WIFI - Wireless Fidelity

Wifi is also known as Wireless Fidelity.
We are all familiar with Wi-Fi, which is available on our mobile phones, laptops, or wherever Wi-Fi is supported. Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that permits to connect wirelessly to a network or to other computer or mobile device. A circular radio frequency range is used to transmit data in Wi-Fi.
Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) is a generic term for the wireless network in the communication norm. Wifi operates like a local area network without the use of a wire or cables.
WLAN stands for Wireless Local Area Network. IEEE 802.11 is the rule for communication. WiFi uses the Physical Data Link Layer (PDLL) to operate.
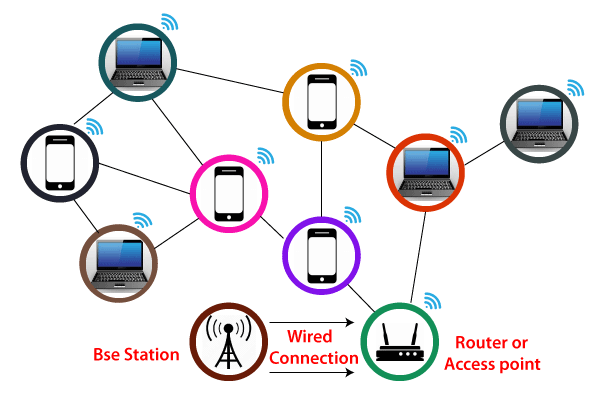
Modern computing devices like laptops and mobile phones, as well as digital cameras and smart TVs, all have Wi-Fi capabilities. The access point or base station to client connection or any client-to-client connection within a certain limit.
The range relies on the router that offers radio frequency via Wi-Fi.
Currently, these frequencies function on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bandwidths.
Because the Wi-Fi adapter within the device is responsible for receiving the Wi-Fi signal, all modern laptops and mobile devices are competent in using both bandwidths. All devices have a default bandwidth of 2.4 GHz.

2.4 GHz bandwidth is capable of covering a large area, but the frequency is low, so the internet speed is lower, and 5 GHz bandwidth can cover a smaller area, but the frequency is high, so the internet speed is higher. Hence, Wifi is a wireless network protocol family based on IEEE 802.11 standards. Moreover, it allows nearby digital devices to exchange data via radio waves.
Worldwide, these are the one of the commonly used computer networks. They are used in house networks to connect desktop or laptop or computers, tablets, smart TV, and printer to a wireless router, as well as in public access points in coffee shop, hotel, library, and airport.In order to qualify as Wi-Fi Certified, a product must pass interoperability certification evaluation. Wi-Fi is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, a non-profit organisation. There were more than 800 companies represented in the Wi-Fi Alliance as of 2017.
Over 3,05 billion Wi-Fi-equipped devices were shipped worldwide each year as per the reports of 2019. Ethernet (wired sibling)and Wi-Fi are developed to function seamlessly together.
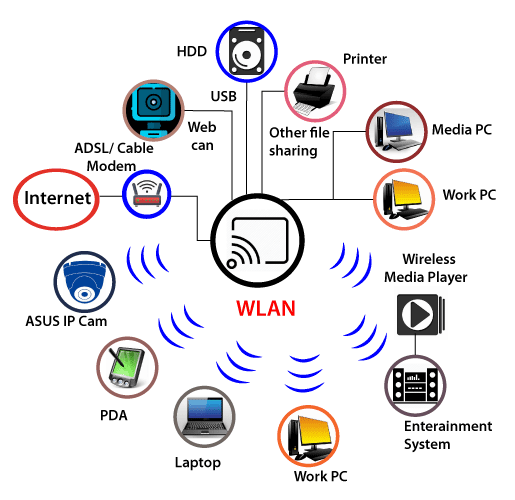
Wi-Fi-enabled devices can be connected via wireless access points and wired devices, and the internet.
Several IEEE 802.11 protocol norms specify the different Wi-Fi versions. The protocol standards also specify how much bandwidth and speed can be achieved using various radio technologies.
Wi-Fi utilisesthe 2.4 gigahertz (120 mm) UHF and 5 gigahertz (60 mm) SHF radio bands, which are segmented into various channels.
