Manual TestingManual testing is a software testing process in which test cases are executed manually without using any automated tool. All test cases executed by the tester manually according to the end user's perspective. It ensures whether the application is working, as mentioned in the requirement document or not. Test cases are planned and implemented to complete almost 100 percent of the software application. Test case reports are also generated manually. Manual Testing is one of the most fundamental testing processes as it can find both visible and hidden defects of the software. The difference between expected output and output, given by the software, is defined as a defect. The developer fixed the defects and handed it to the tester for retesting. Manual testing is mandatory for every newly developed software before automated testing. This testing requires great efforts and time, but it gives the surety of bug-free software. Manual Testing requires knowledge of manual testing techniques but not of any automated testing tool. Manual testing is essential because one of the software testing fundamentals is "100% automation is not possible." Why we need manual testingWhenever an application comes into the market, and it is unstable or having a bug or issues or creating a problem while end-users are using it. If we don't want to face these kinds of problems, we need to perform one round of testing to make the application bug free and stable and deliver a quality product to the client, because if the application is bug free, the end-user will use the application more conveniently. If the test engineer does manual testing, he/she can test the application as an end-user perspective and get more familiar with the product, which helps them to write the correct test cases of the application and give the quick feedback of the application. Types of Manual TestingThere are various methods used for manual testing. Each technique is used according to its testing criteria. Types of manual testing are given below:
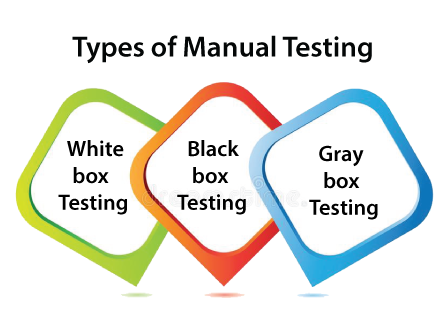
White-box testingThe white box testing is done by Developer, where they check every line of a code before giving it to the Test Engineer. Since the code is visible for the Developer during the testing, that's why it is also known as White box testing. For more information about white box testing, refers to the below link: https://www.javatpoint.com/white-box-testing Black box testingThe black box testing is done by the Test Engineer, where they can check the functionality of an application or the software according to the customer /client's needs. In this, the code is not visible while performing the testing; that's why it is known as black-box testing. For more information about black-box testing, refers to the below link: https://www.javatpoint.com/black-box-testing Gray Box testingGray box testing is a combination of white box and Black box testing. It can be performed by a person who knew both coding and testing. And if the single person performs white box, as well as black-box testing for the application, is known as Gray box testing. To get more details about gray box testing, refers to the below link: https://www.javatpoint.com/grey-box-testing How to perform Manual Testing
