Golden Rules of AccountingMeaningEvery company must present its financial information to all its stakeholders. Also, the information must be accurate. For this purpose, all the business transactions should be recorded accurately in their respective account. There should be uniformity in account and to maintain it, there are three golden rules of accounting. These rules are the prime necessity to form the very basis of passing journal entries which are further useful in forming the basis of accounting and bookkeeping. Types of AccountsIn order to keep the record systematically and to understand and apply the golden rules of accounting, accounts are classified into the following three types: 1. Personal AccountsThese accounts are related to a person, firm, company, or institution. Account of Krishna, Account of XYZ Ltd., Account of the University of Delhi, Capital Account or Drawings Account of the Proprietor, etc. are examples of personal accounts. ObjectiveA personal account is prepared to know how much amount a personal account owes to the business, i.e., how much amount will be received from him and how much will be paid to him. Types of Personal AccountPersonal accounts can be further divided into three categories which include the following:
2. Real AccountsThe accounts of all those items which are measurable in terms of money and are treated as the properties of the business are called real account. They include Cash Account, Plant and Machinery Account, Furniture and Fixtures Account, Land and Building Account, Goodwill Account, etc. ObjectiveThese accounts are prepared to record the value of various properties that are owned by the business in monetary terms and indicate the financial position of the company. Types of Real AccountReal accounts can be further classified into the following two categories:
3. Nominal AccountsThe accounts of all incomes and expenses are termed nominal accounts. They include income accounts such as commission received, interest received, rent received, discount received, etc., and expenses account such as salaries paid, rent paid, commission paid, bad debts, discount allowed, interest paid on a loan, etc. ObjectiveAs we know these accounts do not exist in reality, they are just open with the aim of explaining the nature of head for the payment which is done in cash. Without the presence of the nominal account, it will be very difficult for the management to calculate the amount that is paid individually for salary, rent, commission, etc. Nominal accounts give the information about the following:
Note An important point about the nominal and personal account is that when a prefix or suffix is added to a nominal account then it becomes a personal account or is considered as a personal account. For example:
Golden Rules of Accounting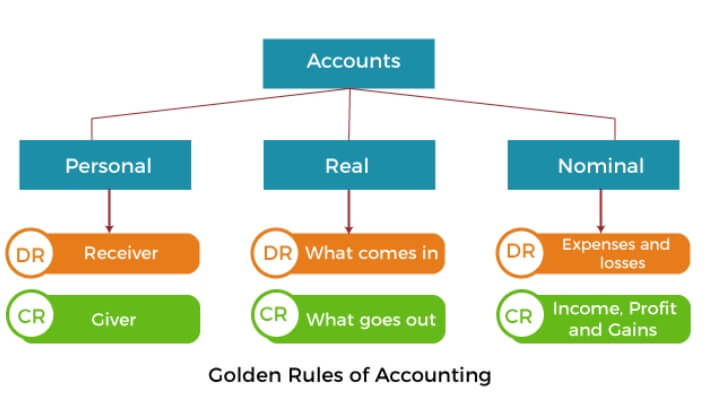
Rule 1: Personal Accounts The golden rule for recording transactions in personal accounts is 'Debit the receiver and credit the giver'. As per rule, the person or person's account who receives something from the business is debited and the person or account who gives something to the business is credited. Rule 2: Real Accounts The golden rule for recording transactions in real accounts is 'Debit what comes in and credit what goes out'. As per this rule, whenever the business receives any property then it will be debited and when it goes, i.e., sold or anything else, it will be credited. Rule 3: Nominal Accounts The golden rule for recording transactions in nominal accounts is 'Debit the expense and losses and credit the incomes and gains'. As per this rule, all those activities of the business which cause an outflow of the cash or cash equivalent, i.e., expenses or losses, are debited while all those activities which cause an inflow of the cash or cash equivalent, i.e., incomes or gains, are credited.
Next TopicIssue Of Shares At Premium
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










