ScrollView
In iOS applications, sometimes, we may need to show the content that doesn't fit into the screen. To show this type of content, we use ScrollView in the application. A ScrollView allows the user to drag the area of the content. It is an instance of the UIScrollView class, which inherits UIView.
The ScrollView allows the scrolling and zooming of its contained views. The tableview and collectionview are the subclasses of UIScrollView, and therefore, these classes provide a great way to display the content that is larger than the screen. In iOS applications, we use tableview to display the vertically scrollable content, and the collectionview to display the horizontally scrollable content.
The origin of the UIScrollView object is adjustable over the content view. A ScrollView tracks the movement of the fingers and adjusts its origin accordingly.
Adding ScrollView to the interface
Adding ScrollView to the interface builder is a bit complex as compare to the other objects. We need to define the auto-layout rules to guide the layout and position of the scroll view on the different screen devices.
Follow the following steps to add the scrollview to the interface using the interface builder (main.storyboard).
- Search for the ScrollView on the main.storyboard and drag the result to the ViewController.
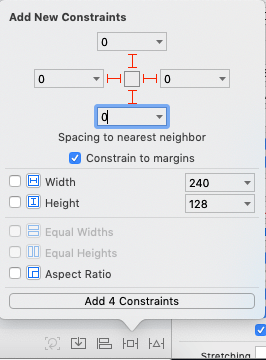
- Define the Auto layout rules (constraints) for the ScrollView, as shown in the following image.
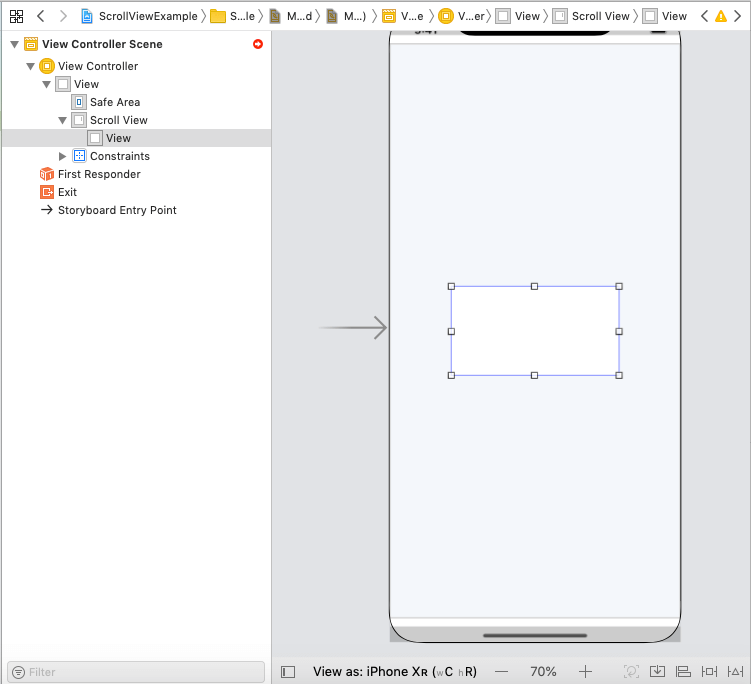
- Add ContentView to the ScrollView and define the auto-layout rules for the content view.
