Globalization TestingGlobalization testing is another type of software testing which is used to test the software that is developed for multiple languages, is called globalization testing, and improving the application or software for various languages is known as globalization. This testing ensures that the application will support multiple languages and multiple features because, in current scenarios, we can see the enhancement in several technologies as the applications are planned in such a way that it is used globally. For example, In India, the Google.com supports most of the languages, and it can also be retrieved by the large numbers of people of the various countries as it is a globalized application. 
Purpose of Globalization testingThe primary purpose of globalization testing is as follows:
Why we need to perform Globalization testingWe need to perform globalization testing to fulfill the following conditions: Understanding the language vocabulary: The application should design in such a way that it can easily understand the multiple languages terms across the world. For example
Zip Code: Suppose we lived in the UK where the Zipcode includes the alphanumeric characters as well as in India the zip code is in the 6 number digit formats. Thus if we select our country like India and entering the pin code of our state, it should accept only the 6-digit code. So in this scenario, the software should receive the zip code based on the UK Zip code format. Therefore it is essential to make sure that the zip code functionality is working fine based on every location. Address and telephone number format: The application should be tested in such a way that it will access the address and phone number format for multiple countries. For example
Types of Globalization TestingGlobalization testing is classified into two different parts, which are as follows: 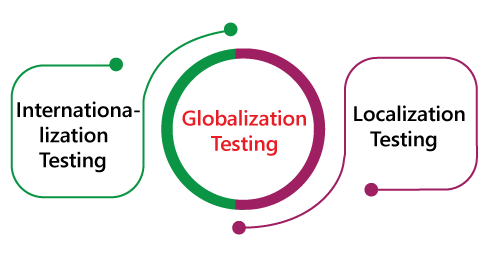
Internationalization TestingThe internationalization testing is the procedure of developing and planning the software or the application (product) or file content, which allows us to localize our application for any given language, culture, and region without demanding any changes in the source code. This testing is also known as I18N testing, and here 18 is the number between I and N in the Internationalization word. The main objective is to perform the internationalization testing, and this testing concentrates on the multiple testing such as functional testing, integration testing, usability testing, user interface testing, compatibility testing, installation testing, and validation testing. In this testing, the application code is independent of language, and it is done at the design level. Why we do the internationalization testingWe will perform the I18N testing to check the following conditions:
Example of internationalization testingLet see an example to understand internationalization testing. Let say if we want our software in the French language, so we have to click on the browser. The browser will take us to the server where the code is in English, and from there, it is executed, and the output is translated into French and displayed in the French language. 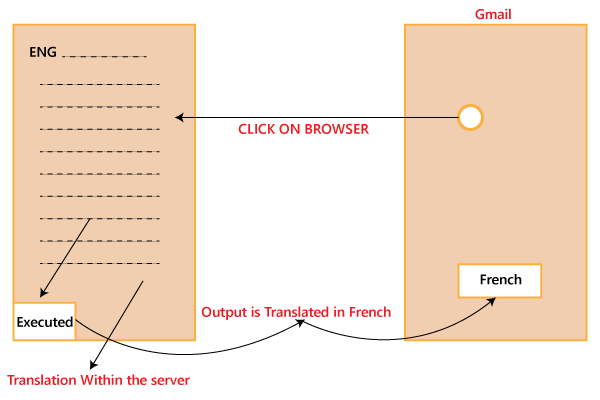
Now the question arises how do we translate into another language? Can we do it with the help of the translator, NO there are some drawbacks of using the translator. If we translate the code from English to any other language with the help of a translator, we face the below consequences:
Let see how the internationalization testing works for the English language: 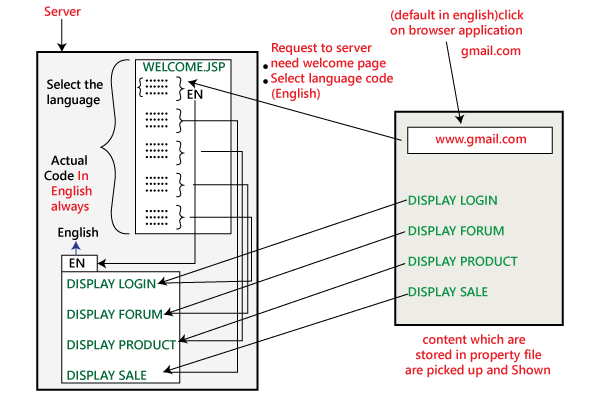
