ER (Entity Relationship) Diagram in DBMS
For example, Suppose we design a school database. In this database, the student will be an entity with attributes like address, name, id, age, etc. The address can be another entity with attributes like city, street name, pin code, etc and there will be a relationship between them. 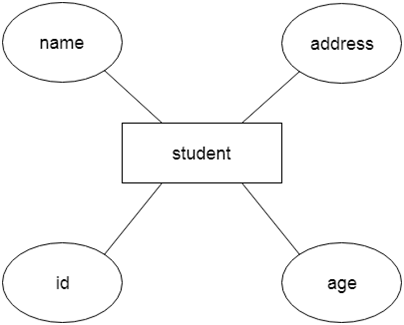
Component of ER Diagram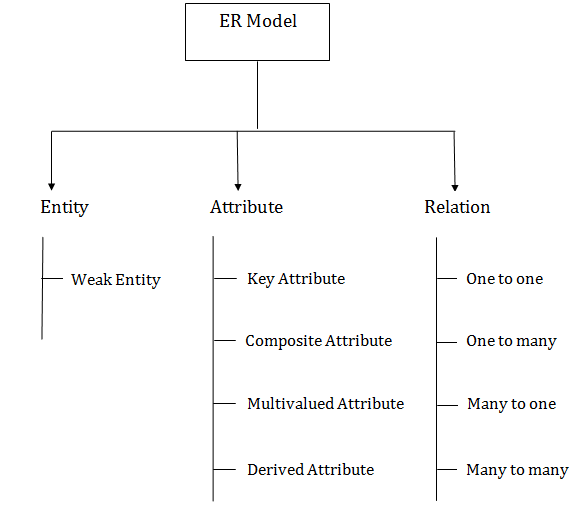
1. Entity:An entity may be any object, class, person or place. In the ER diagram, an entity can be represented as rectangles. Consider an organization as an example- manager, product, employee, department etc. can be taken as an entity. 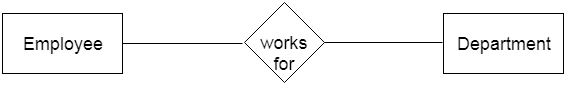
a. Weak Entity An entity that depends on another entity called a weak entity. The weak entity doesn't contain any key attribute of its own. The weak entity is represented by a double rectangle. 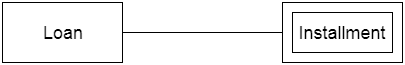
2. AttributeThe attribute is used to describe the property of an entity. Eclipse is used to represent an attribute. For example, id, age, contact number, name, etc. can be attributes of a student. 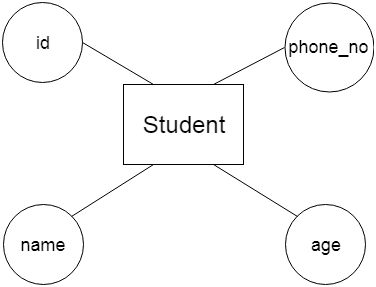
a. Key Attribute The key attribute is used to represent the main characteristics of an entity. It represents a primary key. The key attribute is represented by an ellipse with the text underlined. 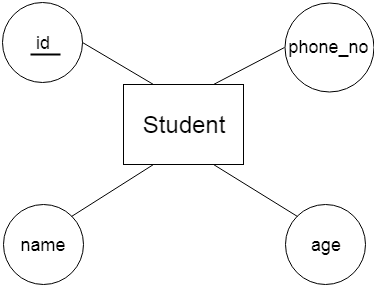
b. Composite Attribute An attribute that composed of many other attributes is known as a composite attribute. The composite attribute is represented by an ellipse, and those ellipses are connected with an ellipse. 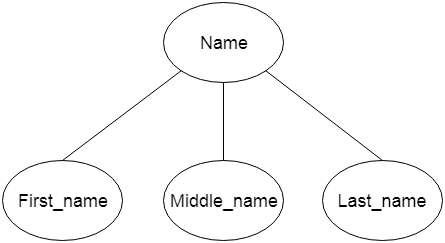
c. Multivalued Attribute An attribute can have more than one value. These attributes are known as a multivalued attribute. The double oval is used to represent multivalued attribute. For example, a student can have more than one phone number. 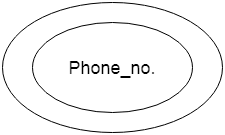
d. Derived Attribute An attribute that can be derived from other attribute is known as a derived attribute. It can be represented by a dashed ellipse. For example, A person's age changes over time and can be derived from another attribute like Date of birth. 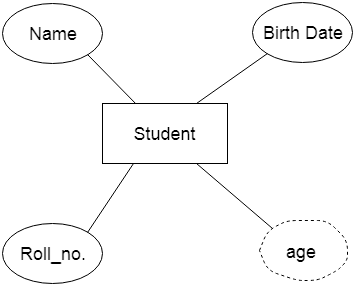
3. RelationshipA relationship is used to describe the relation between entities. Diamond or rhombus is used to represent the relationship. 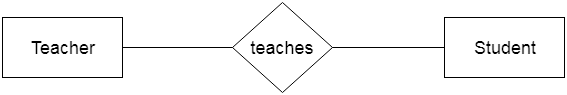
Types of relationship are as follows: a. One-to-One Relationship When only one instance of an entity is associated with the relationship, then it is known as one to one relationship. For example, A female can marry to one male, and a male can marry to one female. 
b. One-to-many relationship When only one instance of the entity on the left, and more than one instance of an entity on the right associates with the relationship then this is known as a one-to-many relationship. For example, Scientist can invent many inventions, but the invention is done by the only specific scientist. 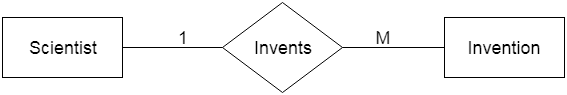
c. Many-to-one relationship When more than one instance of the entity on the left, and only one instance of an entity on the right associates with the relationship then it is known as a many-to-one relationship. For example, Student enrolls for only one course, but a course can have many students. 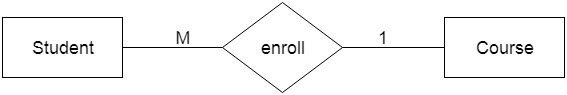
d. Many-to-many relationship When more than one instance of the entity on the left, and more than one instance of an entity on the right associates with the relationship then it is known as a many-to-many relationship. For example, Employee can assign by many projects and project can have many employees. 
Next TopicDBMS Notation for ER diagram
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