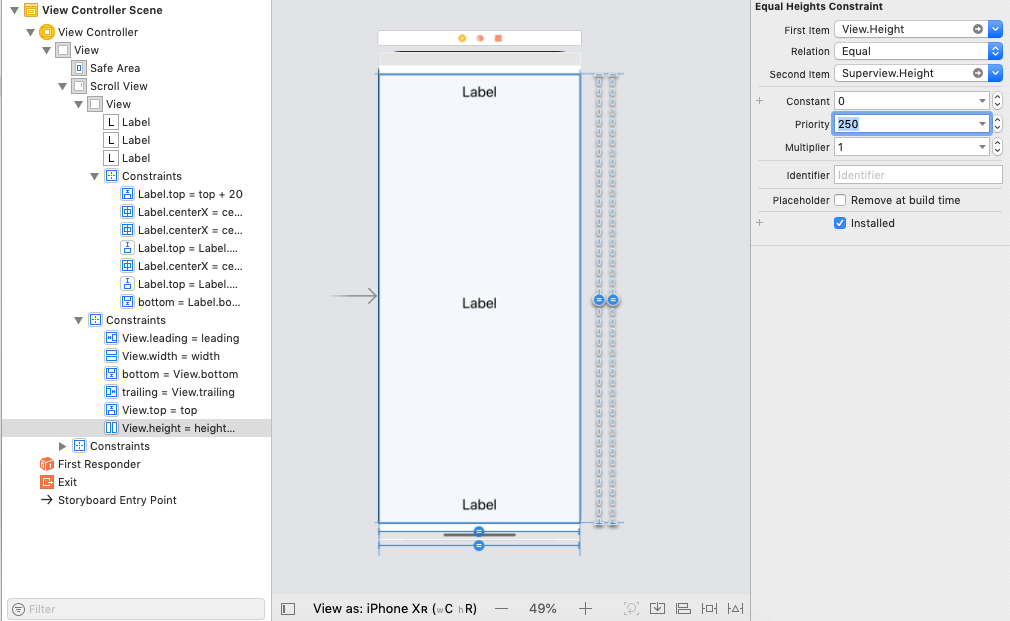
Give the constraint margin 0 to the contentView from ScrollView. We also need to make the height and width of them equal.
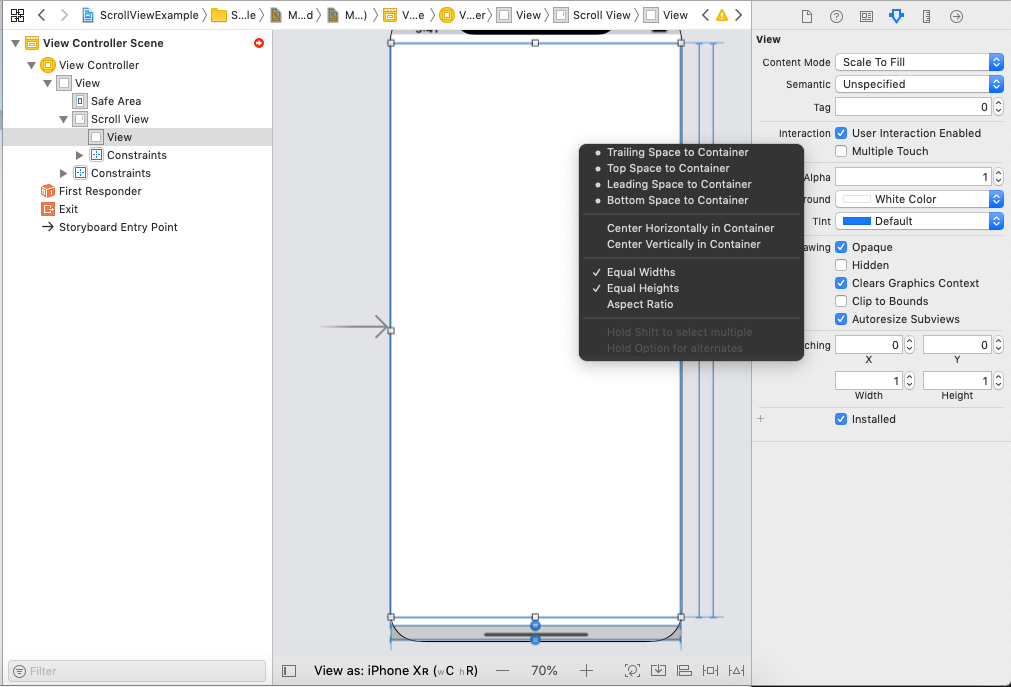
Make the priority of the ContentView to the low, as shown in the below image. This is the most important step in this setup; otherwise, the scrollview doesn't scroll.
