Boruvka's Algorithm - Minimum Spanning TreesIn this tutorial, we will learn about Boruvka's algorithm in Python. It is used to identify the minimum spanning trees. Otakar Boruvka, a Czech mathematician, introduced this algorithm and was known for his work in graph theories. This algorithm is the most famous application for finding the minimum spanning trees in the graph. We will implement this algorithm using Python programming language. It is one of the oldest minimum spanning tree algorithms. On record, Boruvka came up in 1926. It was published as a method of constructing an efficient electricity network. Before jumping to Boruvka's algorithm and implementing it using Python, let's understand the concepts of the minimum spanning tree and take a recall to the graphs. Graphs and Minimum Spanning TreesA graph is called an abstracted structure representing a group of several objects known as nodes (vertices). If two nodes are connected, each of these connections is called Edge. Graphs are used to solve real-life problems, such as social network graphs and neural networks. If we simplify the graph, we can draw the family tree or explain some complex relationship. Types of GraphsThere are two distinct categories of graphs mainly -
Undirected GraphsUndirected graphs are referred in which the edges do not have directions. All edges in an undirected graph are, therefore, measured bidirectional. We define the undirected graph as G = (V, E), where V represents the set of the nodes, and E is a set that contains unordered pair of elements from E, which means edges. In other words, an undirected graph can be explained as we can't define the direction of the edges or the relationship between two nodes is always two-sided. For example - If an edge goes from A to B, there is an edge that goes from B to A. Directed GraphA directed graph is said to be a graph in which the edges have specific directions. We define the undirected graph as G = (V, E), where V represents the set of the nodes, and E is a set that contains an ordered pair of elements from E, which means edges. An ordered pair means the relationship between the two edges can be one-sided. In other words, if an edge goes to A to B, we can't identify there is an edge that goes from B to A. 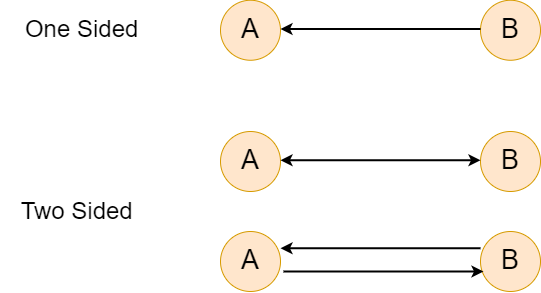
We can also categorize the graphs based on their edges regarding the weight of those edges. These types of graphs are weighted.
Weighted GraphsThe graph is weighted if a number is assigned to an edge. Those numbers represent the Edge's weight, which means the weight between nodes, capacity, etc. We can refer to the importance of anything according to our problem. Weighed Graphs are used to solve many problems, such as the need to find the shortest path, which we will see in the upcoming section. Unweighted GraphsIt is just the opposite of a weighted graph; such graphs don't have weight on their edges, and a graph is also disconnected and connected. A graph can also be connected and disconnected. If there is a path between the two nodes, it is considered the connected graph. On the other hand, if there is no path between two nodes, it is regarded as a disconnected graph. What are Tress and Minimum Spanning Trees?A tree is a non-linear, hierarchical, undirected graph where exactly one path exists between two edges, no more, no less. A subgraph is a graph that consists of a subset of an A's nodes and edges. A spanning tree of graph A is a subgraph of graph A, a tree whose set of nodes is the same as graph A's. A minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree whose sum of all the weight of the edges is as minimum as possible. Here the point to be remembered is that a tree shouldn't be formed in a cycle. Now, let's understand Boruvka's Algorithm Boruvka's AlgorithmBoruvka's algorithm is straightforward and intuitive. It is a greedy algorithm that constructs a globally "optimal" solution using smaller, locally optimal solutions for smaller sub problems. Greedy algorithms are generally concerned with the most optimal solution when the smaller steps add up. Let's breakdown the algorithm in a couple of steps:
Let's take a graph and the find the minimum spanning tree using Boruvka's algorithm. 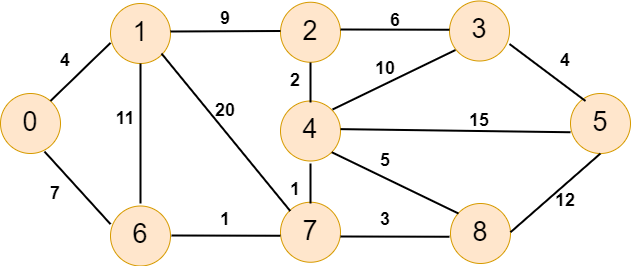
In the above undirected graph, we have nine vertices. Now let's see the following table for the weighted distribution.