We will write one general code in English, and for all other languages, we have multiple property files. Assume that we have 6 various languages, and for that, we have 6 different property files. Let see how this will execute: First, click on the browser, and it will take the request to the server with the following guidelines as we require a Welcome Page and start the language code EN. Then the code where the language is implemented has the property files of English. Now we select the English property file and connect to the particular link. For example, if the next phase of coding is for the login module, then it relates to the Link1, then collects the data stored there and demonstrations it in the English language. The same process will be continuing for the other links, such as forums, sales, and products. The same process will be followed for the different languages also. But here one has to consider that, who wrote these properties files? Firstly, the developer writes the property files in English. Then the person of the experience takes the data and manually writes the property file and gives it back to the developers. After that, the developer places this particular property in the server as we can see in the below image: 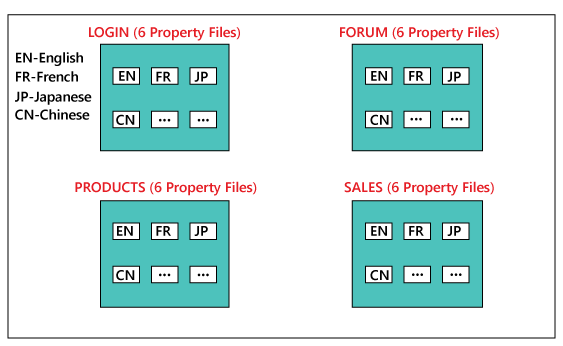
Now let us understand how we will translate into the French language, and we also test it. We will follow the same process as above:
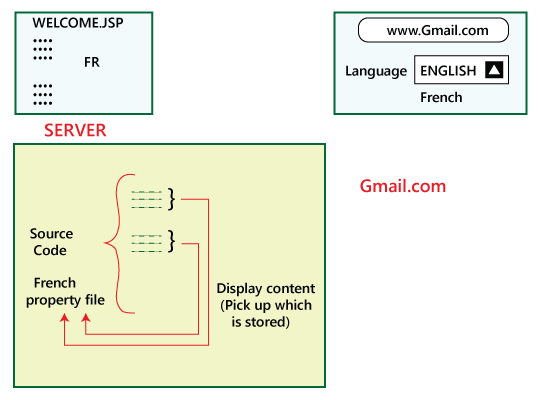
As if now, we have converted the language from English to French. So how do we verify that it is in French or some other language? Move to the French property file and change the contents in that particular file as we can see in the below image: 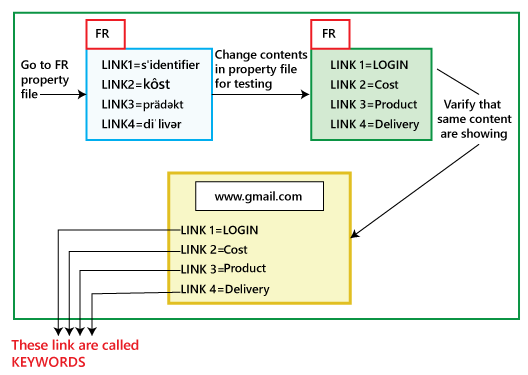
Once we have done modifications in the property file, and we select the French language again and see whether the changes we have done in the content is displaying the same or not. If it shows the same, then the test engineer can do the testing, and we must do the modification in the property file, not in the actual code. Or if it is not showing the same, then we will find the defects which need to fix only in the code. While doing I18N testing, we may find the below defects:
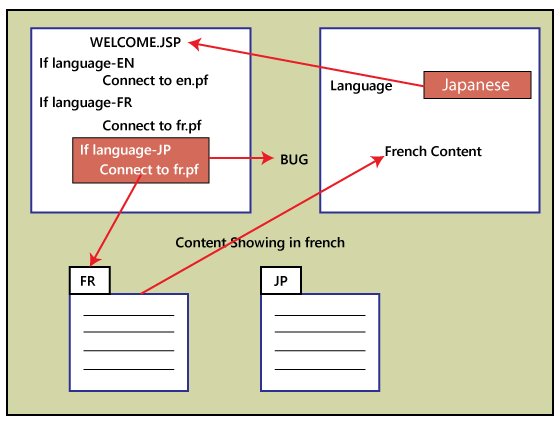
Note: Now, we will understand that if we choose the Japanese language, and it will display the content in French? The above scenarios will occur if the developers will copy and paste the code and forget to modify the specific property file such as Japanese such as jp.pf; they continue with Fr.pf file; that's why the content is still present in the French language.
Localization testing (L10N testing)The localization testing is nothing but the format testing, where we test the format specification based on the country, region, etc. It is also known as L10N testing, and here 10 is the number between L and N in the Localization word. The primary objective of localization is to provide a product the look and feel for a target market, no matter their culture, location, and the languages. This testing is not required to localize the product. Let us understand the various formats testing, which we perform in the localization testing: Date format testingThe software should be designed in such a way that it can follow the date based on its country format. For example
Currency format testingIn this, we do not worry about the functionality of the format, such as $ is converted to Rs. or not. Here we only test whether the $ should be in the first or the last. For example, 200$, $250, Rs.500 (the standard should be as per country standards) Pin code format testingIn this, we have the countries that have the pin code with the characters such as PQ230. Checking the Pin code format is L10N testing, and checking whether PQ is translated to French is I18N testing. The L10N testing contains the Date Format, currency format, and the Pin code format. Image format testingIn this, we can only change the name of the image because the image cannot be changed. Therefore we must have multiple images depending on the country. Advantages of Globalization TestingFollowing are the benefits of globalization testing:
Disadvantages of Globalization TestingThe disadvantages of globalization testing are as follows:
Next TopicMutation Testing
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