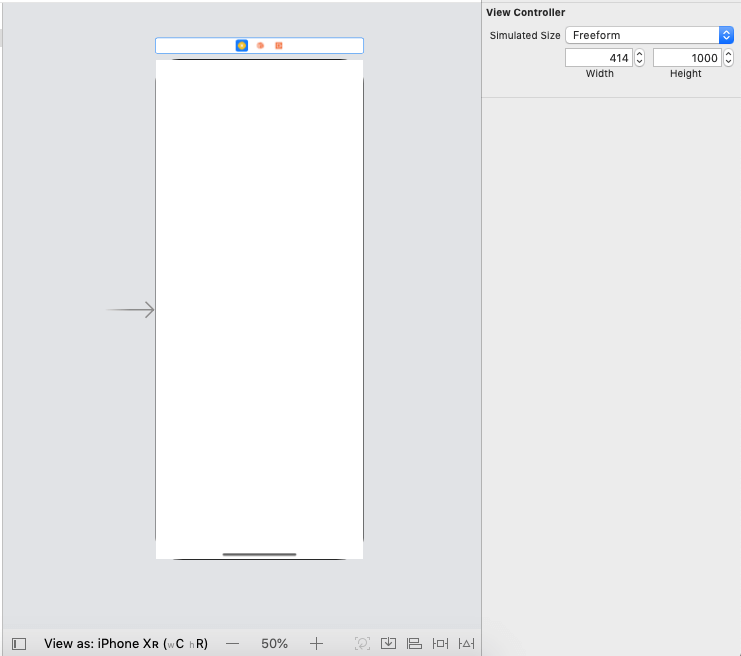
We will have the ScrollView and the ContentView on the storyboard. Since ScrollView works when the content size doesn't fit into the entire screen of the iPhone Screen. We define the size of the ViewController screen into the size inspector in XCode. By default, the simulated size of then ViewController is fixed. However, we need to make it freeform and give the height anything greater than the current Screen height as given in the below image.
Add a UILabel to the top, center, and bottom of the ScrollView and give the vertical spacing between them, to test whether the ScrollView is working or not. After adding the UILabels and changing the background color, the interface builder will be looking like the following window.
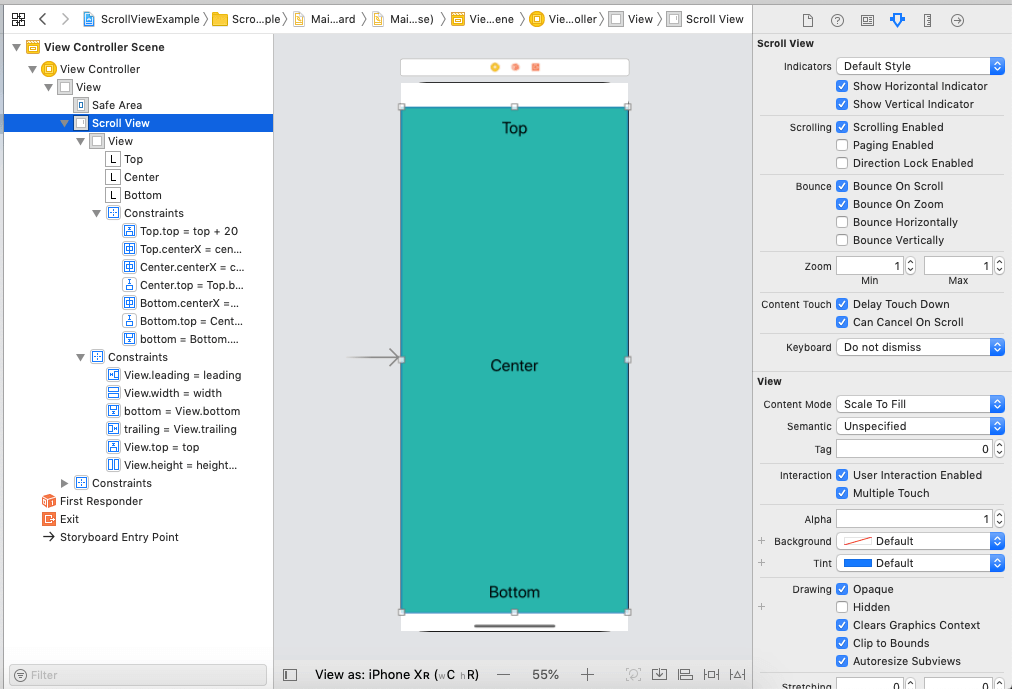
The above setup will make the ScrollView to Scroll to show the whole content on the screen.

