Speech Recognition in Artificial Intelligence
The way people interact with digital gadgets and systems has changed dramatically in recent years due to noteworthy developments in speech recognition technology. Speech recognition is a crucial component of artificial intelligence (AI) that helps close the communication gap between people and machines. Automation, accessibility features, virtual assistants, transcription services, and other uses for machine understanding and interpretation of spoken language are made possible by this technology. The intriguing field of voice recognition in artificial intelligence, along with its services, difficulties, and prospects, will all be covered in this article.
Developing Knowledge of Speech Recognition
Speech recognition technology, also known as Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), makes it possible for computers and artificial intelligence (AI) systems to translate spoken words into text. There are several steps in this process:
- Decoding: Based on the data obtained in the above processes, the last step includes choosing the most probable translation for the spoken words.
- Feature extraction: In this stage, the audio input is processed to extract characteristics such as Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), which give the system the necessary information to recognize the sound.
- Acoustic Analysis: The audio signal is captured by the system, which then dissects it into its constituent elements, such as prosody and phonemes.
- Language Modeling: To increase recognition accuracy, language models are used to comprehend the semantics and grammatical structure of spoken words.
- Acoustic Modeling: To link the retrieved characteristics with recognized phonetic patterns and language context, the system applies statistical models.
What exactly is Speech Recognition in AI?
The technique of recognizing a human voice is known as speech recognition. To detect speech, firms usually develop these programs and incorporate them into different hardware devices. The software will react correctly when it hears your voice or gets your command.
Many companies use cutting-edge technology like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and neural networks to develop voice recognition software. Technologies like Cortana, Alexa, Siri and Google Assistant have altered how people use electronics and technology. They include automobiles, cell phones, home security systems, and more.
Recall that speech and voice recognition are two different things. Speech recognition translates spoken words into text by first identifying them in an audio recording of a speaker. On the other hand, speech recognition can only identify pre-programmed spoken instructions. The sole commonality between these two approaches is the conversion of sound to text.
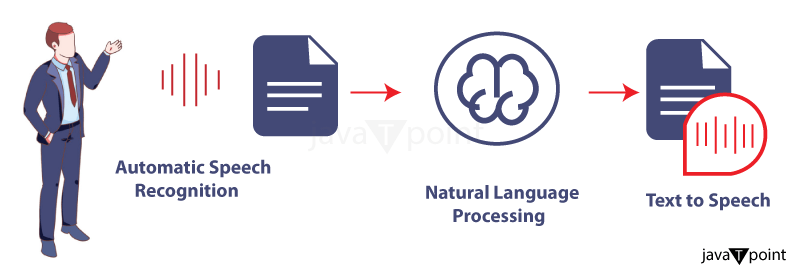
How AI Handles Speech Recognition?
Automatic speech recognition (ASR), sometimes referred to as speech recognition in AI, is a sophisticated method that allows robots to translate spoken language into text or other forms that are comprehensible. Speech recognition technology consists of several steps and parts. Here's a summary of how it functions:
- Audio Input: A microphone is usually used to record the audio input, which starts the process. Any spoken human speech, including commands and conversations, can be used as this audio input.
- Preprocessing: To enhance its quality and prepare it for analysis, the raw audio signal is preprocessed. This might be signal amplification, noise reduction, or other methods to improve the audio data.
- Language Modeling: Language models are used to comprehend the semantics and grammatical structure of spoken words. By assisting the system in understanding the context and connections between words, these models increase the accuracy of word recognition. When it comes to managing homophones?words that sound identically but have distinct meanings-and the order of words and sentence structure changes, language modelling is incredibly crucial.
- Decoding: By integrating the data from the acoustic and linguistic models, the system decodes the spoken words. It assesses several word combinations and determines which transcription is more plausible based on statistical probability.
- Output: The recognized language or a command that may be applied to several different situations is the ultimate output. This output can be utilized for transcription, operating a device, giving instructions to a virtual assistant, and other similar tasks.
Speech Recognition AI and Natural Language Processing
Recognition of Speech Machines can now comprehend and interpret human language thanks to the closely connected sciences of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP). NLP covers various applications, such as language translation, sentiment analysis, and text summarization, whereas voice recognition AI concentrates on translating spoken words into digital text or commands.
Making it possible for robots to comprehend and interpret human language similarly to how humans do is one of the main objectives of natural language processing (NLP). This entails knowing the broader context and meaning of the words and recognizing them individually. For instance, depending on the situation, "I saw a bat" might mean several things. Either the animal or a piece of athletic gear might be the subject.
AI for speech recognition is a branch of natural language processing (NLP) specializing in translating spoken utterances into digital text and commands. Speech recognition artificial intelligence (AI) systems employ sophisticated algorithms to map speech patterns to phonetic units, analyze and interpret speech patterns, and generate statistical models that represent sounds to do this.
