What is RDBMS (Relational Database Management System)RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. All modern database management systems like SQL, MS SQL Server, IBM DB2, ORACLE, My-SQL, and Microsoft Access are based on RDBMS. It is called Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) because it is based on the relational model introduced by E.F. Codd. How it worksData is represented in terms of tuples (rows) in RDBMS. A relational database is the most commonly used database. It contains several tables, and each table has its primary key. Due to a collection of an organized set of tables, data can be accessed easily in RDBMS. Brief History of RDBMSFrom 1970 to 1972, E.F. Codd published a paper to propose using a relational database model. RDBMS is originally based on E.F. Codd's relational model invention. Following are the various terminologies of RDBMS: 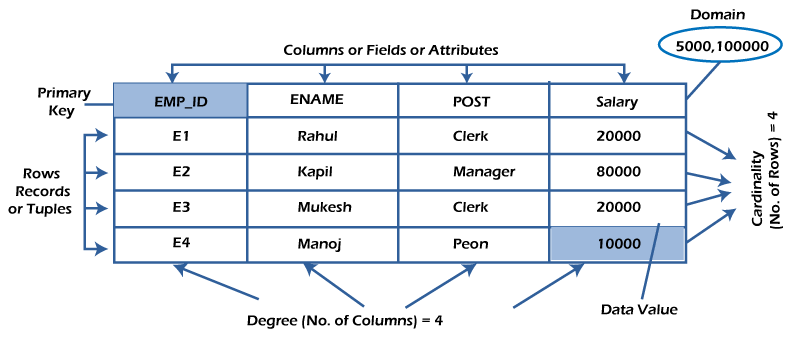
What is table/Relation?Everything in a relational database is stored in the form of relations. The RDBMS database uses tables to store data. A table is a collection of related data entries and contains rows and columns to store data. Each table represents some real-world objects such as person, place, or event about which information is collected. The organized collection of data into a relational table is known as the logical view of the database. Properties of a Relation:
A table is the simplest example of data stored in RDBMS. Let's see the example of the student table.
What is a row or record?A row of a table is also called a record or tuple. It contains the specific information of each entry in the table. It is a horizontal entity in the table. For example, The above table contains 5 records. Properties of a row:
Let's see one record/row in the table.
What is a column/attribute?A column is a vertical entity in the table which contains all information associated with a specific field in a table. For example, "name" is a column in the above table which contains all information about a student's name. Properties of an Attribute:
What is data item/Cells?The smallest unit of data in the table is the individual data item. It is stored at the intersection of tuples and attributes. Properties of data items:
In the below example, the data item in the student table consists of Ajeet, 24 and Btech, etc.
Degree:The total number of attributes that comprise a relation is known as the degree of the table. For example, the student table has 4 attributes, and its degree is 4.
Cardinality:The total number of tuples at any one time in a relation is known as the table's cardinality. The relation whose cardinality is 0 is called an empty table. For example, the student table has 5 rows, and its cardinality is 5.
Domain:The domain refers to the possible values each attribute can contain. It can be specified using standard data types such as integers, floating numbers, etc. For example, An attribute entitled Marital_Status may be limited to married or unmarried values. NULL ValuesThe NULL value of the table specifies that the field has been left blank during record creation. It is different from the value filled with zero or a field that contains space. Data IntegrityThere are the following categories of data integrity exist with each RDBMS: Entity integrity: It specifies that there should be no duplicate rows in a table. Domain integrity: It enforces valid entries for a given column by restricting the type, the format, or the range of values. Referential integrity specifies that rows cannot be deleted, which are used by other records. User-defined integrity: It enforces some specific business rules defined by users. These rules are different from the entity, domain, or referential integrity.
Next TopicDBMS vs RDBMS
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