ScrollView Properties
The UIScrollView class contains the following properties.
| SN |
Property |
Type |
Description |
| 1 |
Delegate |
UIScrollViewDelegate |
It is the delegate of the ScrollView object. |
| 2 |
contentSize |
CGSize |
It represents the size of the content view. |
| 3 |
contentOffset |
CGPoint |
It represents the point at which the origin of the contentview is offset from the origin of ScrollView. |
| 4 |
adjustedContentOffset |
UIEdgeInsets |
It represents the insets from the content inset and the safe area of the scroll view. |
| 5 |
frameLayoutGuide |
UILayoutGuide |
The layout guide based on the untransformed frame rectangle of the scroll view. |
| 6 |
contentLayoutGuide |
UILayoutGuide |
The layout guide based on the untranslated content rectangle of the scroll view. |
| 7 |
isScrollEnabled |
Bool |
It represents the boolean value that tells whether the scroll view is enabled or not. |
| 8 |
isDirectionLockEnabled |
Bool |
It represents the boolean value that tells whether the scroll view can be scrolled in a particular direction. |
| 9 |
isPagingEnabled |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether then paging is enabled in a particular direction. |
| 10 |
scrollsToTop |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that controls whether the scroll to top gesture is enabled or not. |
| 11 |
bounces |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the scroll view bounces over the edge of the content. |
| 12 |
alwaysBounceVertical |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether bouncing always occurs when vertical scrolling reaches the end of the content. |
| 13 |
alwaysBounceHorizontal |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the bouncing always occurs when horizontal scrolling reaches the end of the content. |
| 14 |
isTracking |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the user touches the content to initiate scrolling |
| 15 |
isDragging |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the user has begun scrolling the content. |
| 16 |
isDecelerating |
Bool |
It is a boolean value whether the content was moving in the scrollview when the user stopped dragging or lifted its finger. |
| 17 |
decelerationRate |
UIScrollView.DelcelerationRate |
It is a floating-point value that determines the rate of deceleration after the user lifts their finger. |
| 18 |
indicatorStyle |
UIScrollView.IndicatorStyle |
It represents the style of the scroll indicators. |
| 19 |
showsHorizontalScrollsIndicator |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the horizontal scroll indicator is visible or not. |
| 20 |
