Digital Electronics Interview QuestionsA list of top frequently asked Digital Electronics Interview Questions and answers are given below. 1) What is the difference between Latch And Flip-flop?The difference between latches and Flip-flop is that the latches are level triggered and flip-flops are edge triggered. In latches level triggered means that the output of the latches changes as we change the input and edge triggered means that control signal only changes its state when goes from low to high or high to low. Latches are fast whereas flip-flop is slow. 2) What is the binary number system?The system which has a base 2 is known as the binary system and it consists of only two digits 0 and 1. For Example: Take decimal number 625 In this 625 consist of three bits, we start writing the numbers from the rightmost bit power as 0 then the second bit as power 1 and the last as power 2. So, we can represent a decimal number as ∑digit � 10corresponding position or bit Here 10 is the total number of digits from 0 to 9. 3) State the De Morgan's Theorem?De Morgan's Theorem stated two theorems: 1.The complement of a product of two numbers is the sum of the complements of those numbers. (A. B)' = A' + B' Truth Table: 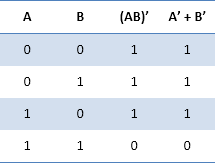
2. The complement of the sum of two numbers is equal to the product of the complement of two numbers. (A + B)' = A'B' Truth Table: 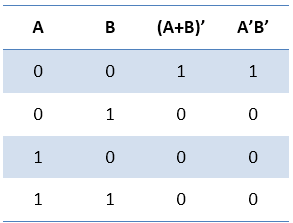
4) Define Digital System?Digital systems are the system that processes a discrete or digital signal. 5) What is meant by a bit?Bits are the binary digits like 0 and 1. 6) What is the best Example of Digital system?Digital Computer. 7) How many types of number system are there?There are four types of number system:
8) What is a Logic gate?The basic gates that make up the digital system are called a logic gate. The circuit that can operate on many binary inputs to perform a particular logic function is called an electronic circuit. 9) What are the basic Logic gates?There are three basic logic gates-
10) Which gates are called as Universal gate and what are its advantages?The Universal gates are NAND and NOR. The advantages of these gates are that they can be used for any logic calculation. 11) What are the applications of the octal number system?The applications of the octal number system are as follows:
12) What are the fundamental properties of Boolean algebra?The basic properties of Boolean algebra are:
13) What are Boolean algebra and Boolean expression?14) What is meant by K-Map or Karnaugh Map?K-Map is a pictorial representation of truth table in which the map is made up of cells, and each term in this represents the min term or max term of the function. By this method, we can directly minimize the Boolean function without following various steps. 15) Name the two forms of Boolean expression?The two forms of Boolean expression are:
16) What are Minterm and Maxterm?A minterm is called Product of sum because they are the logical AND of the set of variables and Maxterm are called sum of product because they are the logical OR of the set of variables. 17) Write down the Characteristics of Digital ICs?The characteristics of digital ICs are -
18) What are the limitations of the Karnaugh Map?The limitations of Karnaugh Map are as follows:
19) What are the advantages and disadvantages of the K-Map Method?The advantages of the K-Map method are as follows-
The disadvantages of the K-Map method are as follows:
20) What are the advantages and disadvantages of Quine-MC Cluskey method?21) Define Pair, Quad, and Octet?Pair: Two adjacent cell of karnaugh map is called as Pair. It cancels one variable in a K-Map simplification. Quad: A Pair of Four adjacent pairs in a karnaugh map is called a quad. It cancels two variables in a K-Map simplification. Octet: A Pair of eight adjacent pair in a karnaugh map is called an octet. It cancels four variables in a K-map simplification. 22) Define Fan-in and Fan-out?Fan-in- The Fan-in of the gate means that the number of inputs that are connected to the gate without the degradation of the voltage level of the system. Fan-out- The Fan-out is the maximum number of same inputs of the same IC family that a gate can drive maintaining its output levels within the specified limits. 23) Write the definition of the Duality Theorem?Duality Theorem states that we can derive another Boolean expression with the existing Boolean expression by:
