V-model/ V and V model /Verification and Validation modelThis model came up to overcome the drawback of the waterfall model. And in this model, testing starts from the requirement stage itself. In this model, first, all the activities go on the downward direction, and at one point in time, it starts moving in the upward direction to re-use the test document for the testing process and forms a V shape. Hence it is known as the V model. When we go for this modelWe go for V and V model for the following reasons:
Before going further in this model, first, we will understand the requirements: RequirementsIt is a document which is collected from the customer; here, we have two different types of requirements documents, which are as follows:
CRS/BRSThe CRS or BRS stands for Customer Requirement Specification or Business Requirement Specification. For the CRS, the details will be written in the simple business (English) language by the BA (business analyst), which cannot be understood by the developers and the test engineers. Let us see one sample example for Customer Requirement Specification to the Gmail application:
SRS/ FSIt stands for Software Requirement Specifications or the Functional Specification; in this, all the details are converted to the detail document, which can be understood by the developers and the test engineers. Let us see one sample example for Software Requirement Specifications to the Gmail application:
Characteristics of a functional requirement
V and V Model ProcessThe entire V model executes in two-phase, the complete review process is done in the verification phase, and the whole testing process is done under the validation phase; that's why it is also known as verification and validation model. Where the verification and validation process includes different stages: 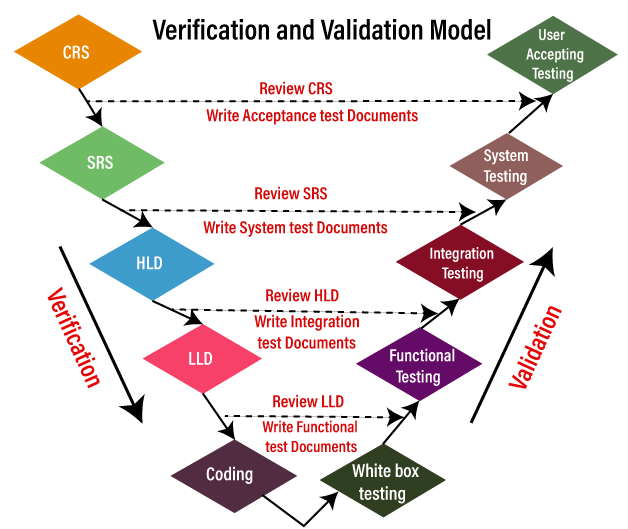
Stage 1 It will start from collecting the CRS (customer requirement specification) document, from the client by the Business Analyst where the test engineer will check the following scenarios:
Note: In all the stages, the Test Documents includes the test plans and test cases.Once the test engineer team reviews the CRS and found any bugs or defects, they will send it to the development team for fixing the bugs. After fixing the bugs, the development team updates the CRS and concurrently developing the SRS document. Stage 2 After completing the CRS, the SRS is sent to the testing team for the review process, and the developers start creating the HLD (high-level design) for the application. And the testing team will test the SRS on the following scenarios:
Once the testing team reviews every detail of the SRS and CRS has been converted correctly to SRS, we will move to our next stage. Stage 3 After the completion of HLD, the developers start creating the LLD (Low-level design) for the application, and in the meantime, the tester will check the following tests on the HLD:
Stage 4 Once the testing team has done reviewing the HLD, the developers write the coding and develops the application, and the testing team will do the following tasks:
Stage 5 After the completion of the coding part, the developers will perform one round of unit testing, which is also called white box testing, and check every line of the code and make sure that the code is correct. After performing the unit testing, the application is sent to the testing team, where they perform multiple testing such as functional testing, integration testing, and system testing, and acceptance testing. And once the testing part is done, the application will finally deliver to the customer. Note: Advantage and Disadvantage of V and V ModelLet us see the pros and cons of the V and V model:
Next TopicManual Testing
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










