PHP OOPs Interview Questions1) What is a PHP session?A PHP session is utilized to store the data or information across numerous website pages on an internet browser that is not put away on the personal computer memory. A PHP session is begun utilizing the method session_start(), and the session factor can be set utilizing the global variable called $_SESSION. 2) Give a brief description of the Constructor and destructor in PHP?One of the fundamental PHP Interview Questions that recruiters love to ask in an interview. The Constructor is used to make an object of its group type, which is utilized to introduce the properties of the item utilizing a technique called _construct (). The Constructor in PHP can be overloaded by passing the various contentions by calling a similar technique with a different number of contentions inside a similar class statement. The Destructor in a PHP is utilized when the life span of a declared object is finished to deliver the memory involved by it or to gather something similar. The destructor can be called utilizing the method _destruct (). 3) Why do developers love to work with PHP?The general purposes of PHP, it can perform framework tasks, for example, make, read, open, close and print them to and from the PC memory. It can get to cookies and set the variables in the program. It can likewise give a limitation to getting to some website pages that give security. The information can likewise be encoded utilizing PHP. 4) What is an Interface in PHP?The interface can be considered as a point of interaction that provides a user to execute multiple different functions as per their personal preference. This can likewise be called the outline of the basic structure. An interface can be utilized and executed in numerous ways inside the execution class. 5) Define data types and state some of the popular PHP data types?PHP is a flexible programming language, and it contains multiple data types to hold different variables along with their particular category. String - an array/collection of characters is called a string Integer - A form of variable, which holds a numeric value without decimal. It can be a positive value integer as well as a negative value integer, depending on the use of the algorithm. Double - it is a type of floating-point number, almost similar to an integer, but it can hold numbers with decimal values. Boolean - 0 or 1 form of data type, which can hold only two forms of data, either true or false, where one stands for true and 0 for false. Array - An array is another data type that holds a collection of identical data which are stored in a sequence and later can easily be called or manipulated using an index. Object - Objects work on the concept of OOPs (object-oriented programming); this data type is declared solemnly to store complex data using encapsulation; these data types are usually deployed in order to call a class. NULL - This is a specific data type whose solemn purpose is to store a null value or no value at all. 6) Briefly explain the concept of OOPs and how can you say that PHP is an object-oriented language?An Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) language will have object-oriented elements, for example, Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, polymorphism, and so on; PHP was principally founded on C++ programming language, which is another most popular object-oriented programming language. A PHP class contains properties and techniques which are utilized to make an object of that class, and each item will have its own properties and values. 7) What do you know about PHP Namespace?A Namespace in PHP is utilized to encapsulate things that are somewhat similar to that of data abstraction in Object-Oriented programming ideas, or we can say that encapsulation is the process of wrapping up big chunks of data under a single unit. Namespaces are used to lay out a relationship among classes, functions, and constants. A Namespace can be characterized by utilizing the catchphrase. The namespace of this particular word is saved in PHP for its inner use to stay away from the struggle with the client-made identifiers. 8) Why do people use echo and print commands in PHP?The echo and print are two fundamental approaches to getting output in PHP. The usefulness of echo and print are indistinguishable in PHP to get the result. The distinctions between echo and print are: echo returns no value while print returns a worth of 1 which can be utilized in articulations. Echo takes numerous arguments through print takes a solitary argument. Echo can be utilized by calling the echo or echo (), while print can be called by utilizing a print keyword. 9) Why do people use require and include commands in PHP?These are the high-level PHP OOP Interview Questions, which is generally asked in tech interviews. The required and included functions for PHP are accessible from PHP 4 or more variants, which are indistinguishable with some distinction. Include explanation incorporates the specific document and assesses it though the required function likewise has a similar component; however, it creates an error upon failure with an error E_COMPILE_ERROR level mistake, which is a compile-time error. In this situation, it stops the execution of the content and ends the runtime flow. The documents will be incorporated in light of the file path given in the content. 10) How to call the parent constructor?The parent constructor can be easily called by implementing this parent::__construct(). But while calling the parent constructor, we face two cases. Case 1: If the child class already contains a constructor, we can't run the parent class constructor directly. To solve this problem, we have to call the above parameter within the child constructor. Example: Output: 