Only one transmitter at a time can communicate locally on a channel that is shared by multiple networks. It is best to utiliseWiFi in a direct line of sight due to its relatively high absorption.
As a rule of thumb, an access point (or hotspot) has a range of about 20 metres (66 feet) for the indoor environment, while some modern access points assert a range of up to 150 metres in the outside environment.
Hotspot coverage can be as tiny as a small room with walls blocking radio waves or huge comprising of an area of square kilometres (miles) utilising several inter-wining access points with roaming allowed between each.
In recent years, Wi-Fi's speed and spectral efficiency have both risen.
Wi-Fi versions operating on appropriate hardware can now get speeds of over 1 Gbit/s at close range as of 2019. (gigabit per second).
History of Wifi
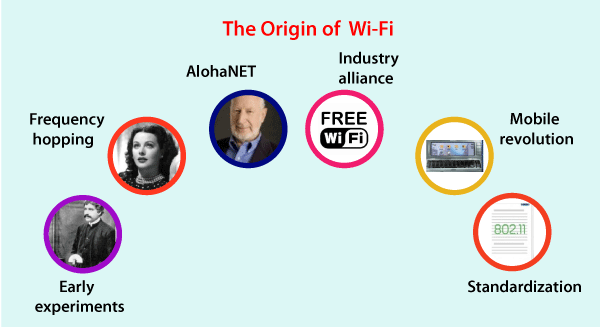
- Wi-Fi is an old concept, but its execution is a new concept. ALOHA System is a wireless network mechanism that was used to link Hawaii island through a network in 1971.
- ALOHA protocol was used for this, and packet transfer was used on the network in order to accomplish this task. IEEE 802.11 protocol is added later.
- 1985 saw the release of a new network for broad use by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), which operates on frequencies between 900 Mhz and 5.8 GHz. Acknowledged as the ISM band. It can transmit data at 4 Mb/s. IBM also presented a Token Ring LAN network for linking numerous computers.
- When waveLAN, a wireless cashier system, was invented in 1988, it operated at speeds of 1 to 2 megabits per second on the Token Ring Local Area Network. IEEE 802.11LAN/MAN standards were introduced in
- This was followed by Vic Hayes (known as the "Father of WiFi") establishing IEEE 802.11 Working Group for Wireless LANs in 1990.
- In 1994, Alex Hills initiated a wireless network research project that covered seven buildings wirelessly.
- This wireless network was later renamed IEEE 802.11a by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) in 1996.
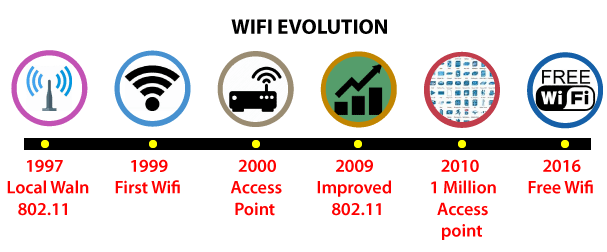
- After all of this, in 1997, the first version of Wi-Fi, 802.11, was released, which supports a maximum link speed of 2 Mb/s.
- When the link speed was increased to 11 Mb/s in 1999, it was called 11b.
- An additional month passed before IEEE 802.11a was officially approved, which provided up to 54 Mb/s link speed over the 5 GHz band, but with less range than 2.4 GHz.
- In 2003, 11g, a faster version, was released. Over 2.4 GHz, the speed ranges from 54 to 108 Mb/s.
- In the years that followed, 11i and 802.11e were added.
- Security was improved in 11i, while Voice over Wireless LAN and multimedia streaming were added to 802.11e.
- This was followed by the development in 2009 of the 802.11n standard, which supports both radiofrequency bands (2.4 and 5GHz).
- Dual-band routers use both of these are utilised concurrently and can reach speeds of up to 600 Mbps. As of 2014, a fresh version was launched in the 5GHz band with a prospective speed of 1733 Mb/s 802.11ac is the name given to this version. This has been the latest release of Wi-Fi up to this point.
