Financial Risk ManagementWhat is Financial Risk?The possibility of losing money invested in a project or business venture is known as financial risk. It is a type of threat that can cause the loss of capital to the interested parties. The failure in controlling monetary policy and default on bonds or other debt issued in the country is a financial risk for the government. A company can also face the possibility of failure in the undertaking of debts which can cause a financial burden on the corporation. 
There are lots of macroeconomic forces, fluctuations in market interest rate, and the chances of default by the sectors or large corporations which increase the financial risk in the financial market. Financial risk can also take place in the life of an individual when his/her decision may jeopardize the income or ability to clear debts. Financial risk arises in every field of life in many shapes and sizes and affects nearly everyone. That's why everyone needs to be aware of it so that future losses can be avoided. However, if you figure out the risk prior and take proper measures to protect yourself then it means not that you can eliminate the risk but it can mitigate their harm and decrease the possibility of a negative outcome. Types of Financial RiskThe list of financial risks is too long. Some of them are discussed below: 
1. Market RiskAs clear from its name, the risk which is related to the marketplace in which the business activities take place, is known as market risk. For example, if you are running a brick-and-mortar clothing store, then the rise in customers' tendency to online shopping would be a market risk. In this situation, only those businesses can survive which can adapt to the online selling system and serve the online crowd. On the other hand, the businesses who stuck to the offline business model will bear losses. Every business sector faces the risk of being outpaced by competitors. The market conditions and customers' demands and preferences change rapidly. So it is a must for a business to keep up with market trends and pricing demands to grab the market and compete with other producers. 2. Foreign Exchange RiskForeign exchange risk refers to the risk associated with any financial instrument denominated in a foreign currency. For example, if an American company invests in India and the domestic investment does well in rupee terms, the American company may nevertheless lose money since the rupee's value has declined against the US dollar. As a result, when the firm redeems its investment at maturity, it will receive fewer US Dollars. The rupee has dropped dramatically in recent years due to the pandemic. Because of which our country's forex risk as an investment destination has skyrocketed. 3. Credit RiskCredit risk refers to the possibility of losing money because the performance of a creditor is not as per the terms of the contract. Such debts are categorized as bad debts. For example, if the goods are delivered to customers on 30-days payment terms and the customer couldn't pay the invoice on time (or in the future also), then the company will suffer a credit risk. This risk can also increase the possibility of a cash flow shortage. So, it is advisable to retain sufficient cash reserves to cover the company's accounts payable. 4. Liquidity RiskLiquidity risk includes all those risks that arise when the organization tries to sell assets or raise funds. This risk is also known as funding risk. If something is becoming a barrier in the path of raising funds fast, then it will be called liquidity risk. For example, a seasonal business can suffer from a shortage of cash flow during the off-season. So here the financial manager should figure out, does the company has enough cash available to meet the potential liquidity risk? And how quickly the company can dispose of old inventory or assets to regulate the cash flow in the business? Interest rate and currency risk are both examples of liquidity risk. As a result, the financial manager must be aware of the impact of a rapid shift in interest rates or exchange rates on the cash flow of the organization. 5. Operational RiskAll other risks that the business can face in its daily operations are called operation risks. These risks include staff turnover, fraud, poor budgeting, theft, unrealistic financial projections, lawsuits, and improper market plans. All these risks can affect the bottom line of the business if they are not dealt with and handled carefully. 