showsVerticalScrollIndicator |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the vertical scroll indicator is visible or not. |
| 21 |
refreshControl |
UIRefreshControl |
It represents the refresh control associated with the scroll view. |
| 22 |
canCancelContentTouches |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that controls. |
| 23 |
delayContentTouches |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that reprents whether the scroll view delays the handling of touch-down gestures. |
| 24 |
directionPressGestureRecognizer |
UIGestureRecognizer |
The underlying gesture recognizer for directional button presses. |
| 25 |
panGestureRecognizer |
UIPanGestureRecongnizer |
The underlying gesture recognizer for pan gestures. |
| 26 |
pinchGestureRecognizer |
UIPinchGestureRecognizer |
The underlying gesture recognizer for pinch gestures. |
| 27 |
zoomScale |
CGFloat |
It is a floating-point value that scales the zooming of the content of the scroll view. |
| 28 |
maximumZoomScale |
CGFloat |
It is a maximum floating-point value that can be applied to the zooming of the content of the scroll view. |
| 29 |
minimumZoomScale |
CGFloat |
It is the minimum floating-point value that can be applied to the zooming of the content of the scroll view. |
| 30 |
isZoomBouncing |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the zooming has exceeded the associated scaling limits. |
| 31 |
isZooming |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the content view is currently zooming or not. |
| 32 |
bouncesZoom |
Bool |
It is a boolean value that represents whether the scroll view animates the content scaling when the scaling exceeds the maximum or minimum limits. |
Example
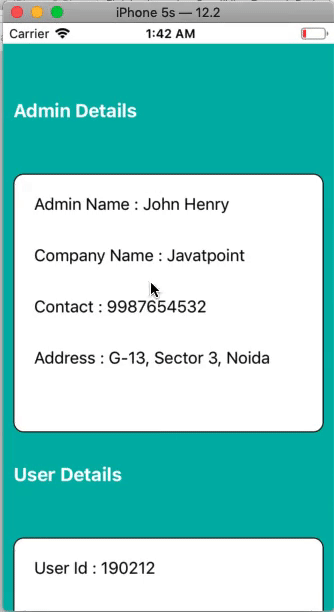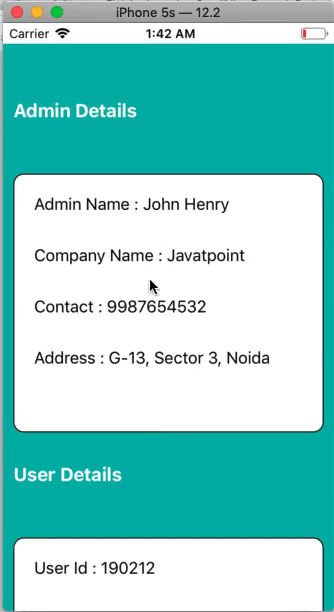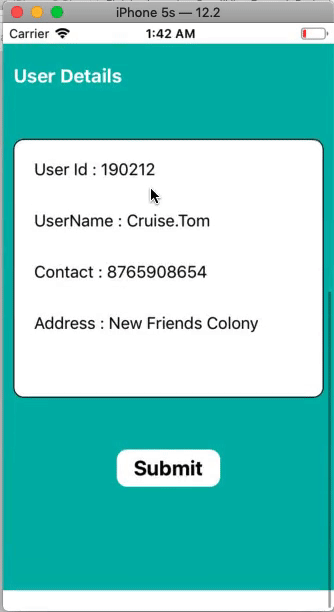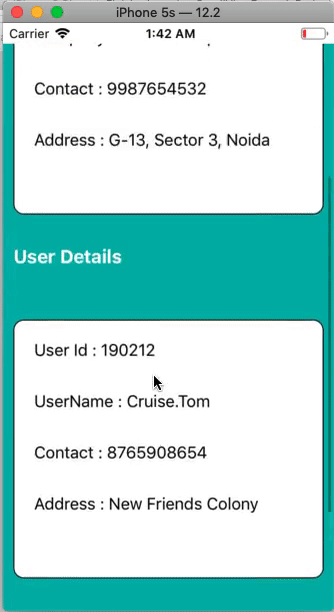
This is a simple example in which we will create a ScrollView and the ContentView. We will create two UIViews inside the scroll view to display the actual content.
Interface Builder
In this example, we will use the scrollview, which contains a content view. The content view will be scrolled to display two uiviews. For this purpose, use the instructions given in this tutorial to add the scrollview to the interface builder and add the scrollview to the interface.
Add the UIView to the ScrollView and define the auto-layout rules for the UIView. After adding the UIView (ContentView) to the scrollview, we need to add two UIViews and a UIButton to the storyboard.
To make the ScrollView, scrollable, we need to change the ViewController size from fixed to freeform and define some vertical spacing among the views.
