Python Tutorial
Python OOPs
Python MySQL
Python MongoDB
Python SQLite
Python Questions
Plotly
Python Tkinter (GUI)
Python Web Blocker
Python MCQ
Related Tutorials
Python Programs
Loggers in DjangoAll the developer encounters with the bugs and resolving those takes some time. When we know the actual problem, and when the error occurs, it becomes more helpful. It means Python's error messages are quite helpful. In this tutorial, we will discuss the logging module and how we can implement it in Django. This module provides many advantages. As a Django developer, it is important that we also master the logging. Django provides excellent support for various logging frameworks and modules. Let's start with a brief introduction to the logging module. What is Logging?Logging is a technique that allows the developer to track some events as the software execute. It is a most important tool for developers. Logging helps to maintain the software and works as the extra set of eyes for the developers. It tracks every event that occurs at all times. After implementing the logging module, we can easily find which part is throwing errors. This method allows us to solve errors quickly. How does it work? Behind the SceneA separate program handles the logging, and that logging program is simply a file-writer. The logger is said to record certain events in the text format. The recorded information is then saved in files. These files are known as logs and saved with the log extension. They contain the log of the event that occurred. Python provides the logging module, which comes with extra features. We will discuss the various features of the logging module. The logging module can handle the following tasks -
If you want to learn more about the logging module, visit our logging module in Python tutorial. Components of Logging ModuleThere are mainly four components in logging module. We will discuss each component as below.
Developers deal with the loggers; it is the same as the function which will be invoked when they are called. When we invoke the function, it provides a detailed report. The logger can generate multiple levels of responses. We can also modify it according to our requirements.
Handlers are used to produce the information. It is like a newspaper that transmits information. We can achieve this by mentioning the info in a log file (The default behavior). The logging module provides many handlers. The same logger can implement multiple handlers. The SMTP handlers are also available, which will mail log records for us. The handlers usually contain business logic for logging information.
A filter is used to handle the log records that are passed from logger to handler. As its name suggest, it filters the messages. There can be multiple handlers available for the multiple messages. By default, any log message that meets log level requirements will be handled. We can use filters with both loggers and handlers.
The formatters are used to format the data. The problem with the handlers is that they cannot send the information as Python data type. To send such type of information, we need to convert first. The logs are by default in Log Record format, and the logging module predefines it. We can send information directly over the internet or in the form of a text file. To convert the format, we need the formatters. Logging in DjangoThe login module can be easily implemented in the Django and can easily configure. To use the logger in Django, we need to follow the following steps.
Let's start the process of using the logger in Django. Create a New ProjectThe logger can be implemented in the existing project. However you can create a new project to understand it in a better way. Use the below command to create a new project in Django. The above command will create the project. Now, we will configure the settings.py project. Configuring Settings\It is first step toward implementing the logger in Django. It is quite easy to configure the settings.py. We need to define the following things -
We use the dictConfig method, however there are other methods available. But dictConfig method is a default of Django. Copy the below code and paste it into settings.py. Let's breakdown the above code - The code may seem large and complex, but it is easy to understand. We have a built-in variable LOGGING from Django. Since we are configuring settings using a dictionary called the dictConfig method. The logging's default values come from this dictionary. Below are some important keys that reside in the LOGGING dictionary. Below are the some important keys which reside in the LOGGING dictionary.
The version key specifies the schema version. It has value, and it's by default value is 1. The next key is disable_exiting_loggers, and it specifies that don't disable loggers. By default, Django comes with its loggers. These loggers are connected with the Django ORM and the inner part of Django. By default, the key is true, so it disables those loggers. The third key is Handlers. As discussed above, handlers handle the message and pass it to the console, file, etc. The handlers themselves are a dictionary. The name of the handlers defines as the dictionary keys. Loggers provide many handlers, but we will use the two handlers here. 1. FileHandler: logger-name -filehandler The FileHandler will store the logs in a file. As you can observe in the above code, we have given the filename as javatpoint-debug.log. Logs file generally stored with the .extension. We need to have the permission to make changes in it. 2. StreamHandler: logger name - console The stream handler will stream the log on console. This method is not recommended to use. There is a limit of characters until the command line show you logs. In case of, big logs data we need to file-handlers. There are more handlers such as mailhandlers, AdminEmailHandlers etc. Loggers will log the server or software information. Loggers are also a dictionary type. It has a similar architecture as handlers. However, there are different attributes and other properties. Django comes with the set of loggers such as django, django.requests, and more. Now type the following command and hit enter. It will create the series of logs and this is happen because of default level of debug. All these logs are actually message from the default loggers. We can also create the customize loggers in the consecutive files. As we can see in the below image, the javatpoint-debug.log file has been created and it consisted all the log records. 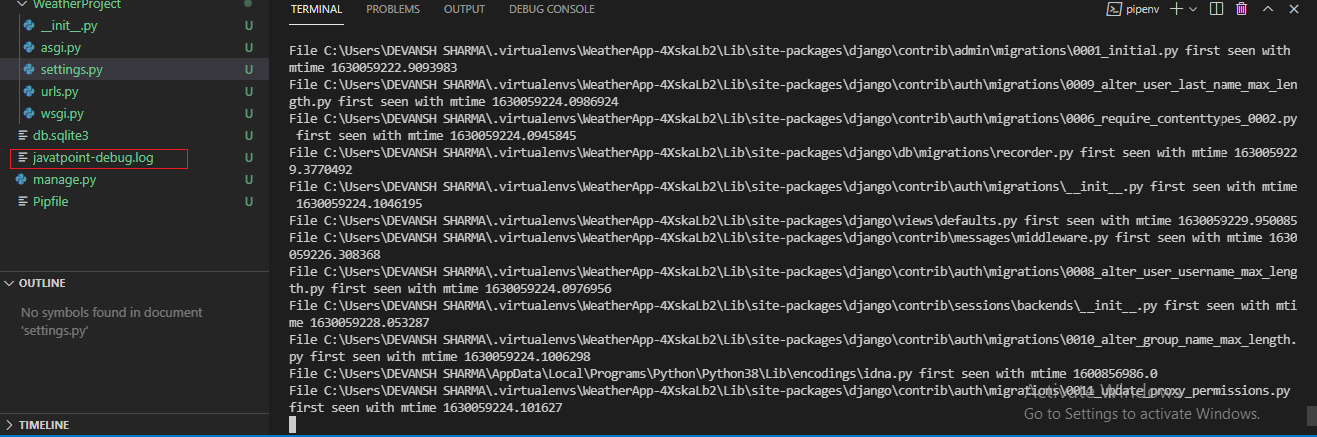
There are lots of log bug or warning or above level shall be notified. ConclusionLogging is an important tool for developers. If the programmer implements it correctly, it can reduce complexity and save a lot of time. The log handlers handle the log easily, and they make it easy to track the event, whether it occurred or not, and the cause. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