6. Other RisksSome other types of risks are legal risk, equity risk, reputational risk, interest rate risk, reinvestment risk, country risk, inflationary risk, political risk, valuation risk, model risk, IT risk, etc. What is Financial Risk Management?The process of understanding and managing the financial risk that the business is facing either at present or in the future is known as financial risk management. It does not mean that the financial manager should eliminate all risks and wrap the business into cotton wool. Rather it's about drawing a line for the same. As we know, the higher the risk, the higher the possibility of profit. So the company can't eliminate the risk. It is all up to the financial manager which risk he wants to take for the benefit of the company, what risk he would rather avoid eliminating loss, and what strategy will he/she develop as per the risk appetite. The strategy of financial risk management is based on the plan of action. It includes the procedures, practices, and policies the company will use to decide the limit of risk that the company will not cross. In other words, we can say that the plan helps the employees in understanding what they can do and what cannot, what decision should be escalating, and who will be responsible for any risk that might arise. Process of Financial Risk ManagementEvery organization has its ways to deal with financial risks. These ways or processes are based on what the business does, what is the target market of the business, and how much risk the business can bear. In this sense, it's the responsibility of the financial manager of the company to identify and assess the risks and decide how the company will manage them. Three stages included in the process of financial risk management are: 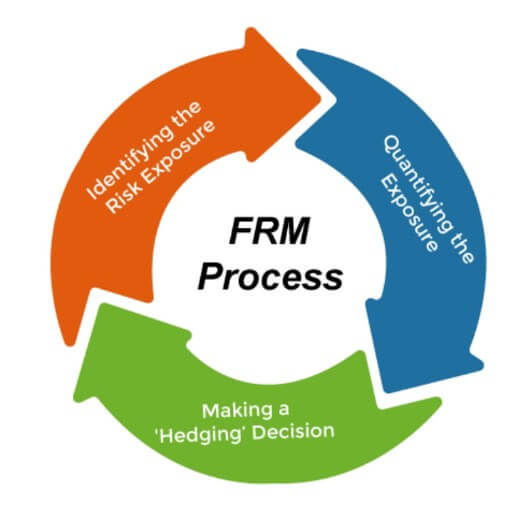
1. Identifying the Risk ExposureThe first step in the process of financial risk management is to identify the risks and their sources or causes. To start the process of identification, the financial manager can first check the balance sheet of the company. It will be helpful in getting a snapshot of the liquidity, debt, interest rates risk, foreign exchange exposure, and the vulnerability of commodity prices that the company is suffering from. After it, the manager should go for the income statement and the cash flow statement also to figure out the risk exposure. These statements will be helpful in understanding the fluctuations of income and cash flow over time and how does it affect the risk profile of the organization. In this step, the financial manager should collect the answer to the following questions: In this step, the financial manager should collect the answer to the following questions:
2. Quantifying the ExposureIn the second step, the financial manager tries to quantify the risk exposure, i.e., put a numerical value for the identified risk. However, due to the uncertainty of risk, an exact numerical value can't be put on risk exposure. Statistical models such as the regression method and standard deviation method are used by the analysts to find out the exposure of the company to various risk factors. With the help of these tools, the amount by which the data points differ from the average to the mean is measured. For example, the financial manager can use computer software like MS Excel in the case of small enterprises to make some straightforward analysis efficiently and accurately. The general rule to quantify the exposure, in this case, is: the risk associated with the data point or cash flow will be greater with the greater standard deviation. 3. Making a 'Hedging' DecisionThis is the third and last step in the process of financial risk management. In this step, the financial manager decides how to deal with the information that is collected after analyzing the sources of risk. Can the organization run with the risk exposure? Is it required to mitigate the risk or hedge against it? This decision is taken with the help of multiple factors such as the goals of the organization, business environment, its risk appetite, and whether the cost of mitigation justifies the decrease in risk. Generally, the financial manager can consider the following action steps:
Tools to Control Financial RiskA person, a corporation, or the government can use a variety of tools to evaluate the amount of financial risk that may occur. Some of the most prevalent strategies for analyzing risks linked with long-term investments or the stock market are presented below:
When financial management assesses a company, for example, he or she can use the debt-to-capital ratio to determine the proportion of debt utilized in relation to the entire capital structure. If the proportion of debt is high then it means the investment is risky and vice versa. Another ratio called the capital expenditure ratio is used to divide cash flow from operations by capital expenditures. It helps in calculating the money left with the business for its operating activities after paying the debts.
Next TopicBonus Issue of Shares
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










