C PointersThe pointer in C language is a variable which stores the address of another variable. This variable can be of type int, char, array, function, or any other pointer. The size of the pointer depends on the architecture. However, in 32-bit architecture the size of a pointer is 2 byte. Consider the following example to define a pointer which stores the address of an integer. Declaring a pointerThe pointer in c language can be declared using * (asterisk symbol). It is also known as indirection pointer used to dereference a pointer. Pointer ExampleAn example of using pointers to print the address and value is given below. 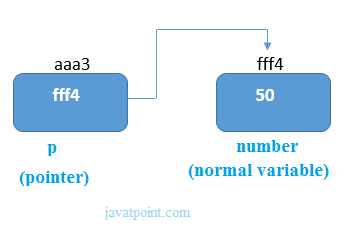
As you can see in the above figure, pointer variable stores the address of number variable, i.e., fff4. The value of number variable is 50. But the address of pointer variable p is aaa3. By the help of * (indirection operator), we can print the value of pointer variable p. Let's see the pointer example as explained for the above figure. Output Address of number variable is fff4 Address of p variable is fff4 Value of p variable is 50 Pointer to arrayPointer to a functionPointer to structure
Advantage of pointer1) Pointer reduces the code and improves the performance, it is used to retrieving strings, trees, etc. and used with arrays, structures, and functions. 2) We can return multiple values from a function using the pointer. 3) It makes you able to access any memory location in the computer's memory. Usage of pointerThere are many applications of pointers in c language. 1) Dynamic memory allocation In c language, we can dynamically allocate memory using malloc() and calloc() functions where the pointer is used. 2) Arrays, Functions, and Structures Pointers in c language are widely used in arrays, functions, and structures. It reduces the code and improves the performance. Address Of (&) OperatorThe address of operator '&' returns the address of a variable. But, we need to use %u to display the address of a variable. Output value of number is 50, address of number is fff4 NULL PointerA pointer that is not assigned any value but NULL is known as the NULL pointer. If you don't have any address to be specified in the pointer at the time of declaration, you can assign NULL value. It will provide a better approach. int *p=NULL; In the most libraries, the value of the pointer is 0 (zero). Pointer Program to swap two numbers without using the 3rd variable.Output Before swap: *p1=10 *p2=20 After swap: *p1=20 *p2=10 Reading complex pointersThere are several things which must be taken into the consideration while reading the complex pointers in C. Lets see the precedence and associativity of the operators which are used regarding pointers.
Here,we must notice that,
How to read the pointer: int (*p)[10]. To read the pointer, we must see that () and [] have the equal precedence. Therefore, their associativity must be considered here. The associativity is left to right, so the priority goes to (). Inside the bracket (), pointer operator * and pointer name (identifier) p have the same precedence. Therefore, their associativity must be considered here which is right to left, so the priority goes to p, and the second priority goes to *. Assign the 3rd priority to [] since the data type has the last precedence. Therefore the pointer will look like following.
The pointer will be read as p is a pointer to an array of integers of size 10. Example How to read the following pointer? ExplanationThis pointer will be read as p is a pointer to such function which accepts the first parameter as the pointer to a one-dimensional array of integers of size two and the second parameter as the pointer to a function which parameter is void and return type is the integer.
Next TopicC Pointer to Pointer
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









