How to use distinct in SQL?SQL DISTINCT clause is used to remove the duplicates columns from the result set. The distinct keyword is used with select keyword in conjunction. It is helpful when we avoid duplicate values present in the specific columns/tables. The unique values are fetched when we use the distinct keyword.
Syntax:Parameters:Expressions: The columns or calculations that we want to retrieve are called expression. Tables: The tables that we want to retrieve the records. There is only one table in the FROM clause. WHERE conditions: The conditions may meet for the records which are selected and it is optional. Note:
Example:Consider the following EMPLOYEES table. 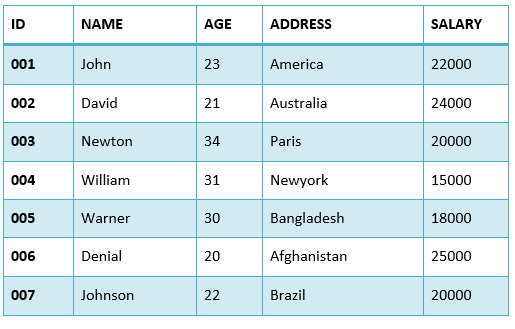
First, let us see the following SELECT query returns the duplicate salary records. When we execute the above SQL query, it fetches all the records including the duplicate records. In the above table, salary of Newton and Johnson is same 20000. 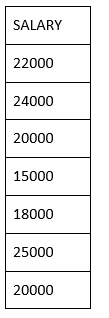
Now, let us use the DISTINCT keyword with the above SELECT query. The above SQL query removes the duplicate records and shows the following result. 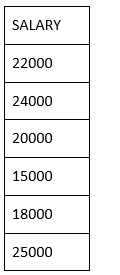
Example: Finding Unique Values in the ColumnLook at the DISTINCT clause to find the unique values within one column in the table. We have a table called suppliers with the following data: 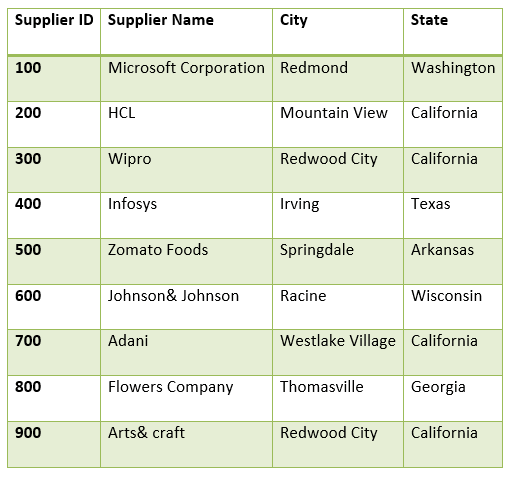
From the above table, we are going to find the unique states. These are six the records. 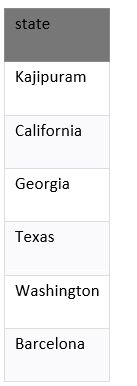
The example returns the unique state from suppliers table and removes the duplicate records from the result set. Example: Finding Unique Values in Multiple ColumnThe SQL DISTINCT clause is used to remove the duplicate records from many fields in the SELECT statement. Enter the SQL statement: Output: These are 8 records: 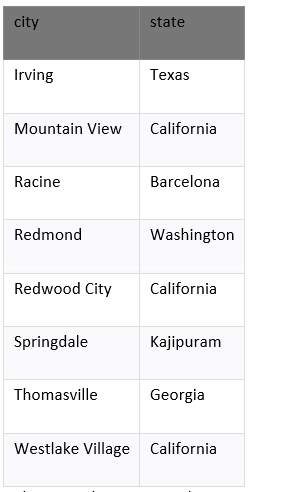
The example returns each unique city and state combination. We see the Redwood City and California, appears in the result set. Example: DISTINCT Clause handles NULL ValuesThe DISTINCT clause considers NULL to the unique value in SQL. We have a table called products which contains the below data. 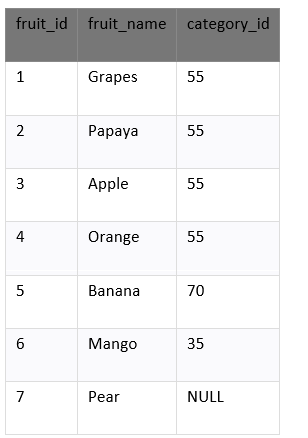
Select the unique values from the field fruit_id which contains the null value. Enter the below SQL syntax: There are four records selected. These are the results which we see below: 
In the above example, the query returns the unique values that are in the category_id column. We see by the first row in the result set, NULL is an exceptional value which is returned by the DISTINCT clause.
Next TopicJoining Three or More Tables in SQL
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









