Density-based clustering in data mininDensity-based clustering refers to a method that is based on local cluster criterion, such as density connected points. In this tutorial, we will discuss density-based clustering with examples. What is Density-based clustering?Density-Based Clustering refers to one of the most popular unsupervised learning methodologies used in model building and machine learning algorithms. The data points in the region separated by two clusters of low point density are considered as noise. The surroundings with a radius ε of a given object are known as the ε neighborhood of the object. If the ε neighborhood of the object comprises at least a minimum number, MinPts of objects, then it is called a core object. Density-Based Clustering - BackgroundThere are two different parameters to calculate the density-based clustering EPS: It is considered as the maximum radius of the neighborhood. MinPts: MinPts refers to the minimum number of points in an Eps neighborhood of that point. NEps (i) : { k belongs to D and dist (i,k) < = Eps} Directly density reachable: A point i is considered as the directly density reachable from a point k with respect to Eps, MinPts if i belongs to NEps(k) Core point condition: NEps (k) >= MinPts 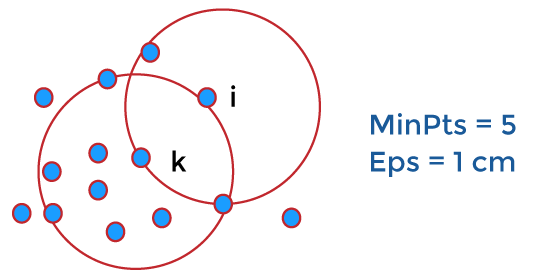
Density reachable: A point denoted by i is a density reachable from a point j with respect to Eps, MinPts if there is a sequence chain of a point i1,…., in, i1 = j, pn = i such that ii + 1 is directly density reachable from ii. 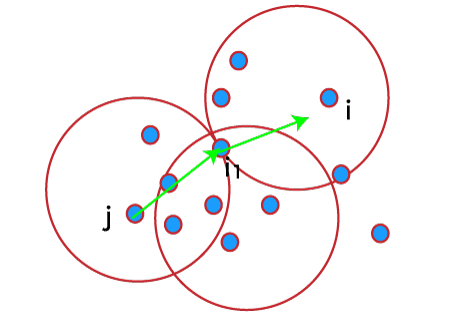
Density connected: A point i refers to density connected to a point j with respect to Eps, MinPts if there is a point o such that both i and j are considered as density reachable from o with respect to Eps and MinPts. 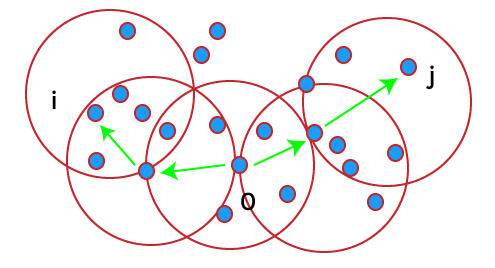
Working of Density-Based ClusteringSuppose a set of objects is denoted by D', we can say that an object I is directly density reachable form the object j only if it is located within the ε neighborhood of j, and j is a core object. An object i is density reachable form the object j with respect to ε and MinPts in a given set of objects, D' only if there is a sequence of object chains point i1,…., in, i1 = j, pn = i such that ii + 1 is directly density reachable from ii with respect to ε and MinPts. An object i is density connected object j with respect to ε and MinPts in a given set of objects, D' only if there is an object o belongs to D such that both point i and j are density reachable from o with respect to ε and MinPts. Major Features of Density-Based ClusteringThe primary features of Density-based clustering are given below.
Density-Based Clustering MethodsDBSCAN DBSCAN stands for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise. It depends on a density-based notion of cluster. It also identifies clusters of arbitrary size in the spatial database with outliers. 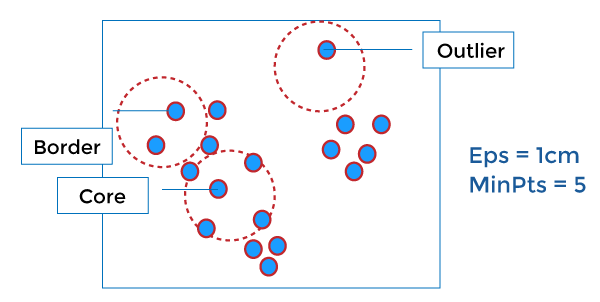
OPTICS OPTICS stands for Ordering Points To Identify the Clustering Structure. It gives a significant order of database with respect to its density-based clustering structure. The order of the cluster comprises information equivalent to the density-based clustering related to a long range of parameter settings. OPTICS methods are beneficial for both automatic and interactive cluster analysis, including determining an intrinsic clustering structure. DENCLUE Density-based clustering by Hinnebirg and Kiem. It enables a compact mathematical description of arbitrarily shaped clusters in high dimension state of data, and it is good for data sets with a huge amount of noise.
Next TopicAggregation in data mining
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