Among the methods employed by AI to recognize speech are:
- Deep Neural Networks (DNNs): Used widely in voice recognition artificial intelligence, DNNs are a machine learning model. DNNs represent intricate links between the speech input and the associated text output by employing a hierarchy of layers.
- Hidden Markov Models (HMMs): AI voice recognition uses Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), which are statistical models. To match input speech to the most likely sound sequence, HMMs first model the probability distribution of speech sounds.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Artificial Intelligence for speech recognition has also made use of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a class of machine learning model that is frequently employed in image recognition. To find pertinent characteristics, CNNs process incoming speech signals by applying filters.
Among the most recent developments in AI voice recognition are:
- End-to-end models: These models are made to translate speech impulses directly into text, eliminating the need for any intermediary stages. These models have demonstrated the potential for raising voice recognition AI's precision and effectiveness.
- Multimodal models: These enable more intuitive and natural interactions between machines and humans by fusing voice recognition Intelligence with other modalities, including vision or touch.
- Transformer-based models: BERT and GPT are two examples of transformer-based models that have shown great success in tasks related to natural language processing and are now being used in artificial intelligence for voice recognition.
- Data augmentation: Increasing the data used for training for speech recognition AI models will increase their accuracy and resilience. Data augmentation strategies include introducing background noise and modifying the speaking tempo.
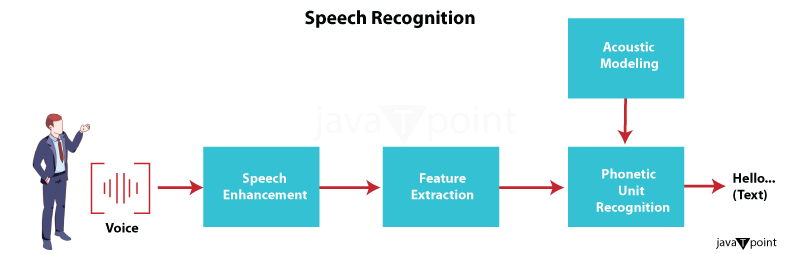
Difficulties with Speech Recognition
Even though voice recognition technology has advanced significantly, several issues still exist:
- Accuracy: It still needs to be improved to recognize speech with great precision, particularly in loud surroundings or when there are a variety of accents.
- Privacy Concerns: As speech-recognizing technologies are incorporated into more aspects of daily life, privacy issues about the gathering and using voice data have surfaced.
- Context Understanding: The field of interpreting spoken language's context and intent is still developing. AI systems frequently have trouble understanding complex or unclear instructions.
- Speaker Variability: It might be challenging to distinguish speech from various speakers and adjust to differing accents and speaking tenor.
Applications of AI for Speech Recognition
In many domains and uses, artificial intelligence is used as a commercial solution for speech recognition. Voice-activated audio content assistants, call centres, ATMs, and more benefit from AI's more natural user interactions with hardware and software and its increased accuracy in data transcription.
- Telecommunications: Speech recognition models offer more efficient call handling and analysis. Better customer service frees agents to focus on what makes them most valuable. Thanks to the availability of text messaging and voice transcription services, customers can now contact companies in real-time, around-the-clock, which enhances their entire experience and makes them feel more connected to the company.
- Medical: Voice-activated Artificial Intelligence is becoming more prevalent in the telecommunications industry. Speech recognition technology models provide more efficient call handling and analysis. Better customer service frees agents to focus on what makes them most valuable.
- Banking: Dialogue Financial and banking organizations utilize AI apps to help customers with their business questions. You may ask a bank, for example, for information on your savings account's current interest rate or account balance. Because they no longer need to perform in-depth research or access cloud data, customer service representatives can reply to requests more rapidly and offer more outstanding assistance.
- Automotive Voice Commands: Hands-free voice control of amenities like climate control, entertainment systems, and navigation is a common feature of modern vehicles.
Finally, A potent commercial product called speech recognition makes it possible for computers, apps, and software to comprehend spoken language and translate it into text. This technology understands what you say and precisely reproduces them as written data on a screen using artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze your voice and language. Feature extraction, Signal processing, language modelling, and decoding are some of the crucial elements in the process.
Artificial Intelligence voice recognition essentially converts spoken words to digital signals that are interpreted and analyzed by robots. Natural language processing (NLP), which allows machines to comprehend and interpret human language, is closely related to this skill. By enabling computers to carry out a variety of language-related activities, including text summarization, sentiment analysis, and language translation, natural language processing (NLP) expands the capabilities of voice recognition. Together, voice recognition and natural language processing (NLP) is propelling the creation of more user-friendly and engaging human-machine interfaces, which will ultimately improve our capacity to connect with and teach technology through spoken language.
|


 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









