SQL ISNULLThis tutorial will teach us to implement the IS NULL condition and IsNull function in SQL and SQL servers. IS NULL Condition in SQLThe user can use the IS NULL condition to verify whether a data value is NULL. If the value is NULL, the condition will return TRUE, or it will return False. The user can implement the IS NULL condition in SQL's SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE clauses. Syntax of IS NULL ConditionThe syntax to implement the IS NULL condition is as follows: Expr IS NULL Parameters Or Arguments in IS NULL ConditionExpr: It specifies the value or statement checked for the NULL value. Implementation of IS NULL ConditionExample 1: We will implement the IS NULL condition with the SELECT clause If the user wants to verify if a value is NULL, then using IS NULL condition as a comparison operator in SQL is advised. Consider an example of implementing the IS NULL condition using the SELECT statement. In this scenario, we will use a Student table. The table contains the following records:
Implement the Below SQL query to create the above table: Now, we will use the SELECT clause to retrieve the record where the value of S_City is NULL. It will return only the record with a NULL value in the S_City field of the Students table. 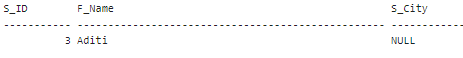
Example 2: We will implement the IS NULL condition with the UPDATE clause in SQL. Let us use an example to understand how to implement the IS NULL condition when performing an UPDATE operation on the table. We will use the same Students table to implement the SQL query. The table is as follows:
Now, Implement the below UPDATE statement in the table above. It will update 1 record in the Students table if you want to see the updated table implement the below query. These are the results that you should see: 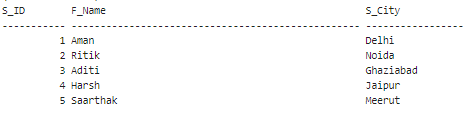
If multiple values are assigned NULL as the data value in the column, then all these values will be modified to Ghaziabad. Since there was only 1 record that met the above condition, only that record is updated. Example 3: We will implement the IS NULL condition with the DELETE clause in SQL. Before implementing the query, let's create a table to implement the IS NULL condition in a DELETE statement. The table name is Orders. It is as follows:
To create the above table in the database, implement the following SQL query. 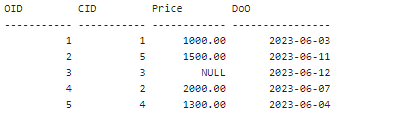
Implement the following DELETE statement: The above SQL query will delete all the records where the Price of Order is NULL. The above table shows only one such entity with OID 3. Implement the below SQL query to display the updated table after implementing the deletion. These are the results that you should see: 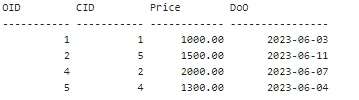
ISNULL() Function in SQLThe ISNULL function is implemented by the user when they want to replace all the values that are assigned as NULL with a specific value. Syntax of ISNULL()The syntax to implement the ISNULL() function in your SQL query is as follows: ISNULL (Expr, Modified_value) Arguments in ISNULL() FunctionThe user is required to pass two arguments in the ISNULL() functions. The arguments are as follows:
The ISNULL function will return the replacement value if the expression contains or is considered NULL. But before assigning a value, the function converts the modified_value to the same data type as the value after evaluating the expression. The conversion is only performed if the data type of both modified_value and expression is different. If the expression is evaluated to a value that is not NULL, then the ISNULL() function will return the value of the expression as it remains unchanged. Implementation of ISNULL() Function in SQLLet us take different scenarios where the user can implement SQL's ISNULL() function. Example 1: Implementing the SQL ISNULL function on the numeric data. We will use the Orders table defined above to implement the ISNULL() function.
The below query will return the second argument as the first argument is NULL. 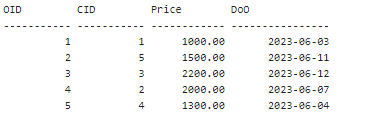
It will update the record with Price as NULL, which will be replaced by 2200.00. The user can also implement the ISNULL() function by directly using NULL as the first parameter. 
It will simply return the second parameter as the first parameter is NULL. Using ISNULL() function with Character StringThe user can also implement the ISNULL() function to replace the NULL with the string in the second parameter. Example 2: In the below example, we will use the ISNULL() to replace the NULL value with another string. 
Let's try another example of using another string as the first argument. 
In this case, it will return the first parameter only as it is not a NULL value. Implementing NULL values With Meaning Full ValuesThere are many instances when the data analysts have extensive data records, and the data needs to be cleaner and may contain several NULL values. These NULL values are replaced with meaningful values by using the ISNULL function. Let us begin with creating a table with name division. It keeps records of every athlete's age in a completion. The table is as follows:
Implement the SQL query below to create the above table and insert the given records. Implement the SELECT query to ensure all the records are in the table. 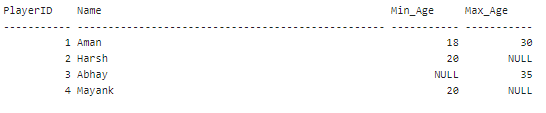
The NULL value in the Max_Age Min_Age column means the particular sport does not require a maximum or minimum age to register. We will replace the NULL values with an appropriate value. Implement the ISNULL() function to change NULL in the Min_Age column to 0 and NULL in the Max_Age column to 99: 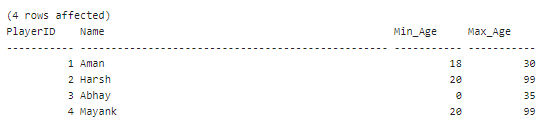
Next TopicSQL Schema
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










