NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
Students looking for NCERT solutions of chapter 15 science for class 10 may use this article as a resource. Students can also discover additional questions and answers for our environment class 10 there. Solving these Chapter 15 Our Environment problems will help pupils pass their board examinations and succeed in competitive exams.

Therefore, in order to develop a solid foundation in the subject of Science, students are suggested to carefully read through these NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment. Discover everything there is to know about NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 15.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Inside Chapter Questions
Page Number: 260
Question 1:
What are trophic levels? Give an example of food chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer:
Trophic Levels:
- A trophic level is a place, level, or position within a food web, a food chain, or an ecological pyramid.
- The producers create the first trophic level as they generate food.
- The main consumers make up the second trophic level.
- The secondary consumers make up the third trophic level.
- The tertiary consumers make up the fourth trophic level.
Example of a food chain:
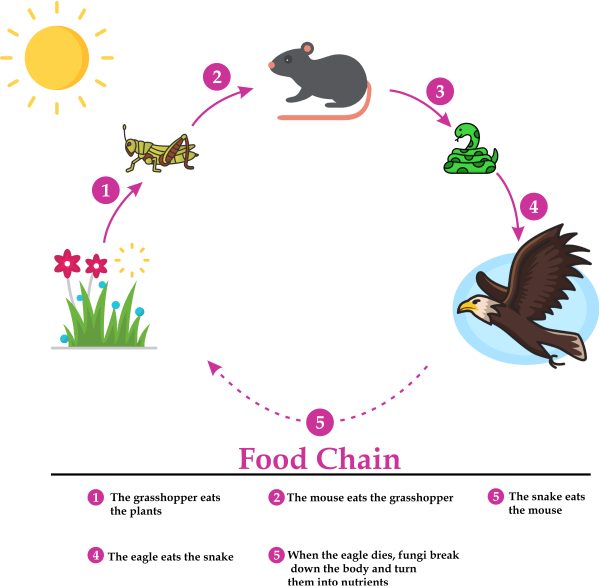
Sun ? Grass ? Grasshopper ? Mouse ? Snake ? Owl
- The grass is the producer in this instance, and the grasshopper is the primary consumer.
- The rat, or secondary consumer, continues to eat the grasshopper. Additionally, the snake consumes the rat.
- Last but not least, the owl eats up the snake, that is tertiary consumer.
Question 2:
What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
Answer:
Ecosystem:
To create a "bubble of life," plants, animals, and other beings, as well as the weather and landscapes, cohabit in an ecosystem.
Decomposers:
- By decomposing dead plants and animals, decomposers in ecosystems serve as environmental cleaners.
- They assist in the nutrient recycling process.
- Allowing the deceased to decompose creates space in the biosphere for new life.
- They help recycle various components back into moisture, soil, and air for use by producers like crop plants.
Page Number: 262
Question 1:
Why are some substances biodegradable and some non-biodegradable?
Answer:
The bacteria and other decomposer organisms (referred to as saprophytes) that are prevalent in our environment all have unique functions. They degrade items made of natural materials, like paper, but not those composed of artificial ones, like plastics.
Products that are degradable by microorganisms are called biodegradable substances.
Products that are not degradable by microorganisms are called non-biodegradable substances.
Question 2:
Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
The following are some ways that biodegradable compounds might harm the environment:
- They might emit a bad odor as they decompose.
- They might release dangerous gases like ammonia, methane, etc., which contribute to global warming.
Question 3:
Give any two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would effect the environment.
Answer:
The following are some ways that non-biodegradable compounds harm the environment:
- They contaminate soil and water resources because microbes cannot break them down.
- When stray animals mistakenly consume these toxins, it can hurt or even kill them.
Page Number: 264
Question 1:
What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Answer:
Ozone (O3) is an isotope of oxygen, a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. It is an important layer in the atmosphere which supports the existence of life on earth. In the upper atmosphere, ozone layer formation occurs. It protects Earth's surface from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet radiation (UV), which can lead to cataracts and skin cancer. Crops are also harmed by it.
Question 2:
How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer:
Poor waste management can harm the ecosystem, including spreading infectious diseases, contaminating the land and water, clogging drains, and extinction of wildlife. By using fewer throwaway items and more readily recyclable materials, we can lessen the problem of garbage disposal.
The two strategies for addressing the issue of waste disposal are:
- Separating biodegradable waste from non-biodegradable trash and then disposing of the former in landfill or manure-conversion facilities.
- Non-biodegradable garbage is burned and incinerated, turning it into ash.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Exercise Questions
Question 1:
Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable item?
- Grass, flowers and leather
- Grass, wood and plastic
- Fruit peels, cake and lime juice
- Cake, wood and grass
Answer:
The correct Options are (c) and (d).
Explanation:
Explanation for Correct Option:
- Biodegradable wastes are substances broken down by bacteria and other natural processes.
- Lime juice, cake, fruit peels, and wood are all biodegradable substances
Explanation for Incorrect Options:
Option (a):
- Wastes that are not degradable by natural processes are known as non-biodegradable compounds.
- Grass and flowers degrade naturally (easily decomposed by microbes).
- Leather cannot decompose naturally.
Option (b):
- Bacteria cannot easily break down waste that is not biodegradable.