24) What is Half-Adder?Half-adder is the circuits that perform the addition of two bits. It has two inputs A and B and two outputs S (sum) and C (carry). It is represented by XOR logic gate and an AND logic gate. 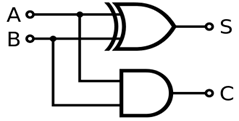
Truth Table of Half adder: 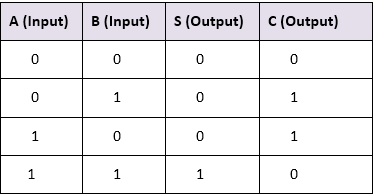
25) What is Full-Adder?Full-adder is the circuits that perform the addition of three bits. It has three inputs A, B and a carry bit. Full adders are represented with AND, OR and XOR logic gate. 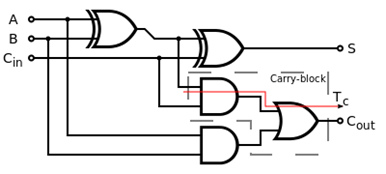
Truth Table of Full-Adder 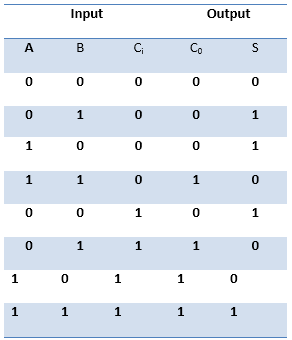
26) What is power dissipation?Period time is the electrical energy used by the logic circuits. It is expressed in milliwatts or nanowatts. Power dissipation = Supply voltage * mean current taken from the supply. 27) What is a Multiplexer?The multiplexer is a digital switch which combines all the digital information from several sources and gives one output. 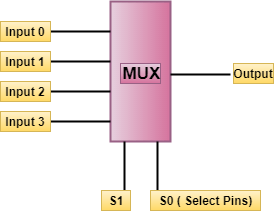
28) What are the applications of Multiplexer (MUX)?The applications of the multiplexer are as follows:
29) What is a Demultiplexer?The demultiplexer is a circuit that receives the input on a single line and transmits this onto 2n possible output line. A Demultiplexer of 2n outputs has n select lines, which are used to select which output line is to be sent to the input. The demultiplexer is also called as Data Distributor. 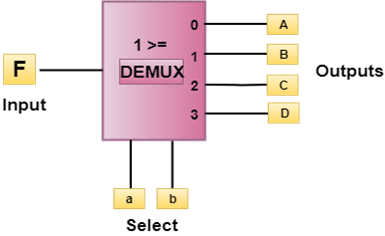
30) What are the applications of Demultiplexer?The applications of the demultiplexer are as follows:
31) What are the differences between Combinational Circuits and Sequential Circuits?The differences between combinational and sequential circuits are as follows:
32) Define Rise Time?Rise time is the time that is required to change the voltage level from 10% to 90%. 33) Define fall time?Fall time is the time that is required to change the voltage level from 90% to 10%. 34) Define Setup time?The minimum time that is required to maintain the constant voltage levels at the excitation inputs of the flip-flop device before the triggering edge of the clock pulse for the levels to be reliably clocked in the flip flop is called the Setup time. It is denoted as tsetup. 35) Define Hold time?The minimum time at which the voltage level becomes constant after triggering the clock pulse in order to reliably clock into the flip flop is called the Hold time. It is denoted by thold. 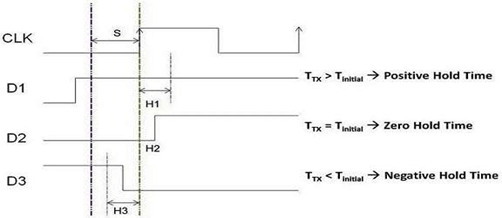
36) What is the difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters?The difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters are as follows:
37) What are the applications of Flip-Flops?The applications of flip-flops are:
38) What is the difference between D-latch and D Flip-flop?D-latch is level sensitive whereas flip-flop is edge sensitive. Flip-flops are made up of latches. 39) What are the applications of Buffer?Applications of buffer are as follows:
|
You may also like:
- Java Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- HR Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- C++ Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- DBMS Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- IAS Interview Questions
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions
- .Net Interview Questions
- C# Interview Questions
- ReactJS Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Accounting Interview Questions