Set up the auto-layout rules for the ScrollView, ContentView, UIviews, and the submit button.
AutoLayout Rules for ScrollView
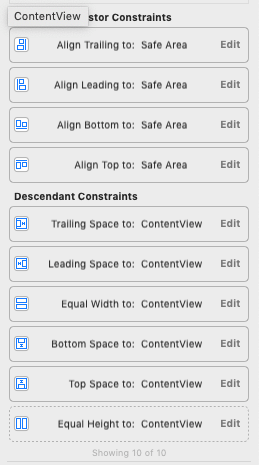
AutoLayout rules for ContentView
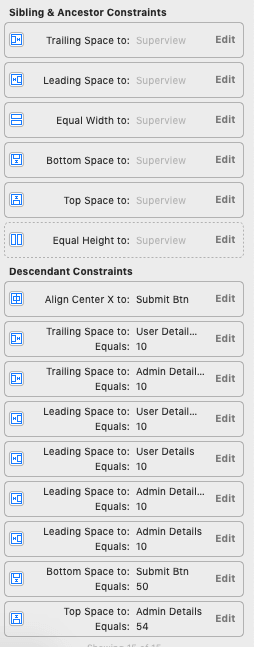
AutoLayout rules for AdminDetailsView
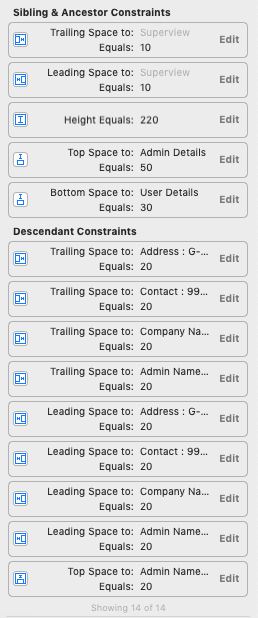
AutoLayout Rules for UserDetailView
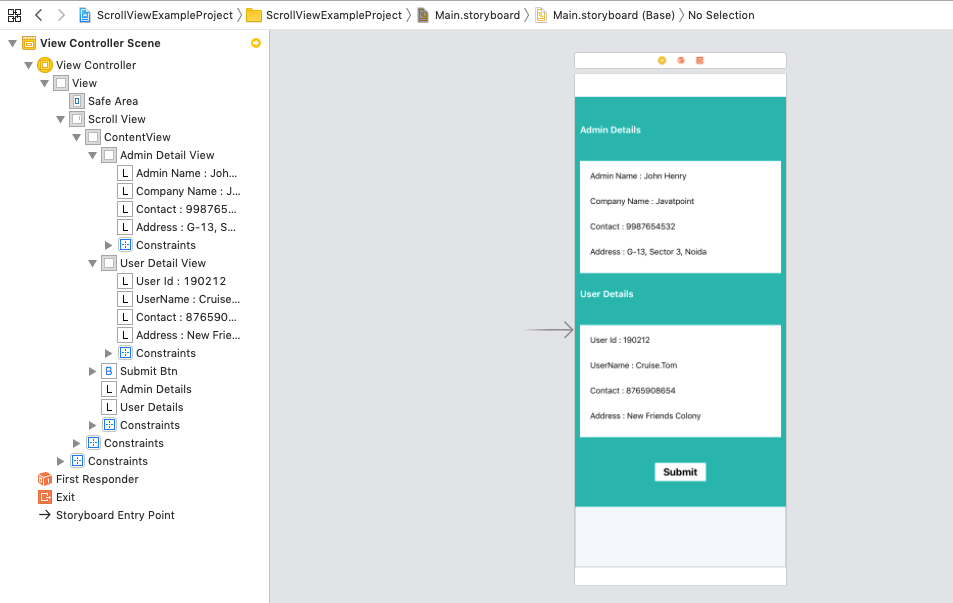
Main.storyboard
ViewController.swift
Output:
| 













 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