Now our graph will look like as below - 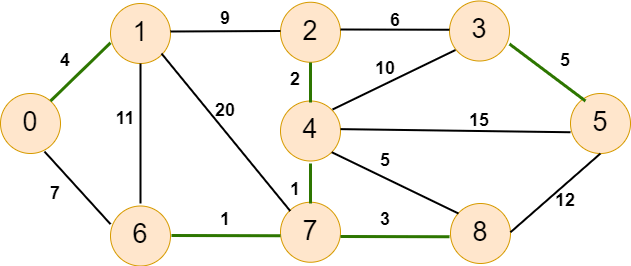
The highlighted line shows the nearest vertices that are bound together. As we can see, now we have the components: {0, 1}, {2, 4, 6, 7, 8} and {3, 5}. Again, we apply the algorithm to try to find the minimum-weight edges.
Now our graph will look like as below - 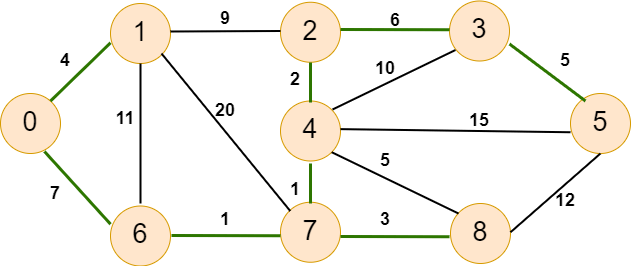
As we can observe, there is only one vertex in the graph, representing the minimum spanning tree. The weight of this tree is 29, which we get after summing all of the edges. So we have seen the working of Boruvka's algorithm. Now we will implement this using Python. ImplementationIn this section, we will write the code for the algorithm. Let's see the following code. Code - Output:
{0: 1, 1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 6, 7: 7, 8: 8}
Added edge [0 - 1]
Added weight: 4
{0: 1, 1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 3, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 6, 7: 7, 8: 8}
Added edge [2 - 4]
Added weight: 2
{0: 1, 1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 5, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 6, 7: 7, 8: 8}
Added edge [3 - 5]
Added weight: 5
{0: 1, 1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 5, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 6, 7: 4, 8: 8}
Added edge [4 - 7]
Added weight: 1
{0: 1, 1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 5, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 4, 7: 4, 8: 8}
Added edge [6 - 7]
Added weight: 1
{0: 1, 1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 5, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 4, 7: 4, 8: 4}
Added edge [7 - 8]
Added weight: 3
{0: 4, 1: 4, 2: 4, 3: 5, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 4, 7: 4, 8: 4}
Added edge [0 - 6]
Added weight: 7
{0: 4, 1: 4, 2: 4, 3: 4, 4: 4, 5: 4, 6: 4, 7: 4, 8: 4}
Added edge [2 - 3]
Added weight: 6
----------------------------------
The total weight of the minimal spanning tree is: 29
Explanation - In the above code, we have created a class named Graph, which holds our data structure used in the complete program. In the constructor, we passed the num_of_nodes as an argument and declared the three fields.
We defined the function add_edge(self, u, v, weight) function to add the Edge to a graph. The add_edge(self, u, v, weight) function adds an edge in the format [first, second, edge_weight] to our graph. Then, we defined the find_vertex() and set_vertex() method. In this method, we treated a dictionary as a tree. We found the root of the component. If we don't find the root node, we recursively search the current node's parent. The union(self, vertex_size, u, v) is defined that a unified two components into one, given two nodes which belong to their respective components. Then, we compared the components in terms of size and attached the smaller one to the large one. Then, we add the size of the smaller one to the size of the larger one because they have the component. Then we implemented Boruvka's algorithm. Example - In this method, we initialized the list of the components for Boruvka's algorithm. We created a list a list to keep track their size initialized to 1, as well as a list of the minimum weight edges. Then, we find the root node of the components that connect both sides of that edge. Now using if condition, we look for the minimum edge that link these two components.
After finding the minimal weight edges for each component, we add them to the minimal spanning tree and reduce the number of components correspondingly. The time complexity of this algorithm is 0(ElogV), where E represents the number of edges while V represents the number of nodes. The O(V+E) is the space complexity of this algorithm. ConclusionThere are many other popular minimum spanning tree algorithms like Prim's or Kruskal's algorithm. However, Boruvka's algorithm is not a well-known different algorithm. It gives pretty much the same result - they all find the minimum spanning tree, and the time complexity is approximately the same. Boruvka's algorithm provides more advantages than the algorithm; it doesn't need to presort the edges or maintain a priority queue to find the minimum spanning tree. In this tutorial, we discussed Boruvka's algorithm, the graphs, and the types. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