- Both grass and timber can be decomposed (easily decomposed by microbes).
- Plastic is not a biodegradable substance.
Thus, fruit peels, cake, lime juice, wood, and grass are biodegradable items.
Question 2:
Which of the following constitutes a food-chain?
- Grass, wheat and mango
- Grass, goat and human
- Goat, cow and elephant
- Grass, fish and goat
Answer:
The Correct Option is (b).
Explanation:
Explanation for Correct Option:
- A series of activities that take place in nature to transfer energy from one creature to another in the form of food is known as a food chain.
- The producer comes first, followed by the primary consumer, the secondary consumer, and so forth.
- The food chain is a cycle in Ecology for the transfer of energy.
- For instance, the grass is a producer consumed by a goat as its primary consumer, which then consumes a person as its secondary consumer.
Explanation for Incorrect Options:
Option (a):
All of the plants mentioned here are producers.
Option (c):
Being a herbivore, the elephant won't eat a cow.
Option (d):
Since goats are herbivores, they won't eat fish.
Thus, Grass, Goats, and human constitutes a food chain.
Question 3:
Which of the following are environment friendly practices?
- Carrying cloth-bags to put purchases in while shopping
- Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
- Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop on her scooter
- All of the above
Answer:
The correct option is (d).
Explanation:
Explanation of Correct Option:
- Environment-friendly practices are designed to lessen pollution and assist the natural world.
- The three R's are supposed to promote nature: reduce, reuse, and recycle.
- Plastic bags are non-biodegradable, and they erode soil and pollute water. So, instead of using plastic bags, use cloth bags.
- Lights and fans should be turned off to conserve energy when not required
- Vehicle smoke contributes to air pollution.
- Walking should therefore be chosen whenever possible.
Therefore, all the actions above (carrying cloth bags when shopping, turning off lights and fans when not in use, and walking to school rather than having your mother drop you off on her scooter) are environmentally beneficial.
Question 4:
What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Answer:
If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level then following case would happen:
- The ecological balance would be impacted, and the food chain would end.
- The carnivores would be unable to obtain food if the herbivores were destroyed, and they would perish.
- The population of herbivores would reach an unsustainable level if carnivores were killed.
- The fertilizer cycle in that area wouldn't be finished if producers were killed.
Question 5:
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer:
Yes, the effects of eliminating every organism at a trophic level will vary depending on the trophic level.
- Herbivores would either be unable to exist without producers, or they would relocate, causing the ecosystem to collapse.
- Carnivores wouldn't have access to food if herbivores were eliminated, allowing producers to expand unchecked.
- If carnivores are removed, herbivores would increase to unsustainable levels and could destroy the producers.
- Without decomposers, dead animals would accumulate and pollute the ecosystem.
- Additionally, the soil's fertility will decrease if deceased animals do not disintegrate, stopping the recycling of nutrients.
- The effect will be the loss of the earth's green cover.
Thus, the presence of species at each trophic level is required to preserve the ecosystem's equilibrium.
Question 6:
What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Answer:
Biological Magnification:
- The introduction of hazardous chemicals into the food chain causes biological magnification.
- With each tropic level, their concentration increases.
- Biological magnification varies at different layers of the ecosystem.
- It will get bigger with each level that comes after.
The Biological Magnification Level:
- At the greatest trophic levels, it reaches its maximum point, while at the lowest trophic levels, it reaches its lowest point.
- Humans have the highest level, and autotrophs like plants have the lowest.
- For instance, when herbivores consume them, hazardous elements like pesticides enter their bodies.
- In addition to humans, pesticides also reach other food chain members.
- Thus, at every trophic level of the food chain, the level of harmful compounds increases.
Question 7:
What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Answer:
Non-biodegradable Wastes:
- These wastes are a source of pollution since they cannot be degraded or broken down by natural means like microorganisms.
- Toxic chemicals, synthetic fibers, insecticides, plastics, and other materials are a few examples of non-biodegradable waste.
Non-biodegradable wastes bring on the following issues:
- Pesticides and other wastes reduce the fertility of the soil and, after repeated use, change the pH level to an undesirable level for plants.
- Additionally, the pesticides gradually build up at each trophic level, negatively impacting the creatures.
- Burning wastes like plastic release hazardous substances into the environment, causing air pollution.
- The main pollution causes in the land, air, soil, and water is non-biodegradable waste.
Question 8:
If all the waste we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Answer:
- Even if all the waste is biodegradable, it could contaminate the environment.
- Biodegradable waste must degrade within a certain time, or the waste's accumulation will result in more pollution.
- Waste buildup creates breeding sites for insects like flies, worms, and mosquitoes, which can spread various diseases.
- Water exposed to waste might become polluted and unfit for human consumption.
Question 9:
Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer:
We should be concerned about the ozone layer's degradation because
- In humans, it causes skin aging, skin cancer, cataracts of the cornea, and skin darkening.
- Numerous phytoplanktons may die. As a result, accelerating global warming.
Steps to limit this damage are:
- The amount of CFCs released into the sky needs to be decreased to lessen the harm to the ozone layer.
- Alternatives safe for the environment should be used in place of CFCs in fire extinguishers and refrigerants.
- Additionally, it's important to prevent the release of CFCs from industrial activity.
|


 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









