File Organization StorageThere are different ways of storing data in the database. Storing data in files is one of them. A user can store the data in files in an organized manner. These files are organized logically as a sequence of records and reside permanently on disks. Each file is divided into fixed-length storage units known as Blocks. These blocks are the units of storage allocation as well as data transfer. Although the default block size in the database is 4 to 8 kilobytes, many databases allow specifying the size at the time of creating the database instance. Usually, the record size is smaller than the block size. But, for large data items such as images, the size can vary. For accessing the data quickly, it is required that one complete record should reside in one block only. It should not be partially divided between one or two blocks. In RDBMS, the size of tuples varies in different relations. Thus, we need to structure our files in multiple lengths for implementing the records. In file organization, there are two possible ways of representing the records:
Let's discuss this in detail. Fixed-Length RecordsFixed-length records means setting a length and storing the records into the file. If the record size exceeds the fixed size, it gets divided into more than one block. Due to the fixed size there occurs following two problems:
However, including a certain number of bytes is the solution to the above problems. It is known as File Header. The allocated file header carries a variety of information about the file, such as the address of the first record. The address of the second record gets stored in the first record and so on. This process is similar to pointers. The method of insertion and deletion is easy in fixed-length records because the space left or freed by the deleted record is exactly similar to the space required to insert the new records. But this process fails for storing the records of variable lengths. Variable-Length RecordsVariable-length records are the records that vary in size. It requires the creation of multiple blocks of multiple sizes to store them. These variable-length records are kept in the following ways in the database system:
In variable-length records, there exist the following two problems:
Thus, the representation of a variable-length record can be divided into two parts:
Slotted-page StructureThere occurs a problem to store variable-length records within the block. Thus, such records are organized in a slotted-page structure within the block. In the slotted-page structure, a header is present at the starting of each block. This header holds information such as:
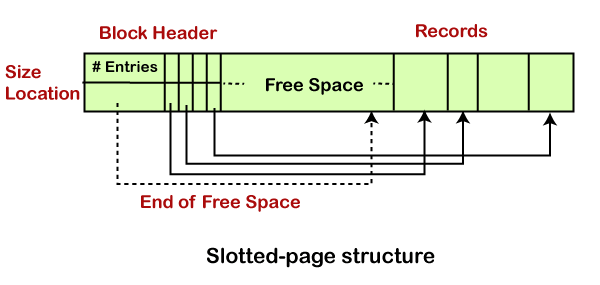
Inserting and Deleting Method The variable-length records reside in a contiguous manner within the block. When a new record is to be inserted, it gets the place at the end of the free space. It is because free space is contiguous as well. Also, the header fills an entry with the size and location information of the newly inserted record. When an existing record is deleted, space is freed, and the header entry sets to deleted. Before deleting, it moves the record and occupies it to create the free space. The end-of-free-space gets the update. Then all the free space again sets between the first record and the final entry. The primary technique of the slotted-page structure is that no pointer should directly point the record. Instead, it should point to the header entry that contains the information of its location. This stops fragmentation of space inside the block but supports indirect pointers to the record.
Next TopicSelection of RAID Levels
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










