SQL Inner JoinINNER JOIN in SQL is the most common and important type of join which allows users to access matching data from two or more database tables. When the join condition is met between the tables, then it returns all the common rows from them. The Venn diagram of INNER JOIN is shown in the following picture. The shaded region of the Venn diagram shows the intersection values of two tables: 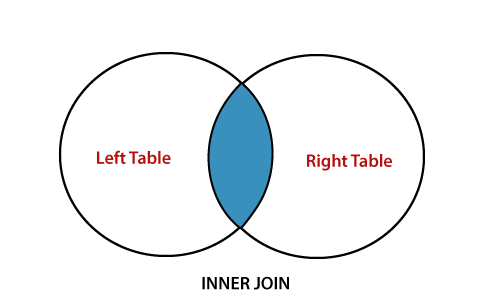
Syntax of INNER JOIN in SQLExample of Inner Join in SQLLet's take two tables named Employee_Details and Department to understand the concept of INNER JOIN. The Employee_Details table contains Emp_ID, Emp_Name, Dept_ID, and Emp_Salary columns. The Department table contains Dept_Id and Dept_Name columns. We can check the data of Employee_Details and Department table using the following two different queries: Output:
Output:
The following query joins these above two tables using INNER JOIN in structured Query Language: Explanation of above INNER JOIN query: This query joins the Employee_Details and Department table and accesses the records from both the tables where Department.Dept_Id = Employee_Details.DeptId. It only fetches the details of those employees from both the tables whose Dept_Id in the Employee table matches with the Dept_Id of the Department table. If the Dept_Id is NULL or not matching, then that row would not show in the output. Output:
Next TopicSQL IN Operator
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









