SQL COUNT DISTINCTBefore understanding the concept of Count Function with the DISTINCT keyword, we have to know about the Count and Distinct keywords. So, let's start with the Count function. What is Count in SQL?The COUNT is a function in Structured Query Language that shows the number of records from the table in the result. In SQL, it is always used in the SELECT query. The syntax of the Count function is given below: In the count example, we have to define the name of the column in parentheses just after the COUNT keyword. Example of Count FunctionFirstly, we have to create a new table on which the count function is to be executed. The following query creates the Teacher_Details table with Teacher_ID as the primary key using the CREATE TABLE statement: The following SQL queries insert the record of new teachers into the above table using INSERT INTO statement: Let's see the record of the above table using the following SELECT statement:
The following query counts the total values of the Teacher_Age column from the Teacher_Details table: Output: 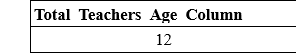
The output of the above SELECT query is twelve because the Teacher_Age field does not hold any NULL value. The following query counts the total values of Teacher_Interview_Column from the above table: This query will show the below output on the screen: 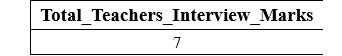
The output of the above SELECT query is 7 because two five cells of the Teacher_Interview_Marks column contain NULL. And these five NULL values are excluded. That's why the SELECT query displays 7 instead of 12 in the result. What is Count(*) Function?This is also similar to the Count function, but the only difference is that it also displays the number of NULL values from the table. The syntax of the Count (*) Function is given here: Example: Let's take the above Teacher_Details:
The following query counts the total values of the Total_Interview_Marks column from the above table: The above SELECT with COUNT(*) query will give the below result on the screen: 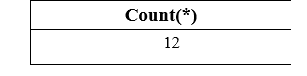
What is DISTINCT in SQL?The DISTINCT keyword shows the unique rows of the column from the table in the result. The syntax of the DISTINCT keyword is given here: In the DISTINCT query, we can also define the condition in the WHERE clause for retrieving the specific values. Example of DISTINCT First, create a new table on which the Distinct keyword is to be run. The following query creates the Bike_Details table using the CREATE TABLE statement: The following SQL queries insert the record of new bikes into the table using the INSERT INTO statement: The records of the above table are shown by using the following SELECT query:
Table: Bike_Details The following SQL query the distinct values of the Color column from the above Bike_Details table: Output: 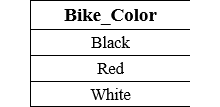
As we can see, Black, Red, and White are three distinct values in the Bike_Color column. Count Function with DISTINCT keywordThe DISTINCT keyword with the COUNT function in the SELECT query displays the number of unique data of the field from the table. The Syntax of Count Function With DISTINCT keyword is given below: Examples of Count Function with DISTINCT keywordThe following two SQL examples will explain the execution of Count Function with Distinct keyword: Example 1: The following query creates the College_Students table with four fields: The following INSERT query inserts the record of students into the College_Students table: The following query shows the details of the College_Students table:
Table: College_Students The following SQL statement counts the unique values of the Student_Age column from the College_Students table: This query will give the below table in the output: 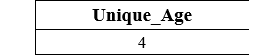
The output shows the four values because the Teacher_age column contains 4 unique values. Example 2: The following query creates the IT_Employee table with four fields: The following INSERT query inserts the record of IT employees into the IT_Employee table: The following query shows the details of the IT_Employee table:
Table: IT_Employee The following SQL statement counts only the unique values of the Emp_Age column from the above IT_Employee table: This query will give the below output: 
Next TopicSQL UNION
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