- CISRO wireless LAN (Local Area Network) was selected as Australia's contribution to the exhibition in Australia -A History of the World in 100 Objects in the National Museum of Australia in 2016.
Usage and Application of Wifi
Many applications exist for Wi-Fi, including in all segments where computers or digital media are used. Wi-Fi can also be used for entertainment.
As an example, the following applications are described:
- We use Wi-Fi every day. With Wi-Fi, we can connect to the internet from any Wi-Fi-capable device.Wi-Fi allows us to have wireless communication, including streaming or casting audio or video to any device.
- Data transfer rates are also very fast when using Wi-Fi to share files, data, etc., among two or more computer or mobile phone.
- Another important attribute is the capability to print any document using a Wi-Fi printer.
- Wi-Fi can also be used as a HOTSPOT, providing Wireless Internet access for a specific area. While the main network connection is active, consumers of Wi-Fi-enabled devices can access the primary network connection via Hotspot, which provides them with temporary internet connectivity. To create a hotspot, Wi-Fi adapters spread radio signals by utilising the owner's network connection.
- Also one can create a Point-to-Point network using Wi-Fi or WLAN technology. Two sites that are hard to reach by wire, such as two corporate office buildings, can be connected using this method.
- VoWi-Fi is also recognised as voice-over Wi-Fi, which is another useful tool. Few years ago, telecom firmsput forward theVoLTE (Voice over LTE) (Voice over Long-Term Evolution ). In recent years, VoWi-Fi has become increasingly popular, allowing us to make calls and anyone using our home Wi-Fi network. The only requirement is that our mobile phone must be connected to Wi-Fi. Instead of using the mobile SIM network, voice is transferred over Wi-Fi, resulting in very high voice quality. VoWi-Fi is already supported by a large number of mobile phones.
- Internet via Wi-Fi in offices: In offices, all computer systems are linked to the Internet via Wi-Fi. In the case of Wi-Fi, there is no need for complicated wiring. Also, the network's speed is excellent. It's possible to present an entire Wi-Fi project, such as a spreadsheet or ppt, to all participants at once.
- A cable break in Wi-Fi does not result in a loss of network connectivity, as it would be in the case of a cable.
- By deploying routers at specific locations, a city can also provide network connectivity using W-Fi. Because of its flexibility, schools, colleges, and universities have already implemented Wi-Fi networks.
- As a positioning system, Wi-Fi can be used to recognise a device's area by detecting the placements of Wi-Fi hotspots.
Types or Kinds of Wifi
As mentioned earlier, Wi-Fi has numerous kinds or standards. Here, the names of the standards are defined.
- Wi-Fi-1 (802.11b, launched in 1999) - This version has link speed from 2Mb/s to 11 Mb/s over 2.4 GHz frequency band
- Wi-Fi-2 (802.11a) launched in 1999. After a month of releasing the previous version, 802.11a, was released, and it provides upto 54 Mb/s link speed over the 5 GHz band
- Wi-Fi-3 (802.11g) was launched in 2003. In this version, the speed was risen up to 54 to 108 Mb/s over 2.4 GHz
- 802.11i launched in 2004. This is equivalentto802.11g, but only the security feature was enhanced in this version
- 802.11e launched in 2004. This is also the same as 802.11g; only Voice over Wireless LAN and multimedia streaming are included.
- Wi-Fi-4 (802.11n) launched in 2009. This version holds up both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio frequencies, and it provides up to 72 to 600 Mb/s speed.
- Wi-Fi-5 (802.11ac) launched in 2014. It supports a speed of 1733 Mb/s in the 5 GHz band.
In 2020, Huawei launched 802.11ax, the latest version that can support 3.5 Gb/s; recognised as Wi-Fi 6.
Working or Functioning of Wifi
What is the Wi-Fi protocol?
First and foremost, Wi-Fi is a wireless communication system that transmits networks using electromagnetic waves. The radiofrequency is utilised in Wi-Fi because we understand that there are several types of electromagnetic waves based on their frequency, including X-rays, Gamma-rays, radio waves, microwaves, etc.