Case 2: If the child class does not contain a constructor, the parent constructor can be called directly without using the same method Example: Output: 
11) Parent constructor is called implicitly when an object of the class is created?Implicit calling an explicit calling depends on whether the child class has a constructor of its own or not, if the child class contains a constructor, the parent constructor will be called explicitly, but if the child class does not contain any constructor, the parent constructor will be called implicitly Example: explicit calling Output: 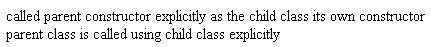
Example: implicit calling Output: 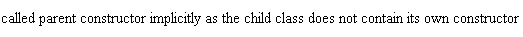
12) What is Object-Oriented Programming?Object-oriented programming, or OOPs, is a software development approach where the development process revolves around the concept of classes and objects. For instance, taking a real-life example, a class employee is a class declared around a particular employee in an organization, and all his traits, habits, salary, address, phone number, etc. will be encapsulated inside the class. And objects refer to the occurrence of the class declared. OOPs works on four major pillars that include Data encapsulation: Wrapping up chunks of data under a single main title to make the development process convenient. Data abstraction: Hiding the background working of methods and functions helps on reducing development complexity by exposing only the operation details and hiding the implementation details. Data inheritance: Transferring important data from a parent class to a child class, which helps in reusability. Polymorphism - The ability of a code to have multiple inputs and a common output. 13) What is a class?Classes are basically a structure for an object, where it helps the user to store both variables as well as functions, and altogether they form a collection like a package, which is called an object. Example: Output: 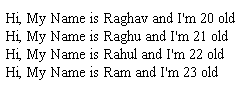
14) What is an object?Objects are made from Classes; it can be considered as an occasion of a class that is made dynamic. Object in computer programs is like the genuine word object. Each programming object has a few properties and ways of behaving. Syntax: Example: Output: 
As you can clearly see, we can make multiple different objects with different names for the same class. 15) How can you say that classes and objects are different but interrelated?They look very similar but have many differences:
16) What are Constructor and Destructor?Constructor: Constructor is an extraordinary kind of function which will be called consequently at whatever point there is any object made from a class. i.e. the constructor is called automatically when we create an object Syntax: Note - Old-style constructors are DEPRECATED in PHP 7.0 and will be eliminated in a future variant. You ought to continuously utilize __construct() in new code.Destructor: Destructor is an extraordinary kind of function that will be called naturally at whatever point any item is erased or leaves the scope. i.e., the destructor is called automatically when we destroy an object Syntax: 17) Give a basic explanation of the Member Variable and Member function?Member Variable: Variables that are declared inside a particular class is called member variable of that particular class. The data declared inside a particular member variable of a call can only be accessed by the member functions of that particular class only, and no other function outside this class can access it or use it. Member function - Functions that are defined inside a particular class are called member functions of that particular class. The function is basically used to access the member variable and use them; these member functions can only access the member variable of that particular class and are not eligible to access any variable outside this scope. 18) What are the different types of visibility? OR What are the access modifiers?There are three types of access modifiers in PHP.
NOTE: By default, in PHP, a class part in public except if proclaimed private or protected.19) Give a basic explanation about polymorphism?It is basically "A certain something can use in various structures". In fact, it is the capacity to reclassify strategies for determined classes. For instance, One Class (Car) can expand to two classes (Audi and BMW). Polymorphism depicts an example in object-situated programming in which classes have different usefulness while sharing a typical connection point. |
You may also like:
- Java Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- HR Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- C++ Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- DBMS Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- IAS Interview Questions
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions
- .Net Interview Questions
- C# Interview Questions
- ReactJS Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Accounting Interview Questions







