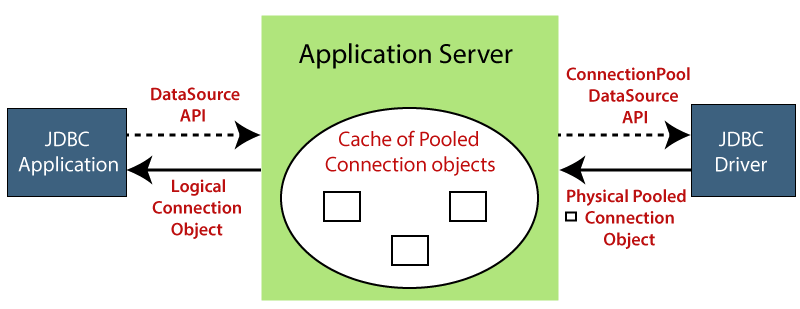
It increases the speed of data access and reduces the number of database connections for an application. It also improves the performance of an application. Connection pool performs the following tasks:
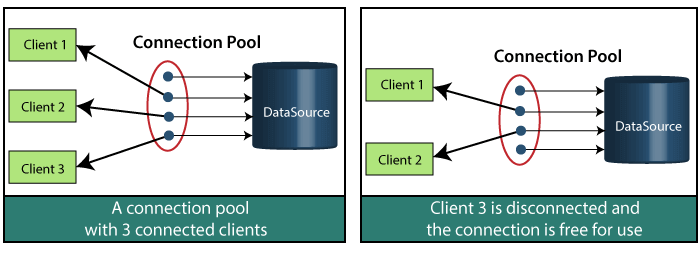
In the above figure, there are clients, a connection pool (that has four available connections), and a DataSource. In the first figure, there are three clients connected with different connections, and a connection is available. In the second figure, Client 3 has disconnected, and that connection is available. When a client completes his work, it releases the connection, and that connection is available for other clients. HikariCPThe default connection pool in Spring Boot 2 is HikariCP. It provides enterprise-ready features and better performance. HikariCP is a JDBC DataSource implementation that provides a connection pooling mechanism.
We can also configure a connection pool manually, if we do not want to use the default connection pool. Suppose, we want to use Tomcat JDBC connection pool instead of HikariCP. We will exclude HikariCP dependency and add the tomcat-jdbc dependency in the pom.xml file, as shown below. The above approach allows us to use Tomcat connection pool without having to write a @Configuration class and programmatically define a DataSource bean. On the other hand, we can also skip the connection pool scanning algorithm that Spring Boot uses. We can explicitly specify a connection pooling datasource by adding the property spring.datasource.type in the application.properties file. We have set up the Tomcat connection pool. Now, we will add some properties in application.properties that optimize its performance and suiting some specific requirements. If we want to connect to MySQL database, we need to include the JDBC driver in the application's classpath: After that, define the datasoure properties in application.properties file. Use the following properties if you are using MySQL database: Use the following properties if you are using Oracle database: Note: Spring Boot 2 uses HikariCP as the database connection pool, by default. If the HikariCP is not present in the classpath, Spring Boot choose tomcat pooling by default.Why should we use Spring Boot JDBC?The functionality of Spring JDBC and Spring Boot JDBC is the same except the implementations. There are following advantages of Spring Boot JBDC over Spring JDBC:
JDBC vs. Hibernate
In the next section, we will learn the connectivity of MySQL in an Spring Boot application.
Next TopicSpring Boot JDBC Example
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