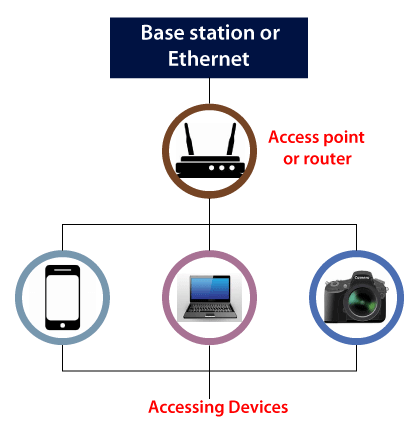
- Base station network or Ethernet(802.3) connection: It is the primary host network from which the router receives its network connection.
- Access Point or Router - Network bridge, also known as an access point or router, connects wired and wireless networks. A wired Ethernet connection is accepted, and the wired connection is converted to a wireless connection, which is then spread via radio waves.
- Accessing Device - There are several ways to gain access to information. From our mobile, computer, etc., we access Wi-Fi and surf the web using Wi-Fi.
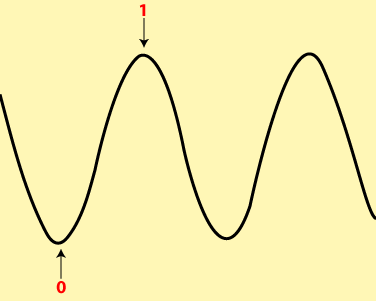
Also, routers and our devices read data in binary form. In this case, routers transmit radio waves to our devices, obtaining and reading the waves in binary form. All of us are familiar with the binary representation of a wave, in which the topmost pick is 1 and the lower pick 0 in binary.
Terminology of WIFI
Another term for Wi-Fi is "wireless LAN."
- SSID (Service Set Identifier)-WiFi networks are identified and distinguished from one another by their service set identification (SSID) numbers, which are 32 characters long. All gadgets are trying to communicate to the same SSID (Service Set Identifier). SSID stands for "Service Set Identifier" and is the title of the wireless network.
- WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access- Pre-Shared Key): It's a programme created by the Wi-Fi Alliance Authority to safeguard wireless networks using Pre-Shared Key authentication. WPA comes in three varieties: WPA, WPA2, and WPA3. An encryption method for Wi-Fi signals to keep out unwanted users.
- Ad hoc networks are used by Wi-Fi in order to transmit data. A point-to-point network without an interface, it's a wireless mesh network.
Advantages of WIFI
The advantages of Wi-Fi Tt include
- A versatile network connection and the absence of complicated wiring requirements for installation.
- Everywhere in the Wi-Fi range can access it.
- Independent users are not required to obtain regulatory approval.
- In addition, Wi-Fi Extenders make it possible to expand the network.
- It's easy and quick to set up.
- Only the SSID and password need to be configured.
- As part of its security measures, Wi-Fi networks encrypt radio signals using WPA encryption.
- It is also more affordable.
- Hotspots are another feature that it offers.
- Roaming is supported as well.
Wi-Fi Disadvantages
- Mobile phones, laptops, and other devices with batteries consume a lot of power when using Wi-Fi.
- Even when encryption is in place, security issues can still arise.
- Wi-Fi can be attacked and accessed in the same way that recognised devices become unidentified to the router.
- In comparison to a direct cable connection, the speed is slower.
- People can be harmed by it because it emits radiation like cell phones.
- Thunderstorms, for example, can interfere with Wi-Fi signals.
- Because it lacks a firewall, unauthorised access to Wi-Fi is possible.
- Since a router is required to access the internet via Wi-Fi, we can't access the internet if the power goes out.
Alternatives to Wifi
Alternatives to Wi-Fi include several other wireless technologies:
- As a short-range network, Bluetooth is a great option.
- Mobile networks, used by mobilephonesand WiMax, for serving the users with long-range wireless internet connection
- For long-range wireless with a low data rate, there is LoRa
- Reusing existing cables is one option.
- Home wires, like as telephone and power lines, are used by G.hn
- There are a number of wired computer networking technologies that are viable alternatives to Wi-Fi, such as:
- IEEE 802.3ah twisted pair
|







 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now











