Storage System in DBMSA database system provides an ultimate view of the stored data. However, data in the form of bits, bytes get stored in different storage devices. In this section, we will take an overview of various types of storage devices that are used for accessing and storing data. Types of Data StorageFor storing the data, there are different types of storage options available. These storage types differ from one another as per the speed and accessibility. There are the following types of storage devices used for storing the data:
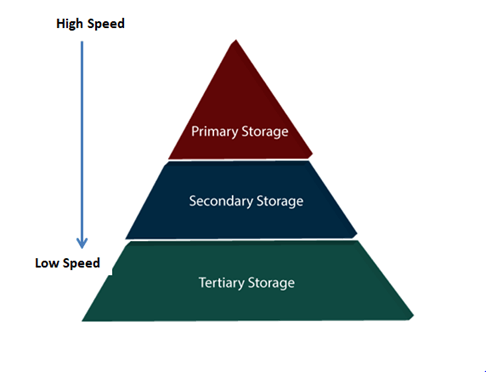
Primary StorageIt is the primary area that offers quick access to the stored data. We also know the primary storage as volatile storage. It is because this type of memory does not permanently store the data. As soon as the system leads to a power cut or a crash, the data also get lost. Main memory and cache are the types of primary storage.
Secondary StorageSecondary storage is also called as Online storage. It is the storage area that allows the user to save and store data permanently. This type of memory does not lose the data due to any power failure or system crash. That's why we also call it non-volatile storage. There are some commonly described secondary storage media which are available in almost every type of computer system:
Tertiary StorageIt is the storage type that is external from the computer system. It has the slowest speed. But it is capable of storing a large amount of data. It is also known as Offline storage. Tertiary storage is generally used for data backup. There are following tertiary storage devices available:
Storage HierarchyBesides the above, various other storage devices reside in the computer system. These storage media are organized on the basis of data accessing speed, cost per unit of data to buy the medium, and by medium's reliability. Thus, we can create a hierarchy of storage media on the basis of its cost and speed. Thus, on arranging the above-described storage media in a hierarchy according to its speed and cost, we conclude the below-described image: 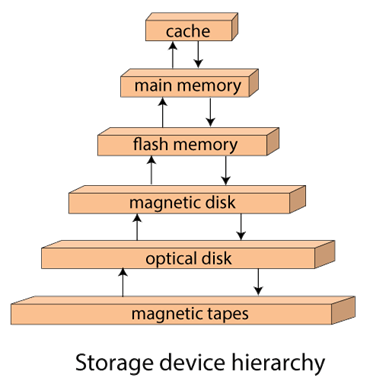
In the image, the higher levels are expensive but fast. On moving down, the cost per bit is decreasing, and the access time is increasing. Also, the storage media from the main memory to up represents the volatile nature, and below the main memory, all are non-volatile devices.
Next TopicDBMS Tutorial
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










