SQL Commands
Types of SQL CommandsThere are five types of SQL commands: DDL, DML, DCL, TCL, and DQL. 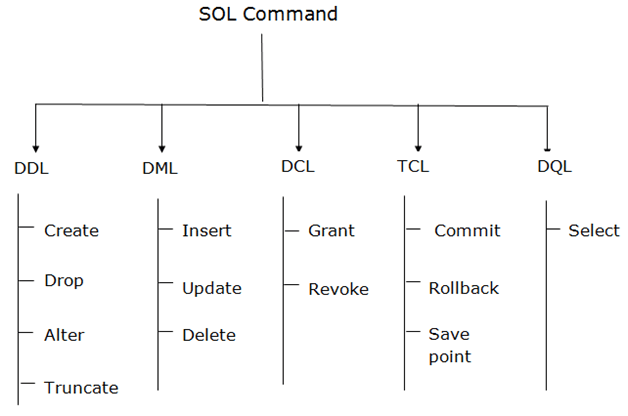
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
Here are some commands that come under DDL:
a. CREATE It is used to create a new table in the database. Syntax: Example: b. DROP: It is used to delete both the structure and record stored in the table. Syntax Example c. ALTER: It is used to alter the structure of the database. This change could be either to modify the characteristics of an existing attribute or probably to add a new attribute. Syntax: To add a new column in the table To modify existing column in the table: EXAMPLE d. TRUNCATE: It is used to delete all the rows from the table and free the space containing the table. Syntax: Example: 2. Data Manipulation Language
Here are some commands that come under DML:
a. INSERT: The INSERT statement is a SQL query. It is used to insert data into the row of a table. Syntax: Or For example: b. UPDATE: This command is used to update or modify the value of a column in the table. Syntax: For example: c. DELETE: It is used to remove one or more row from a table. Syntax: For example: 3. Data Control LanguageDCL commands are used to grant and take back authority from any database user. Here are some commands that come under DCL:
a. Grant: It is used to give user access privileges to a database. Example b. Revoke: It is used to take back permissions from the user. Example 4. Transaction Control LanguageTCL commands can only use with DML commands like INSERT, DELETE and UPDATE only. These operations are automatically committed in the database that's why they cannot be used while creating tables or dropping them. Here are some commands that come under TCL:
a. Commit: Commit command is used to save all the transactions to the database. Syntax: Example: b. Rollback: Rollback command is used to undo transactions that have not already been saved to the database. Syntax: Example: c. SAVEPOINT: It is used to roll the transaction back to a certain point without rolling back the entire transaction. Syntax: 5. Data Query LanguageDQL is used to fetch the data from the database. It uses only one command:
a. SELECT: This is the same as the projection operation of relational algebra. It is used to select the attribute based on the condition described by WHERE clause. Syntax: For example:
Next TopicDBMS SQL Operator
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










