Branches of AccountingThe process of recording financial transactions that take place in a business is known as accounting. This process includes summarising, analyzing, and reporting various financial transactions. With the help of these transactions, the financial performance of a company can be calculated. Accounting has several branches which play different financial roles to various parties. Here, 12 types of branches of accounting are given: 1. Financial AccountingUnder this branch of accounting, recording and clarifying the business transactions and preparing and presenting the financial statements is done. Financial accounting works on the principles of GAAP and focuses on the historical data and performance of the company. For example, the reports and records can be analyzed by a financial accountant to check the previous quarter's performance and make the required changes in the next quarter. This is helpful in analyzing the balance sheet and preparing the P&L Account. This information is used by various interesting parties such as management, stakeholders, creditors, etc. in regards to loans, investments, or acquisitions. The information that can be collected with the help of financial accounting is related to the following:
2. Managerial AccountingThis accounting is used to supply the information to the internal structure of the company, i.e., management. These accountants have the responsibility to monitor the use of money instead of its amount. The rules of GAAP are not necessary to follow in managerial accounting and are a point of focus in the needs of management. The CIMA has prepared a set of accounting principles which are called Global Management Accounting Principles (GMAP). This accounting concept helps in improving the administration of the company, enhancing its profit, and providing management with financial reports that leave effects on planning and budgets. Managerial accounting forecasts to advise management on the most profitable business practices so that the required goals can be met. This accounting is useful in conducting internal examinations through Cost to Volume Profit (CVP) or break-even point. These are the factors that affect decision-making. 
3. Cost AccountingCost accounting is generally considered a subset of management accounting. Under this branch, the point of focus is evaluating costs. For this purpose, cost accounting considers all the factors of manufacturing so that the cost of a project or venture can be determined accurately. A cost accountant prepares and presents reports by analyzing manufacturing costs. It helps the decision-makers in getting effective information about how to reduce costs or when and where to spend more. It supervises various projects to control waste and cost. The prime use of cost accounting is to analyze actual costs over budget so that future monetary actions can be determined. 
4. AuditingAuditing can be done internally or externally by the company. This branch of accounting helps in examining and monitoring an accurate report for the business, compliance with various tax regulations, and financial integrity. There are generally two types of auditors that are hired by the company:
5. Tax AccountingUnder this branch of accounting, state and federal tax rules are included which is used during tax planning or preparing the tax returns. Tax accounting focuses on the effects of tax policies on a business and tries to minimize the taxes or the consequences of tax decisions through advisory services. These accountants are responsible to calculate the income and other taxes that are dependent on the business structure. As we know, taxes and income brackets are different for different companies. Tax accounting had proper tax laws whether the company is a sole proprietorship, corporation, or limited liability cooperation (LLC). 
6. Fiduciary AccountingUnder fiduciary accounting, those accounts are handled and entrusted to the person who takes care of the property's custody and management. These accountants are responsible for tracking and reporting receipts and disbursements from accounts to ensure proper allocations of funds. This accounting mainly serves the following:
7. Project AccountingThere are some industries like constructions or engineering, that work on various large projects that demand a dedicated and separate work of accounting. Project accounting focuses on a particular project of such companies and hence falls under the project management umbrella. Under this accounting, a proper analysis of costs and preparation of reports is done at regular time intervals. This is done to check the financial changes or progress of that project. It provides the historical data so that future project decisions including cost-saving measures or budget adjustments can be taken easily. 8. Forensic AccountingUnder this branch, legal matters of the company are handled which are related to bankruptcy, fraud, or any mismanagement. That's why it is also known as legal accounting. Forensic accounting conducts investigations for the court and litigation cases, figures out damages, and oversees disputes resolutions. It serves the following:

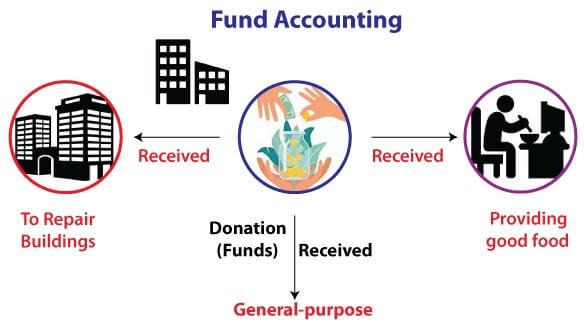
9. Fund AccountingThis branch of accounting works with Non-profit Organizations (NPO) to allocate their funds correctly and accurately. These accountants are responsible to separate and distribute the NPO's funds as per the company's policies or in accordance with the laws that are governing NPOs. Fund accounting is mainly used by the followings:
10. Government AccountingThis branch of accounting helps in handling the state and federal fund allocation and disbursement. It is also called public accounting as it indirectly serves the general public. Government accounting can be including social accounting, a measure of cost humans, climate change, or the proper use and allocation of welfare funds. Under this accounting, the movement of money from various agencies is tracked. Other than this, it is also kept in mind that the budgets are available to meet the demand. An accountant of this branch works under the state or federal government and manages the funds for their various welfare programs which can be related to housing, education, or healthcare. 
11. Political Campaign AccountingThis branch of accounting oversees the development and implementation of a political campaign's finance system. This includes transaction accounting or monitoring donations to make certain compliance with various political campaigns that are governed by federal and state laws. Political campaign accounting can be applied in the local, state, or national political races. 12. International AccountingAs the company expands its global business in the international markets, the need for international accounting rises. This branch of accounting helps in understanding the laws and regulations of the foreign countries which are required to run the business there without any barrier and legal issue. International accountants follow GAAP as well as they have enough knowledge in International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). IFRS are the accounting standards that are applicable and followed in most global economies.
Next TopicFinancial Accounting
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