Software Build Process
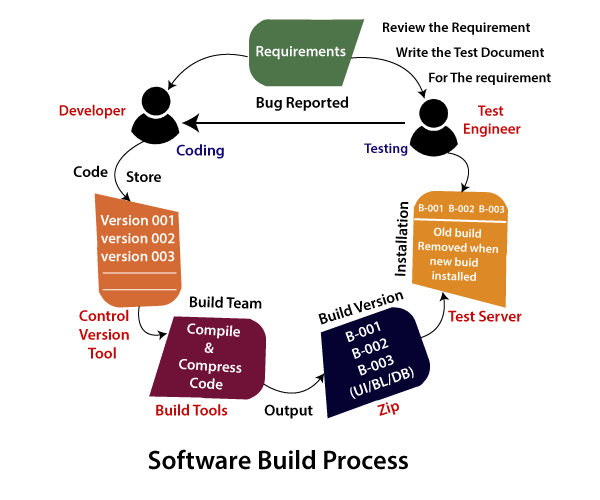
Note1
Note2Build team The main job of the build team is to create the application or the Build and converting the high-level language into low-level language. Build It is software, which is used to convert the code into application format. And it consists of some set of features and bug fixes that are handed over to the test engineer for testing purposes until it becomes stable. Control version tool It is a software or application, which is used for the following purpose:
Example of Build processLet see one example to understand how to build process work on the real scenarios: As soon as the test engineer gets the bug, they will send it to the developers, and they need some time to analyze; after that, he/she only fixes the bug (Test engineer can't give the collection of bug). The developer is decided how many bugs he can fix according to their time. And the test engineer is decided, which bug should be fixed first according to their needs because the test engineers cannot afford to stop testing. And the test engineer getting the mail, they can only know that which bug is fixed by the list of the bug fixes. The time will increase because at the first Build, and developers should write the code in the different features. And at the end, he/she can only do the bug fixes and the numbers of days will be decreased. 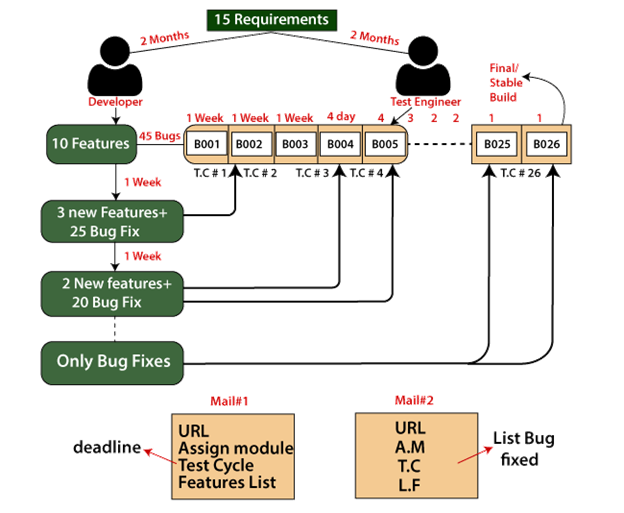
Note3Test cycle The test cycle is the time duration given to the test engineer to test every Build. Differences between the two build The bugs found in one build and can be fixed any of the future Build, which depends on the test engineer's requirement. Each new Build is the modified version of the old one, and these modifications could be the bug fixes or adding some new features. How frequently we were getting the new Build In the beginning, we used to get weekly builds, but in the latest stage of testing, when the application was getting stable, we used to get the new Build once in 3 days, two days, or a daily basis as well. How many builds we get If we consider one year of any project duration, we got 22-26 builds. When we get the bug fixes Generally, we understand the bug fixes only after the test cycle is completed, or the collection of bugs is fixed in one build, and handover in the next builds. Advantages of Manual Testing
Disadvantages of Manual Testing
Manual testing toolsIn manual testing, different types of testing like unit, integration, security, performance, and bug tracking, we have various tools such as Jira, Bugzilla, Mantis, Zap, NUnit, Tessy, LoadRunner, Citrus, SonarQube, etc. available in the market. Some of the tools are open-source, and some are commercial. For more information about testing tools, refers to the below link: https://www.javatpoint.com/software-testing-tools 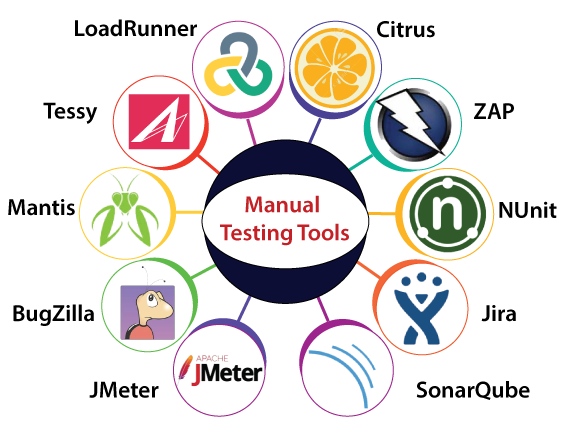
Let's us understand them one by one: LoadRunnerIt is most commonly used performance testing tools. LoadRunner is mainly used to support performance testing for the wide range of procedures, number of approaches, and application environments. The main purpose of executing the LoadRunner tool is to classify the most common sources of performance issues quickly. 
