SQL Arithmetic OperatorsIn Structured Query Language, the arithmetic operators are used to perform mathematical operations on the numerical values stored in the database tables. We can use these operators with the SELECT statement in SQL. We can also use the WHERE clause in the SELECT statement for performing operations on particular rows. These types of operators are used between two numerical operands for performing addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations. The arithmetic operators in SQL are categorized into the following five types:
SQL Addition Operator (+)The SQL Addition Operator performs the addition on the numerical columns in the table. If you want to add the values of two numerical columns in the table, then you have to specify both columns as the first and second operand. You can also add the new integer value in the value of the integer column. Syntax of SQL Addition Operator: Addition Operator with WHERE ClauseThe addition operator can also be used with the WHERE clause in the SQL SELECT query. The syntax for using the WHERE clause with the addition operator is given below: Implementation of Addition operator in SQL: The following CREATE query creates the Employee table with five fields: The following INSERT query inserts the record of employees into the Employee table: The following SELECT query shows the data of the Employee table:
The following query adds the Emp_Salary and Emp_Bonus of each employee of the Employee table using the addition operator: Output: 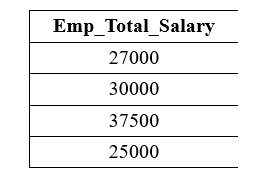
The following query adds 15000 to the salary of each employee in the Emp_Salary column of the Employee table: Output: 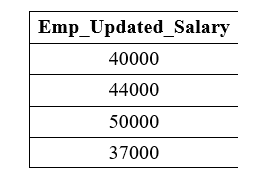
The following query performs the addition operation on the above Employee table with the WHERE clause: It shows only records of those employees whose Emp_Salary is greater than 25000: Output: 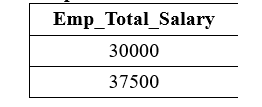
SQL Subtraction Operator (-)The SQL Subtraction Operator performs the subtraction on the numerical columns in the table. If we want to subtract the values of one numerical column from the values of another numerical column, then we have to specify both columns as the first and second operand. We can also subtract the integer value from the values of the integer column. Syntax of SQL Subtraction Operator: Subtraction Operator with WHERE ClauseThe subtraction operator can also be used with the WHERE clause in the SELECT query. The syntax for using the WHERE clause with the subtraction operator is given below: Implementation of Subtraction operator in SQL: The following CREATE query creates the Employee table with five fields: The following INSERT query inserts the record of employees into the Employee table: The following SELECT query shows the data of the Employee table:
The following query subtracts the values of the Emp_Panelty column from the Emp_Salary column of the Employee table using the subtraction operator: Output: 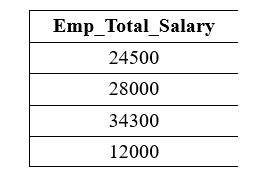
The following query performs the subtraction operation on the above Employee table with the WHERE clause: It shows only records of those employees whose Employee_ID is 103: Output: 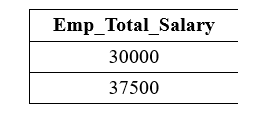
The following query subtracts 10000 from the salary of each employee of the Employee table: Output: 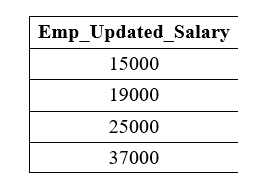
SQL Multiplication Operator (*)The SQL Multiplication Operator performs the multiplication on the numerical columns in the table. If you want to multiply the values of two numerical columns, then you have to specify both columns as the first and second operand. You can also multiply the integer value with the values of an integer column. Syntax of SQL Multiplication Operator: Multiplication Operator with WHERE ClauseThe multiplication operator (*) can also be used with the WHERE clause in the SELECT query. The syntax for using the WHERE clause with the multiplication operator is given below: Implementation of Multiplication operator in SQL: The following CREATE query creates the Cars table with four fields: The following INSERT query inserts the record of cars into the Cars table: The following SELECT query shows the data of the Cars table:
The following query multiplies the values of the Car_Amount column with the Car_Price column of the Cars table using the Multiplication operator: Output: 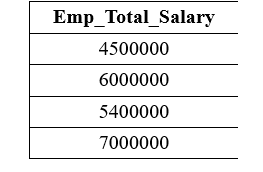
The following query performs the multiplication operation on the above Cars table with the WHERE clause: It shows only those records of cars whose Car_Price is greater than and equal to 1000000. Output: 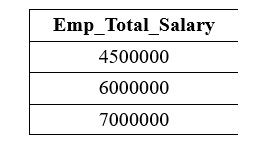
SQL Division Operator (/)The SQL Division operator divides the numerical values of one column by the numerical values of another column. Syntax of SQL Division Operator: Division Operator with WHERE ClauseThe SQL division operator can also be used with the WHERE clause in the SELECT query. The syntax for using the WHERE clause with the division operator is given below: Implementation of Division operator in SQL: The following CREATE query creates the Cars table with four fields: The following INSERT query inserts the record of cars into the Cars table: The following SELECT query shows the data of the Cars table:
The following query divides the values of the Car_Price column by the Car_Amount column of the Cars table using the Multiplication operator: Output: 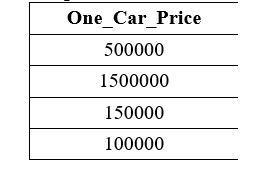
The following query performs the division operation on the above Cars table with the WHERE clause: It shows the record of those cars whose Car_Number is 9258 from the Cars table. Output: 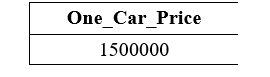
SQL Modulus Operator (%)The SQL Modulus Operator provides the remainder when the numerical values of one column are divided by the numerical values of another column. Syntax of Modulus Operator in SQL: Implementation of Modulus operator in SQL: The following CREATE query creates the Student table with four fields: The following INSERT query inserts the record of the student into the Student table: The following SELECT query shows the data of the Student table:
The following query divides the marks Student_English column by Marks of Student_Maths of each student in the Student table: Output: 
The following query performs the modulus operation on the above Student table with the WHERE clause: It shows the record of those students whose Student_Id is greater than 202. Output: 
Next TopicHow to Use GROUP BY in SQL
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