Features of LoadRunner
CitrusCitrus is an integration testing tool, which is the most commonly used test framework. It is written in Java programming language. It is mostly used to request and respond to server-side and client-side and validate the XML JSON files. To accomplish the end-to-end use case testing, citrus supports several HTTP, JMS, and SOAP protocols. 
Characteristics of Citrus Following are some of the important features of Citrus tool:
ZAPZAP is an open-source web application security scanner. It is stands for Zed Attack Proxy. Just like some other tools, it is also written in the JAVA programming language. It is the most effective Open Web Application Security Projects [OWASP]. 
Features of ZAP
NUnitNUnit is one of the most frequently used unit testing tools. It is an open-source tool and primarily derived from the JUnit. It was completely written in the C# programming language and suitable for all .Net languages. In other words, we can say that the NUnit tool is entirely redesigned to become the advantage of many .Net language qualities. For example:

Characteristics of NUnit
JIRAThe most regularly used bug tracking tool is JIRA, which is an open-source tool. It is used for bug tracking, project management, and issue tracking. In this tool, we can easily track all kinds of bugs or defects related to the software and produced by the test engineers. 
Features of JIRA
To get the complete information about the Jira tool, refer to the below link: https://www.javatpoint.com/jira-tutorial. SonarQubeAnother testing tool of manual testing is SonarQube, which improves our workflow with continuous code quality and code security. It is flexible with the use of plug-ins. It is completely written in the JAVA programming language. It offers fully automated evaluation and integration with Ant, Maven, Gradle, MSBuild, and constant integration tools. SonarQube has the ability to record a metrics history and gives the evolution graph. 
Features of Sonarqube Below are some of the significant features of the SonarQube tool:
JMeterJMeter is an open-source tool that is used to test the performance of both static and dynamic resources and dynamic web applications. It is completely designed on the JAVA application to load the functional test behavior and measure the application's performance. It facilitates users or developers to use the source code for the development of other applications. 
Features of JMeter Below are some of the essential characteristics of JMeter:
For more information about JMeter, refers to the below link: https://www.javatpoint.com/jmeter-tutorial. BugzillaAnother bug tracking tool used in manual testing is Bugzilla. It is most widely used by many organizations to track the various bugs of the application. Bugzilla is an open-source tool that helps the customer and the client to keep track of the defects. Bugzilla is also considered a test management tool because in this, we can easily link other test case management tools such as ALM, Quality Centre, etc. 
Features of Bugzilla Bugzilla has some additional features which help us to report the bug easily:
MantisMantis is a web-based bug tracking system. ManitsBT stands for Mantis Bug Tracker. It is used to follow the software defects and performed in the PHP programming language. It is also an open-source tool. 
Features of Mantis Some of the standard features of the particular tool are as follows:
To get more details about bug tracking tools, refer to the following link: https://www.javatpoint.com/defect-or-bug-tracking-tool. TessyAnother integration testing tool is Tessy, which is used to perform the integration and unit testing for the embedded software. It also helps us to discover the code coverage of the software or an application. It can easily manage the entire test organization, including business needs, test management, coverage quantity, and traceability. Tessy contains three primary functions, which are as follows:

Features of TESSY The standard features of the TESSY are as follows:
For more information about integration testing tools, refers to the following link: https://www.javatpoint.com/integration-testing-tools. OverviewIn this article, we have seen detailed information about Manual testing, which includes the definition of manual testing, the need of manual testing, type of manual testing, manual testing tools, the process of manual testing, and some important benefits and drawbacks of it. Finally, we can say that, it is a process where the test engineer needs to be very persistent, innovative, and responsive. In manual testing, the test engineer needs to think and perform like end-user interpretation. In order to implement manual testing, a test engineer needs productive skill and imagination. And they need to think of multiple situations or scenarios to test a specific application. Even though we can test nearly all applications with the help of automation testing at present, still manual testing is necessary as it is the base of software testing.
Next TopicAutomation Testing
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









